
A vestigial organ in humans is
(a) Ear pinna
(b) Nictitating membrane
(c) Mammary glands in males
(d) Knee bones
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: The plica semilunaris is a fold seen in the conjunctiva at the inner corner of the human eye. It's the third eyelid, of other animals, led to the idea that it might be the vestige of such a structure, which is still part of the eye in some primates, including gorillas.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The structures present in an organism that has lost all or most of its original function within the course of evolution are called vestigial organs.
In humans, the vestigial organs include many organs, which are still present in our body, like the muscles of the ear(Auricular muscles), wisdom teeth, vermiform appendix, the coccyx, body hair, and also the semilunar fold within the corner of the eye (nictitating membrane).
Hence the mentioned vestigial organ in the above case in humans is the nictitating membrane.
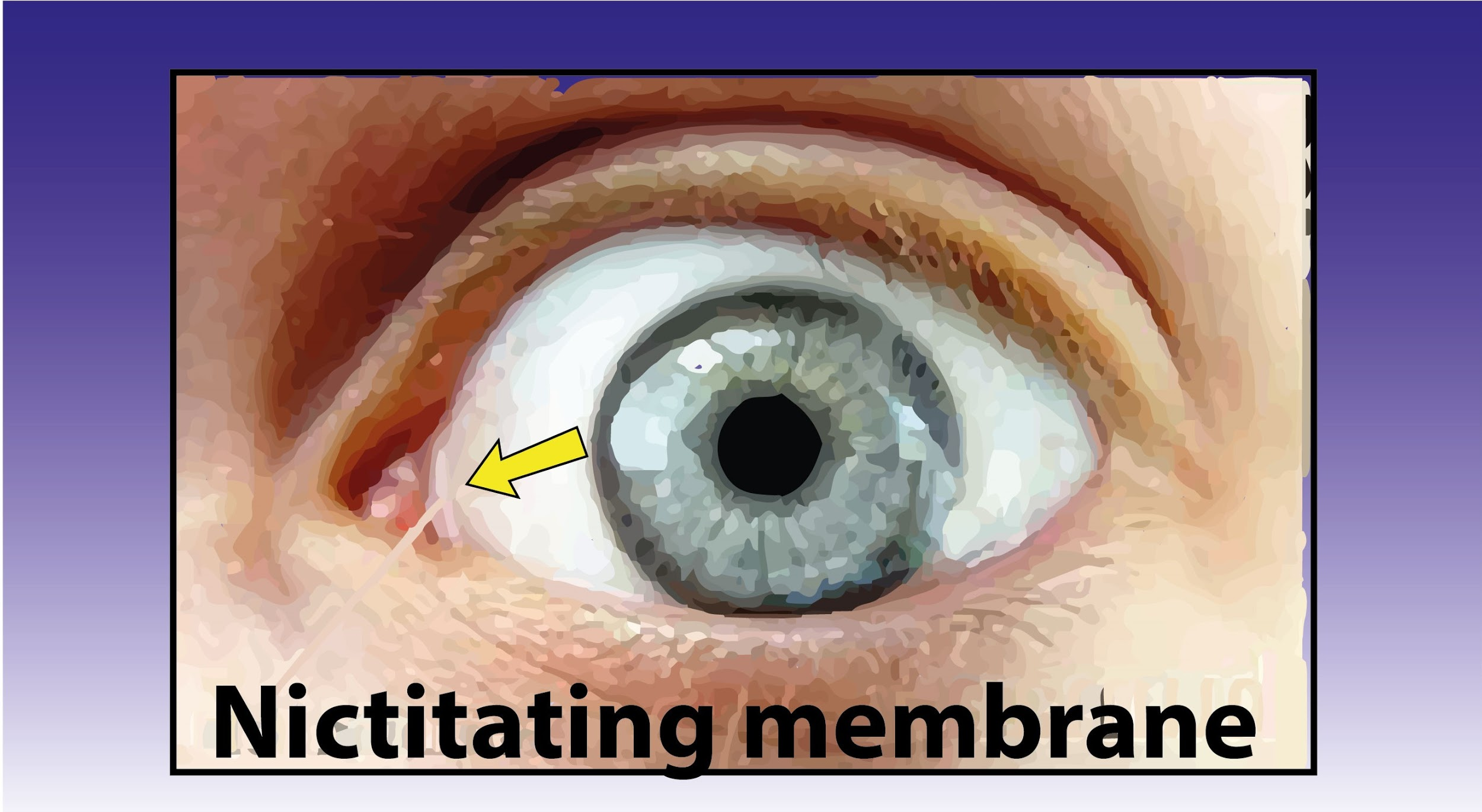
So, the correct answer is ‘(b) Nictitating membrane.’.
Additional Information:
- Structures that have no apparent function and appear to be residual parts from a past ancestor(the useful organ in ancestral life) are called vestigial structures.
- Examples of vestigial structures include the organs like the human appendix, the pelvic bone of a snake, and the wings of flightless birds.
- Vestigial structures can become detrimental, but in most cases these structures are harmless; however, these structures, like any other structure, require extra energy and are at risk for disease.
- Vestigial structures, especially non- harmful ones, take a long time to be phased out since eliminating them would require major alterations that could result in negative side effects.
Note: Vestigial structures are often homologous to structures that are non- functional in some organisms and while in others they function normally in other species. Therefore, vestigial structures are often considered as the evidence for evolution, the method by which beneficial heritable traits arise in populations over an extended period.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The structures present in an organism that has lost all or most of its original function within the course of evolution are called vestigial organs.
In humans, the vestigial organs include many organs, which are still present in our body, like the muscles of the ear(Auricular muscles), wisdom teeth, vermiform appendix, the coccyx, body hair, and also the semilunar fold within the corner of the eye (nictitating membrane).
Hence the mentioned vestigial organ in the above case in humans is the nictitating membrane.

So, the correct answer is ‘(b) Nictitating membrane.’.
Additional Information:
- Structures that have no apparent function and appear to be residual parts from a past ancestor(the useful organ in ancestral life) are called vestigial structures.
- Examples of vestigial structures include the organs like the human appendix, the pelvic bone of a snake, and the wings of flightless birds.
- Vestigial structures can become detrimental, but in most cases these structures are harmless; however, these structures, like any other structure, require extra energy and are at risk for disease.
- Vestigial structures, especially non- harmful ones, take a long time to be phased out since eliminating them would require major alterations that could result in negative side effects.
Note: Vestigial structures are often homologous to structures that are non- functional in some organisms and while in others they function normally in other species. Therefore, vestigial structures are often considered as the evidence for evolution, the method by which beneficial heritable traits arise in populations over an extended period.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




