
(a) What is soap?
(b) Describe the structure of a soap molecule with the help of a diagram.
(c) Explain the cleansing action of soap. Draw a diagram to illustrate your answer.
Answer
567.6k+ views
Hint: We know that soaps are very important in life. We usually wash our hands using soap to remove dirt. It helps in cleansing our body, clothes etc. It has a cleansing property. It saves us from bacteria which are harmful.
Complete step by step solution:
(a) The sodium and potassium salts of the long chain carboxylic acids are referred to as soaps. It consists of a long hydrocarbon chain having carboxylic acid on one end. This has an ionic bond with metal ions which is usually sodium or potassium.
(b) The structure of a soap molecule is given below:
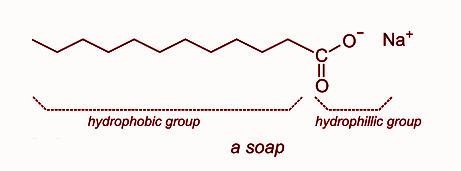
This is the structure of sodium stearate which is an example of soap molecule. It has a hydrophilic and hydrophobic part in it. The hydrophobic end is nonpolar and insoluble in water. In the above molecule, the hydrophobic part is ${\text{ - }}{{\text{C}}_{17}}{{\text{H}}_{35}}$. The hydrophilic end is polar and soluble in water. In the molecule, the hydrophilic end is $ - {\text{COONa}}$.
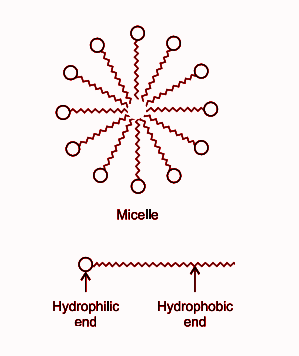
(c) Micelles is the name of soap molecules. Hydrophobic end is attached to the dust, oil, grease, dirt or the materials which we want to remove, detaching takes place, gets suspended in water and can easily be removed.
When a dirt is put in water containing soap, then the non-polar end of soap in micelle attach to an oil particle present on the surface of dirt. The soap micelles trap the oily particles by the nonpolar end. The polar end attaches to the water when the dirt is agitated in soap solution.
The structure of a micelle and the cleansing action of soap molecule is given below:
Note: There is a chance of making a mistake that we may confuse soaps with detergent. The main difference between soap and detergent is that the cleansing action of soap does not work properly with hard water. While detergent works well with hard water too.
Complete step by step solution:
(a) The sodium and potassium salts of the long chain carboxylic acids are referred to as soaps. It consists of a long hydrocarbon chain having carboxylic acid on one end. This has an ionic bond with metal ions which is usually sodium or potassium.
(b) The structure of a soap molecule is given below:

This is the structure of sodium stearate which is an example of soap molecule. It has a hydrophilic and hydrophobic part in it. The hydrophobic end is nonpolar and insoluble in water. In the above molecule, the hydrophobic part is ${\text{ - }}{{\text{C}}_{17}}{{\text{H}}_{35}}$. The hydrophilic end is polar and soluble in water. In the molecule, the hydrophilic end is $ - {\text{COONa}}$.
(c) Micelles is the name of soap molecules. Hydrophobic end is attached to the dust, oil, grease, dirt or the materials which we want to remove, detaching takes place, gets suspended in water and can easily be removed.
When a dirt is put in water containing soap, then the non-polar end of soap in micelle attach to an oil particle present on the surface of dirt. The soap micelles trap the oily particles by the nonpolar end. The polar end attaches to the water when the dirt is agitated in soap solution.
The structure of a micelle and the cleansing action of soap molecule is given below:

Note: There is a chance of making a mistake that we may confuse soaps with detergent. The main difference between soap and detergent is that the cleansing action of soap does not work properly with hard water. While detergent works well with hard water too.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




