
A vector has components along the X-axis equal to 25 units and along the Y-axis equal to 60 units. Find the magnitude and the direction of the vector.
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint:The component along the X-axis and that along Y-axis is given. Then, the resultant vector is the sum of both the components with their respective axis. Squaring them will give the magnitude of the resultant vector and an inverse of the Y-component divided by the X-component will give the direction.
Formula Used:The direction of the vector id given by: \[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left(
{\dfrac{{{R_y}}}{{{R_x}}}} \right)\]
The direction of the vector id given by: \[\left| R \right| = \sqrt {R_x^2 + R_y^2} \]
Complete step by step solution:The physical quantities having both magnitude as well as direction are known as vectors. The given vector has a component along the X-axis equal to 25 unit and along the Y- axis equal to 60 units. The X-axis and Y-axis are perpendicular to each other. Mutually perpendicular components of a vector are called rectangular components.
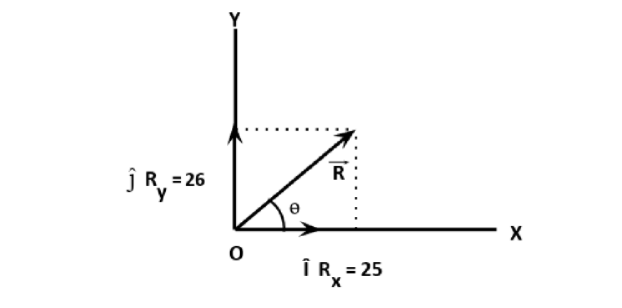
Form the given figure, \[\hat i{R_x} = 25\hat i\]and \[\hat j{R_y} = 60\hat j\] are the rectangular components along X and Y directions respectively. Vector \[\overrightarrow R \] is the resultant vector
such that
\[\overrightarrow R = \hat i{R_x} + \hat j{R_y}\]
From the figure,
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{R_x}}}{R} \to \cos \theta = \dfrac{{25}}{R}\] \[ \to (1)\]
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{R_y}}}{R} \to \sin \theta = \dfrac{{60}}{R}\] \[ \to (2)\]
Therefore, \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{R_y}}}{{{R_x}}} \to \tan \theta = \dfrac{{60}}{{25}} =
\dfrac{{12}}{5}\]
\[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{R_y}}}{{{R_x}}}} \right) = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{12}}{5}}
\right) = 67.3801{\text{ radians}}\]
Thus, \[\theta = 67.3801\] is the direction of the vector.
The magnitude of the vector will be
\[\left| R \right| = \sqrt {R_x^2 + R_y^2} = \sqrt {{{(25)}^2} + {{(60)}^2}} = \sqrt {4225} = 65\]
Note:The coordinates of a point that are given in units (\[\hat i{R_x} = 25\hat i\]units and \[\hat j{R_y}
= 60\hat j\]units) are the magnitudes of its mutually perpendicular components or rectangular
components \[\hat i{R_x}\] and\[\hat j{R_y}\]. This means that a vector can have only two rectangular components in a plane. If any resultant vector is represented with three rectangular components, then that resultant vector is represented in space co-coordinates.
Formula Used:The direction of the vector id given by: \[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left(
{\dfrac{{{R_y}}}{{{R_x}}}} \right)\]
The direction of the vector id given by: \[\left| R \right| = \sqrt {R_x^2 + R_y^2} \]
Complete step by step solution:The physical quantities having both magnitude as well as direction are known as vectors. The given vector has a component along the X-axis equal to 25 unit and along the Y- axis equal to 60 units. The X-axis and Y-axis are perpendicular to each other. Mutually perpendicular components of a vector are called rectangular components.

Form the given figure, \[\hat i{R_x} = 25\hat i\]and \[\hat j{R_y} = 60\hat j\] are the rectangular components along X and Y directions respectively. Vector \[\overrightarrow R \] is the resultant vector
such that
\[\overrightarrow R = \hat i{R_x} + \hat j{R_y}\]
From the figure,
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{R_x}}}{R} \to \cos \theta = \dfrac{{25}}{R}\] \[ \to (1)\]
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{R_y}}}{R} \to \sin \theta = \dfrac{{60}}{R}\] \[ \to (2)\]
Therefore, \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{R_y}}}{{{R_x}}} \to \tan \theta = \dfrac{{60}}{{25}} =
\dfrac{{12}}{5}\]
\[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{{R_y}}}{{{R_x}}}} \right) = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{{12}}{5}}
\right) = 67.3801{\text{ radians}}\]
Thus, \[\theta = 67.3801\] is the direction of the vector.
The magnitude of the vector will be
\[\left| R \right| = \sqrt {R_x^2 + R_y^2} = \sqrt {{{(25)}^2} + {{(60)}^2}} = \sqrt {4225} = 65\]
Note:The coordinates of a point that are given in units (\[\hat i{R_x} = 25\hat i\]units and \[\hat j{R_y}
= 60\hat j\]units) are the magnitudes of its mutually perpendicular components or rectangular
components \[\hat i{R_x}\] and\[\hat j{R_y}\]. This means that a vector can have only two rectangular components in a plane. If any resultant vector is represented with three rectangular components, then that resultant vector is represented in space co-coordinates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




