
A water wave in a shallow tank passes through a gap in a barrier. What happens to the speed and what happens to the wavelength of the wave as it passes through the gap?
A. speed-decreases; wavelength decreases
B. speed-decreases; wavelength-remains constant
C. speed-remains constant; wavelength-decreases
D. speed-remains constant; wavelength-remains constant
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: Diffraction happens with water waves in a tank with ripples. Curved waves will be resulted when the straight waves of water pass through the gap in the barrier. Wavelength of the water will not be changed when passed through the barrier as the speed will not be changed, so they remain constant.
Complete step by step answer:
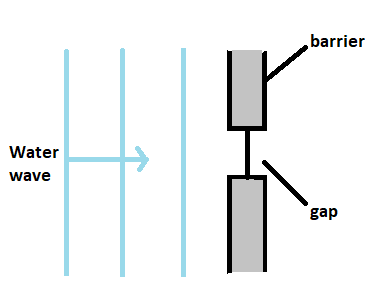
We are given that a water wave in a shallow tank passes through a gap in a barrier.
We have to find what happens to the speed and wavelength of the water wave after passing through the gap in the barrier.
Diffraction is a phenomenon that happens when a wave encounters an obstacle or a gap or a slit when they pass through objects.
Diffraction occurs when the size of the obstacle or gap is of similar linear dimensions (size) to the wavelength of the incident wave.
Diffraction increases when wavelength increases and decreases when the wavelength decreases.
Here it is given that the water wave already passes through the gap which means diffraction occurred and it happens only when the wavelength of the incident water wave and the gap is the same.
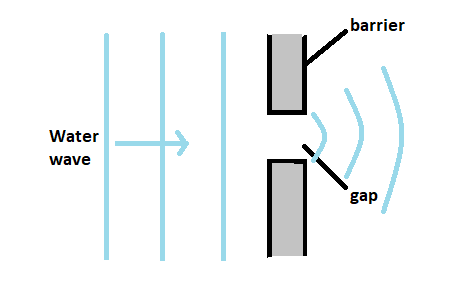
When water is spread out, normally its speed does not change.
Here when the water wave is passed through the gap, the water will be spread out which does not change the speed of the water wave.
Hence, the speed and wavelength of the water wave remains constant as it passes through the gap.
“speed-remains constant; wavelength-remains constant”.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Diffraction can also occur when the wavelength of the incident wave is larger than the size of the obstacle or the object but it is hard to happen when the size of the incident wave is less than the gap. Longer wavelengths will diffract more than the shorter wavelengths. So the wavelength of the incident must be always greater than or equal to the size of the gap for diffraction to occur.
Complete step by step answer:

We are given that a water wave in a shallow tank passes through a gap in a barrier.
We have to find what happens to the speed and wavelength of the water wave after passing through the gap in the barrier.
Diffraction is a phenomenon that happens when a wave encounters an obstacle or a gap or a slit when they pass through objects.
Diffraction occurs when the size of the obstacle or gap is of similar linear dimensions (size) to the wavelength of the incident wave.
Diffraction increases when wavelength increases and decreases when the wavelength decreases.
Here it is given that the water wave already passes through the gap which means diffraction occurred and it happens only when the wavelength of the incident water wave and the gap is the same.

When water is spread out, normally its speed does not change.
Here when the water wave is passed through the gap, the water will be spread out which does not change the speed of the water wave.
Hence, the speed and wavelength of the water wave remains constant as it passes through the gap.
“speed-remains constant; wavelength-remains constant”.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Diffraction can also occur when the wavelength of the incident wave is larger than the size of the obstacle or the object but it is hard to happen when the size of the incident wave is less than the gap. Longer wavelengths will diffract more than the shorter wavelengths. So the wavelength of the incident must be always greater than or equal to the size of the gap for diffraction to occur.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




