
(a) What is biogas ? Name the major component of biogas.
(b) What are the raw materials used for making biogas ?
(c) Describe the construction and working of a biogas plant with the help of a labelled diagram.
(d) Write any two uses of biogas.
(e) Write any two advantages of using biogas.
Answer
521.4k+ views
Hint: Biogas naturally recycles waste products and converts them into useful energy, thereby preventing pollution caused by waste in landfills and reducing the impact of toxic chemicals released from sewage treatment plants.
Complete answer:
a) Biogas is a renewable energy source produced by the anaerobic breakdown of organic matter by certain bacteria. It is a compound composed of methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. Agricultural waste, food waste, animal dung, manure, and sewage can all be sources of it. The process of producing biogas is also known as anaerobic digestion.
b) Water and cow dung are the raw materials used for making biogas.
c) Building and operation of a biogas plant:
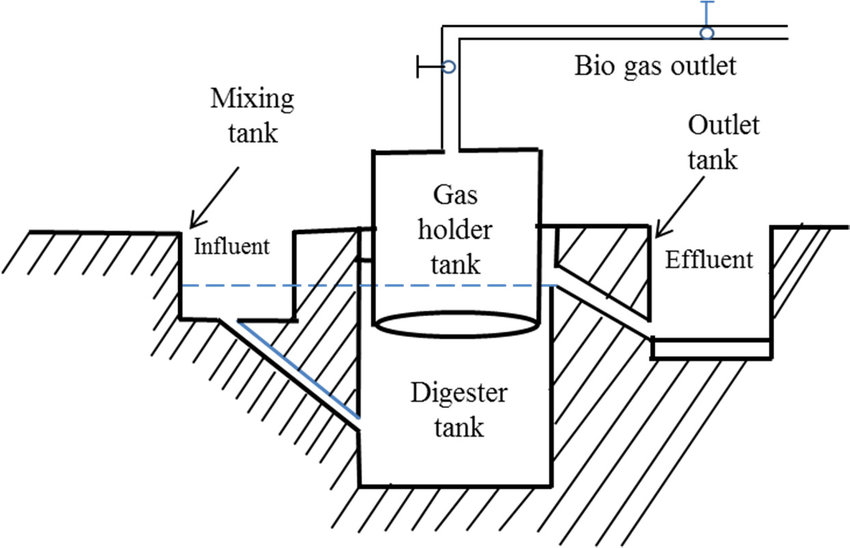
A biogas plant consists of a digester, which is a wall-shaped underground tank made of bricks with a dome-shaped roof D. The dome serves as a gas reservoir. At the top of the dome, there is a gas outlet S with a valve V. A sloping inlet chamber I is linked to a mixing tank M, and a rectangular outlet chamber O is linked to the overflow tank F.
d) To make the slurry, cow dung and water are mixed in equal parts in mixing tank M. This slurry is pumped into the digester tank via the inlet chamber, filling it to the cylindrical level. The cow dung is then anaerobically degraded, resulting in the formation of biogas, which collects in the dome. The biogas pressure on the slurry forces the spent slurry into the overflow tank F through outlet chamber O. from where it is removed.
e) Two uses of biogas:
(i) For cooking purpose
(ii) For lightning purpose
f) Two advantages of biogas:
(i) Smoke-free cooking
(ii) High calorific value
Note: When manure is anaerobically digested, the biogas produced is mostly methane and carbon dioxide, with minor amounts of hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, and other gases. Each of these gases poses a safety risk. Explosion, asphyxiation, disease, and hydrogen sulfide poisoning are all risks associated with biogas.
Complete answer:
a) Biogas is a renewable energy source produced by the anaerobic breakdown of organic matter by certain bacteria. It is a compound composed of methane, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide. Agricultural waste, food waste, animal dung, manure, and sewage can all be sources of it. The process of producing biogas is also known as anaerobic digestion.
b) Water and cow dung are the raw materials used for making biogas.
c) Building and operation of a biogas plant:

A biogas plant consists of a digester, which is a wall-shaped underground tank made of bricks with a dome-shaped roof D. The dome serves as a gas reservoir. At the top of the dome, there is a gas outlet S with a valve V. A sloping inlet chamber I is linked to a mixing tank M, and a rectangular outlet chamber O is linked to the overflow tank F.
d) To make the slurry, cow dung and water are mixed in equal parts in mixing tank M. This slurry is pumped into the digester tank via the inlet chamber, filling it to the cylindrical level. The cow dung is then anaerobically degraded, resulting in the formation of biogas, which collects in the dome. The biogas pressure on the slurry forces the spent slurry into the overflow tank F through outlet chamber O. from where it is removed.
e) Two uses of biogas:
(i) For cooking purpose
(ii) For lightning purpose
f) Two advantages of biogas:
(i) Smoke-free cooking
(ii) High calorific value
Note: When manure is anaerobically digested, the biogas produced is mostly methane and carbon dioxide, with minor amounts of hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, and other gases. Each of these gases poses a safety risk. Explosion, asphyxiation, disease, and hydrogen sulfide poisoning are all risks associated with biogas.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




