
A. What is the chemical name of bleaching powder?
B. What is the chemical formula of bleaching powder?
C. What are the materials used for the preparation of bleaching powder?
D. State one use of bleaching powder (other than bleaching)
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Chlorine is a powerful oxidizer and it is the active agent in many household bleaches. Since pure chlorine is a toxic corrosive gas, these products usually contain hypochlorite, which releases chlorine when needed. "Bleaching powder" usually means a formulation containing calcium hypochlorite.
Complete step by step answer:
Answer (A). Chemical name of the bleaching powder is calcium hypochlorite. It is also called calcium oxychloride. It is called oxychloride because in it calcium ion is directly attached to one chloride atom and other chlorine is actually attached to oxygen which is in direct attachment with calcium.
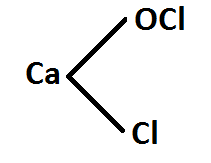
Answer (B). Chemical formula of bleaching powder is $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$. Free chlorine available in bleaching powder is actually what makes it a useful product because this free chlorine actually does the bleaching and other tasks in bleaching powder.
Answer (C). Bleaching powder is synthesized by the action of chlorine gas on dry slaked lime (\[Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}\]).
\[Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to CaOC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Answer (D). Bleaching powder is a strong oxidizing agent, therefore used as an oxidizer in many industries. It is used as a disinfectant for disinfecting water to make it potable water. It's used to disinfect surfaces too, especially in the kitchen and bathroom.
Additional information: Calcium hypochlorite is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, chlorine powder, or chlorinated lime.
Note: (i) Bleaching powder is a pale yellow powder. It has a strong smell of chlorine.
(ii) It is soluble in water but a clear solution is never formed due to presence of impurities.
(iii) It loses chlorine by the action of carbon dioxide.
Complete step by step answer:
Answer (A). Chemical name of the bleaching powder is calcium hypochlorite. It is also called calcium oxychloride. It is called oxychloride because in it calcium ion is directly attached to one chloride atom and other chlorine is actually attached to oxygen which is in direct attachment with calcium.

Answer (B). Chemical formula of bleaching powder is $CaOC{{l}_{2}}$. Free chlorine available in bleaching powder is actually what makes it a useful product because this free chlorine actually does the bleaching and other tasks in bleaching powder.
Answer (C). Bleaching powder is synthesized by the action of chlorine gas on dry slaked lime (\[Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}\]).
\[Ca{{(OH)}_{2}}+C{{l}_{2}}\to CaOC{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\]
Answer (D). Bleaching powder is a strong oxidizing agent, therefore used as an oxidizer in many industries. It is used as a disinfectant for disinfecting water to make it potable water. It's used to disinfect surfaces too, especially in the kitchen and bathroom.
Additional information: Calcium hypochlorite is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, chlorine powder, or chlorinated lime.
Note: (i) Bleaching powder is a pale yellow powder. It has a strong smell of chlorine.
(ii) It is soluble in water but a clear solution is never formed due to presence of impurities.
(iii) It loses chlorine by the action of carbon dioxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




