
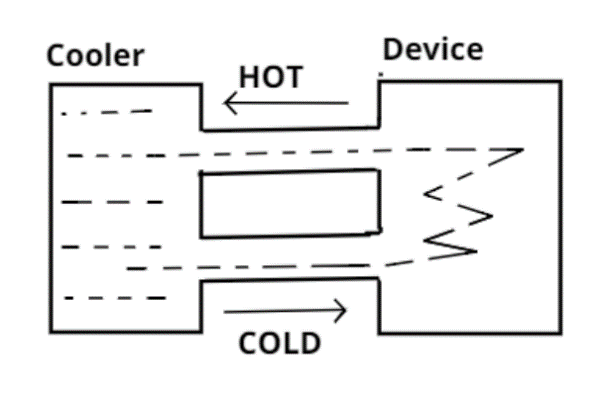
A water cooler of storage capacity 120 liters can cool water at a constant rate of P within a closed circulation system ( as shown schematically in the figure), the water from the cooler is used to cool an external device that generates constantly 3Kw of heat (thermal road). The temperature of water fed into the device cannot exceed ${30^0}C$ and the entire stored 120 liters of water is initially cooled to ${10^0}C$. The entire system is thermally insulated. The minimum value of P in watts for which the device can be operated for 3 hours is:
(Specific heat of water is $4.2KJK{g^{ - 1}}{K^{ - 1}}$ and the density of water is $1000kg{m^{ - 3}}$).

Answer
601.2k+ views
Hint: In this question let the rate of cooling be P, use the density and the total volume of the water to get the total mass of the water in the entire system. Use the concept that heat generated by the external device in 3 hours is the product of time in seconds and the thermal load of the external device and the heat energy used by the water heater is the product of the mass of the water in the cooler. This will help approaching the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Storage capacity of a water cooler = 120 liters
Rate of cooling = P
External device constant thermal load = 3 KW = $3 \times {10^3}$W
Initial temperature of the water cooler that has 120 liters of water = ${10^o}C$
The temperature of the water which is fed into the device cannot exceed ${30^o}C$
Specific heat capacity (s) of the water = 4.2 KJ$k{g^{ - 1}}{K^{ - 1}}$= 4200 J$k{g^{ - 1}}{K^{ - 1}}$
Density ($\rho $) of the water = 1000 kg/m3.
Now we have to find out the minimum value of the P (in watts) for which the device can be operated for 3 hours
Therefore, t = 3 hours.
Now as we know that 1 hour = 60 min = $\left( {60 \times 60} \right) = 3600$ seconds
Therefore, 3 hours = 3(3600) seconds
Therefore, t = 3(3600) seconds
Now the mass (m) of the water is the product of the volume of the water and specific density of the water.
As we know 1 lit = 0.001 cubic meter
So 120 liter = 0.120 cubic meter
So the mass of the water, m = $0.120 \times \rho $
$ \Rightarrow m = 0.120 \times 1000 = 120$kg
Now the heat generated by the external device in 3 hours is the product of time in seconds and the thermal load of the external device.
Therefore, heat generated = $3\left( {3600} \right)\left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right)$ Joule
Now the heat energy used by the water heater is the product of the mass of the water in the cooler and the specific heat capacity of the water and change in temperature.
Therefore, heat energy used by the water heater = $m \times s \times \Delta T = 120 \times 4200 \times \left( {30 - 10} \right)$ Joule
Now the heat absorbed by the coolant is the difference of the heat generated and the heat energy used by the water heater.
Therefore, heat absorbed by the coolant = $3\left( {3600} \right)\left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right)$ - $120 \times 4200 \times \left( {30 - 10} \right)$ Joule
Now the heat absorbed by the coolant is the product of the rate of cooling and the time of operation in seconds.
