
A vertical tower stands on a horizontal plane and is surmounted by a vertical flag staff of height \[h\]. At a point on the plane, the angles of elevation of the bottom and the top of the flag staff are \['\alpha '\] and \['\beta '\] respectively. Prove that height of tower \[\left( h \right)\] \[h = \left( {\dfrac{{h\tan \alpha }}{{\tan \beta - \tan \alpha }}} \right)\] .
Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint: In the above question, we have to calculate the height of the tower. To solve this question, we will draw a diagram by following the statements given the question and with the help of this diagram we will evaluate the answer. For this we have to remember that in a right-angle triangle \[\tan x = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{base}}\] .
Formula used:
In this question, we have to keep in mind the value of \[\tan x\] in a right-angle triangle.
\[\tan x = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{base}}\] .
Complete step by step solution:
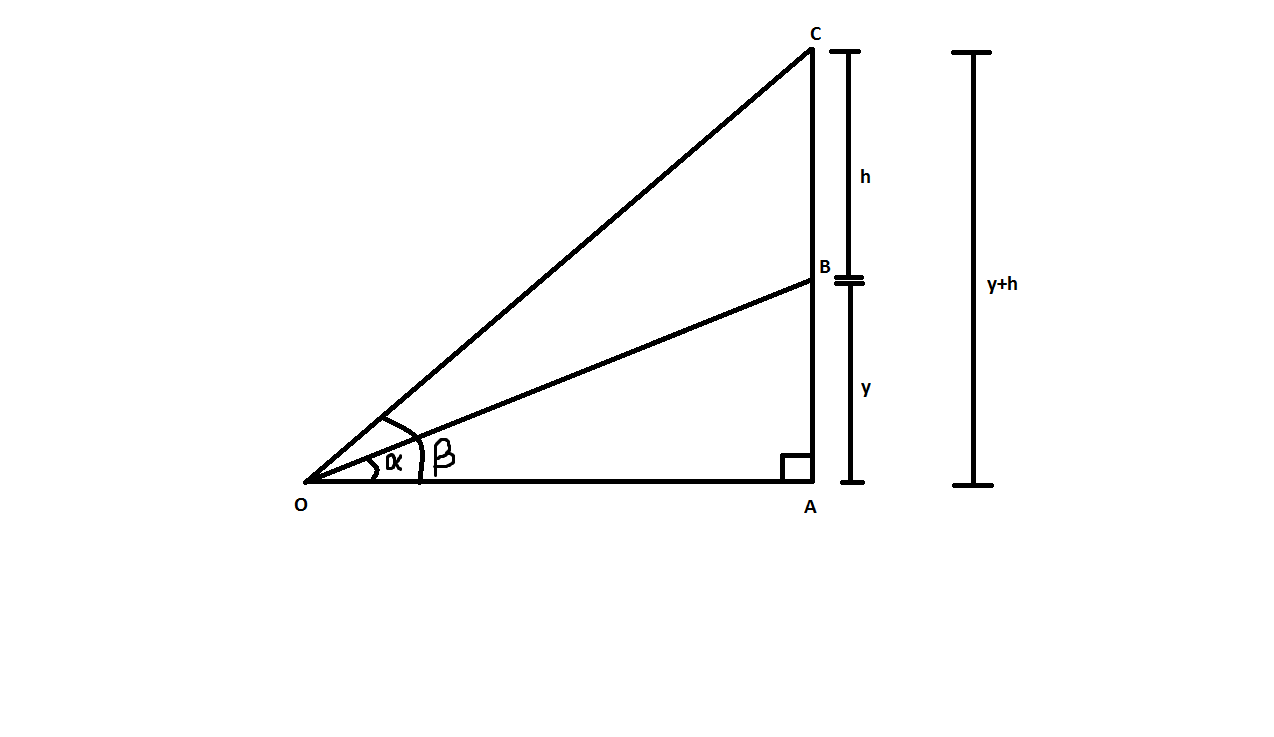
To solve the above question, let the height of the tower \[AB\] be \[y\] .
