
ABCD is a rhombus whose diagonals intersect at E. Then \[\overrightarrow{EA}+\overrightarrow{EB}+\overrightarrow{EC}+\overrightarrow{ED}\] equals
A. \[\overrightarrow{0}\]
B. \[\overrightarrow{AD}\]
C. \[2\overrightarrow{BC}\]
D. $2\overrightarrow{AD}$
Answer
604.8k+ views
Hint: We will start by using a fact that all the sides of a rhombus are equal and the diagonal bisect each other at right. Then, we will use the fact that if two vectors are the same in magnitude but different in direction then their resultant is zero and finally we will use this fact of the rhombus to make pair of vectors and solve them.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Now, we have been given that ABCD is a rhombus whose diagonals intersect at E and we have to find the value of \[\overrightarrow{EA}+\overrightarrow{EB}+\overrightarrow{EC}+\overrightarrow{ED}\].
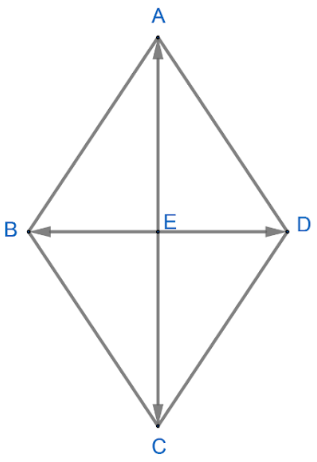
Now, we know that the diagonals of a parallelogram are perpendicular and bisect each other, so we have,
$\begin{align}
& EA=EC...............\left( 1 \right) \\
& EB=ED................\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that if two vectors which are same in magnitude but opposite in direction are added their resultant is zero. Therefore, we have from (1) and (2),
$\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{EA}+\overrightarrow{EC}=0...............\left( 3 \right) \\
& \overrightarrow{EB}+\overrightarrow{ED}=0...............\left( 4 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, adding (3) and (4) we have;
\[\overrightarrow{EA}+\overrightarrow{EB}+\overrightarrow{EC}+\overrightarrow{ED}=0\]
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: It is important to note that we have used the property of rhombus and diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other. So, we have used this and another fact that the sum of two equal and the opposite vector is zero to find the solution to the question.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Now, we have been given that ABCD is a rhombus whose diagonals intersect at E and we have to find the value of \[\overrightarrow{EA}+\overrightarrow{EB}+\overrightarrow{EC}+\overrightarrow{ED}\].

Now, we know that the diagonals of a parallelogram are perpendicular and bisect each other, so we have,
$\begin{align}
& EA=EC...............\left( 1 \right) \\
& EB=ED................\left( 2 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that if two vectors which are same in magnitude but opposite in direction are added their resultant is zero. Therefore, we have from (1) and (2),
$\begin{align}
& \overrightarrow{EA}+\overrightarrow{EC}=0...............\left( 3 \right) \\
& \overrightarrow{EB}+\overrightarrow{ED}=0...............\left( 4 \right) \\
\end{align}$
Now, adding (3) and (4) we have;
\[\overrightarrow{EA}+\overrightarrow{EB}+\overrightarrow{EC}+\overrightarrow{ED}=0\]
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: It is important to note that we have used the property of rhombus and diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other. So, we have used this and another fact that the sum of two equal and the opposite vector is zero to find the solution to the question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