$ \Rightarrow Pt = 3\left( {3600} \right)\left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right) - 120 \times 4200 \times \left( {30 - 10} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{3\left( {3600} \right)\left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right) - 120 \times 4200 \times \left( {30 - 10} \right)}}{t}$
$ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{3\left( {3600} \right)\left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right) - 120 \times 4200 \times \left( {30 - 10} \right)}}{{3 \times 3600}}$
Now simplify this we have,
$ \Rightarrow P = \left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right) - \dfrac{{4200 \times 20}}{{3 \times 30}}$
$ \Rightarrow P = 3000 - 933.33 = 2066.66 \simeq 2067$
So this is the required answer.
Note – When water is heated eventually its temperature rises up, but say another liquid other than water is heated then its temperature will rise up but however it can’t be said that in both the cases the rate of change of temperature with the amount of heat given will be the same. This happens due to the different specific heat of the two liquids. Thus specific heat is simply defined as the measure of the heat applied to per unit mass so as to raise the temperature by 1 degree Celsius.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Storage capacity of a water cooler = 120 liters
Rate of cooling = P
External device constant thermal load = 3 KW = $3 \times {10^3}$W
Initial temperature of the water cooler that has 120 liters of water = ${10^o}C$
The temperature of the water which is fed into the device cannot exceed ${30^o}C$
Specific heat capacity (s) of the water = 4.2 KJ$k{g^{ - 1}}{K^{ - 1}}$= 4200 J$k{g^{ - 1}}{K^{ - 1}}$
Density ($\rho $) of the water = 1000 kg/m3.
Now we have to find out the minimum value of the P (in watts) for which the device can be operated for 3 hours
Therefore, t = 3 hours.
Now as we know that 1 hour = 60 min = $\left( {60 \times 60} \right) = 3600$ seconds
Therefore, 3 hours = 3(3600) seconds
Therefore, t = 3(3600) seconds
Now the mass (m) of the water is the product of the volume of the water and specific density of the water.
As we know 1 lit = 0.001 cubic meter
So 120 liter = 0.120 cubic meter
So the mass of the water, m = $0.120 \times \rho $
$ \Rightarrow m = 0.120 \times 1000 = 120$kg
Now the heat generated by the external device in 3 hours is the product of time in seconds and the thermal load of the external device.
Therefore, heat generated = $3\left( {3600} \right)\left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right)$ Joule
Now the heat energy used by the water heater is the product of the mass of the water in the cooler and the specific heat capacity of the water and change in temperature.
Therefore, heat energy used by the water heater = $m \times s \times \Delta T = 120 \times 4200 \times \left( {30 - 10} \right)$ Joule
Now the heat absorbed by the coolant is the difference of the heat generated and the heat energy used by the water heater.
Therefore, heat absorbed by the coolant = $3\left( {3600} \right)\left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right)$ - $120 \times 4200 \times \left( {30 - 10} \right)$ Joule
Now the heat absorbed by the coolant is the product of the rate of cooling and the time of operation in seconds.
$ \Rightarrow Pt = 3\left( {3600} \right)\left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right) - 120 \times 4200 \times \left( {30 - 10} \right)$
$ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{3\left( {3600} \right)\left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right) - 120 \times 4200 \times \left( {30 - 10} \right)}}{t}$
$ \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{3\left( {3600} \right)\left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right) - 120 \times 4200 \times \left( {30 - 10} \right)}}{{3 \times 3600}}$
Now simplify this we have,
$ \Rightarrow P = \left( {3 \times {{10}^3}} \right) - \dfrac{{4200 \times 20}}{{3 \times 30}}$
$ \Rightarrow P = 3000 - 933.33 = 2066.66 \simeq 2067$
So this is the required answer.
Note – When water is heated eventually its temperature rises up, but say another liquid other than water is heated then its temperature will rise up but however it can’t be said that in both the cases the rate of change of temperature with the amount of heat given will be the same. This happens due to the different specific heat of the two liquids. Thus specific heat is simply defined as the measure of the heat applied to per unit mass so as to raise the temperature by 1 degree Celsius.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