We are given that the angle of elevation of the bottom of the flag staff is \[\alpha \] and the angle of elevation at the top of the flag staff is \[\beta \] .
Also, we know that the value of \[\tan x\] in a right-angle triangle is \[\tan x = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{base}}\] .
In the \[\vartriangle OAC\] ,
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{AC}}{{AO}}\]
Here \[\theta = \beta \]and \[AC = y + h\] ,
\[\tan \beta = \dfrac{{y + h}}{{AO}}\]
On Cross multiplying we get,
\[ \Rightarrow AO = \dfrac{{y + h}}{{\tan \beta }}\] .
Now we will consider the \[\vartriangle OAB\]
Here,
\[
\tan \alpha = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AO}} \\
\Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{y}{{AO}} \\
\Rightarrow AO = \dfrac{y}{{\tan \alpha }} \\
\]
Equate both the values of \[AO\] ,
\[\dfrac{{y + h}}{{\tan \beta }} = \dfrac{y}{{\tan \alpha }}\]
\[
\Rightarrow y\tan \beta = y\tan \alpha + h\tan \alpha \\
\Rightarrow y\tan \beta - y\tan \alpha = h\tan \alpha \\
\Rightarrow y\left[ {\tan \beta - \tan \alpha } \right] = h\tan \alpha \\
\]
In the last step we will find the value of \[y\] ,
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{h\tan \alpha }}{{\tan \beta - \tan \alpha }}\] .
Hence, we have proved that \[ y = \dfrac{{h\tan \alpha }}{{\tan \beta - \tan \alpha }}\] .
Note: To find solutions to such problems, it is very essential to draw the diagrams first. The diagrams are very helpful in finding the solutions to such questions. Also, remember the value of \[\tan x\] in a right-angle triangle, which is, \[\tan x = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{base}}\] . This will help you to solve sums similar to this question.
Formula used:
In this question, we have to keep in mind the value of \[\tan x\] in a right-angle triangle.
\[\tan x = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{base}}\] .
Complete step by step solution:

To solve the above question, let the height of the tower \[AB\] be \[y\] .
We are given that the angle of elevation of the bottom of the flag staff is \[\alpha \] and the angle of elevation at the top of the flag staff is \[\beta \] .
Also, we know that the value of \[\tan x\] in a right-angle triangle is \[\tan x = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{base}}\] .
In the \[\vartriangle OAC\] ,
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{AC}}{{AO}}\]
Here \[\theta = \beta \]and \[AC = y + h\] ,
\[\tan \beta = \dfrac{{y + h}}{{AO}}\]
On Cross multiplying we get,
\[ \Rightarrow AO = \dfrac{{y + h}}{{\tan \beta }}\] .
Now we will consider the \[\vartriangle OAB\]
Here,
\[
\tan \alpha = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AO}} \\
\Rightarrow \tan \alpha = \dfrac{y}{{AO}} \\
\Rightarrow AO = \dfrac{y}{{\tan \alpha }} \\
\]
Equate both the values of \[AO\] ,
\[\dfrac{{y + h}}{{\tan \beta }} = \dfrac{y}{{\tan \alpha }}\]
\[
\Rightarrow y\tan \beta = y\tan \alpha + h\tan \alpha \\
\Rightarrow y\tan \beta - y\tan \alpha = h\tan \alpha \\
\Rightarrow y\left[ {\tan \beta - \tan \alpha } \right] = h\tan \alpha \\
\]
In the last step we will find the value of \[y\] ,
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{h\tan \alpha }}{{\tan \beta - \tan \alpha }}\] .
Hence, we have proved that \[ y = \dfrac{{h\tan \alpha }}{{\tan \beta - \tan \alpha }}\] .
Note: To find solutions to such problems, it is very essential to draw the diagrams first. The diagrams are very helpful in finding the solutions to such questions. Also, remember the value of \[\tan x\] in a right-angle triangle, which is, \[\tan x = \dfrac{{perpendicular}}{{base}}\] . This will help you to solve sums similar to this question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




