
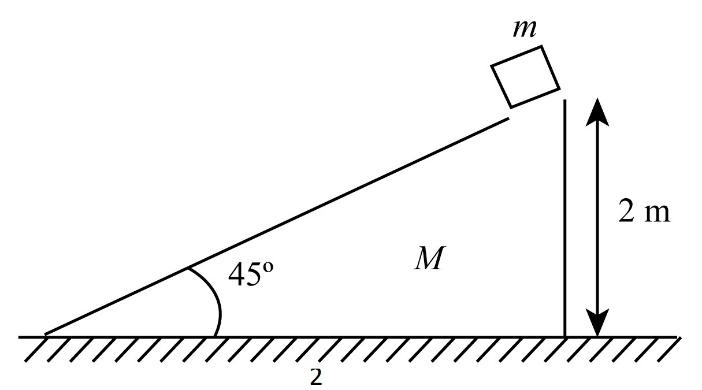
A wedge of mass m and a cube of mass $ m$ are shown in figure. The system is released. Considering no frictional force between any two surfaces, the distance moved by the wedge, when the cube just reaches on the ground is $M$
(A) $\dfrac{{m2\sqrt 2 }}{{\left( {m + M} \right)}}$
(B) $2m$
(C) $2\sqrt 2 m$
(D) $\dfrac{{2m}}{{m + M}}$

Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: For this question's solution, we will find the displacement of the block w.r.t. to earth and the wedge's displacement. After this, we will use the information that the displacement of the center of mass is zero to determine the required distance that wedge moved.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us assume that the distance moved by the wedge is $X$, and the distance moved by block w.r.t wedge is $x$.
But from the given diagram, we can say that if the wedge is at rest, then the block will cover the horizontal distance of $2\;{\rm{m}}$, so the displacement of the block w.r.t. earth becomes $ - 2\;{\rm{m}}$.
Now write the equation of the displacement of the block’s displacement w.r.t earth.
Therefore, we get
${d_{BE}} = {d_{BW}} + {d_{WE}}$
Here, ${d_{BE}}$ is the displacement of the block w.r.t. earth, ${d_{BW}}$ is the displacement of the block w.r.t. the wedge, and ${d_{WE}}$ is the displacement of the wedge w.r.t . to earth.
Substitute the values in the above equation.
$\begin{array}{l}
{d_{BE}} = - 2 + X\\
{d_{BE}} = X - 2
\end{array}$ …… (1)
Now we know that the displacement of the center of mass will be zero or constant; therefore, we will use the center of mass equation. So, we get,
\[\begin{array}{l}
{X_{cm}}\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right) = {m_1}x + {m_2}x\\
{X_{cm}} = \dfrac{{{m_1}x + {m_2}x}}{{\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}
\end{array}\]
Here, ${X_{cm}}$ is the displacement of the center of mass, ${m_1}$ is the mass of the block, ${m_2}$ is the mass of the wedge, ${x_1}$ is the displacement of the block w.r.t. earth, and ${x_2}$ is the displacement of the wedge.
Substitute the value in the above equation.
$ 0 = \dfrac{{m\left( {X - 2} \right) + MX}}{{\left( {m + M} \right)}}\\$
$\implies mX + MX = \left( {m \times 2} \right)\\$
$\implies \left( {m + M} \right)X = 2m\;\\$
$\implies X = \dfrac{{2m}}{{\left( {m + M} \right)}} $
Therefore, the wedge's distance when the cube just reached on the ground is, $\dfrac{{2m}}{{m + M}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Remember the center of the mass equation because, in this question, all the values that we determine or assume are used in the center of mass equation. Also, use the positive sign for the block's displacement if the block's movement is in the wedge's motion direction and use negative sign if the block's movement is in the opposite direction of the wedge's motion.
Complete step by step answer:
Let us assume that the distance moved by the wedge is $X$, and the distance moved by block w.r.t wedge is $x$.
But from the given diagram, we can say that if the wedge is at rest, then the block will cover the horizontal distance of $2\;{\rm{m}}$, so the displacement of the block w.r.t. earth becomes $ - 2\;{\rm{m}}$.
Now write the equation of the displacement of the block’s displacement w.r.t earth.
Therefore, we get
${d_{BE}} = {d_{BW}} + {d_{WE}}$
Here, ${d_{BE}}$ is the displacement of the block w.r.t. earth, ${d_{BW}}$ is the displacement of the block w.r.t. the wedge, and ${d_{WE}}$ is the displacement of the wedge w.r.t . to earth.
Substitute the values in the above equation.
$\begin{array}{l}
{d_{BE}} = - 2 + X\\
{d_{BE}} = X - 2
\end{array}$ …… (1)
Now we know that the displacement of the center of mass will be zero or constant; therefore, we will use the center of mass equation. So, we get,
\[\begin{array}{l}
{X_{cm}}\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right) = {m_1}x + {m_2}x\\
{X_{cm}} = \dfrac{{{m_1}x + {m_2}x}}{{\left( {{m_1} + {m_2}} \right)}}
\end{array}\]
Here, ${X_{cm}}$ is the displacement of the center of mass, ${m_1}$ is the mass of the block, ${m_2}$ is the mass of the wedge, ${x_1}$ is the displacement of the block w.r.t. earth, and ${x_2}$ is the displacement of the wedge.
Substitute the value in the above equation.
$ 0 = \dfrac{{m\left( {X - 2} \right) + MX}}{{\left( {m + M} \right)}}\\$
$\implies mX + MX = \left( {m \times 2} \right)\\$
$\implies \left( {m + M} \right)X = 2m\;\\$
$\implies X = \dfrac{{2m}}{{\left( {m + M} \right)}} $
Therefore, the wedge's distance when the cube just reached on the ground is, $\dfrac{{2m}}{{m + M}}$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
Remember the center of the mass equation because, in this question, all the values that we determine or assume are used in the center of mass equation. Also, use the positive sign for the block's displacement if the block's movement is in the wedge's motion direction and use negative sign if the block's movement is in the opposite direction of the wedge's motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




