
What is an abscission zone? Name its components and their functions.
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: In deciduous trees, an abscission zone is formed at the bottom of the petiole. It's composed of a top layer that has cells with weak walls and a bottom layer that expands within the autumn, breaking the weak walls of the cells within the top layer. This enables the leaf to be shed.
Complete answer:
Abscission is a process that initiates the removal/shedding of a region of the plant following the formation of a protective layer that protects the inner tissues from desiccation. Leaf abscission is quite a common phenomenon.
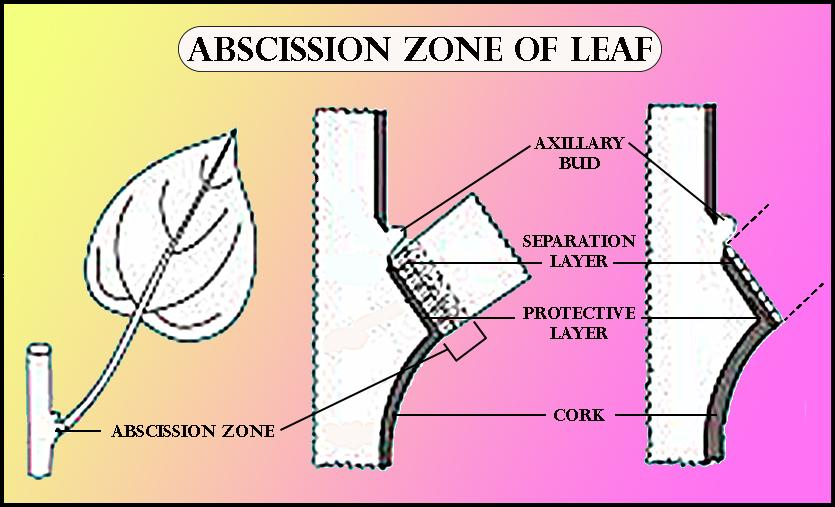
The protective layer and the region of separation, which is the abscission layer are collectively termed as the abscission zone. This zone initiates the method of abscission. The protective layer provides protection and acts as a defense against infections. The cells during this layer may become lignified.
During the method of abscission, walls of the cells forming the abscission layer undergo dissolution due to which the petiole remains attached to the stem only by the vascular elements. Thereafter, due to wind or the gravity pull, the leaf is separated from the parent plant. The abscission layer results in the formation of a protective layer across the area left by the abscission.
Additional Information:
Cells within the abscission zone divide and arrange a layer of cork cells. Layers of parenchyma cells are situated on each side of the abscission zone, which produces and injects suberin and lignin under the abscission zone into the new layer of cork cells. Suberin and lignin make a durable and waterproof layer for the plant once the organ is detached.
Detachment can occur when layers of parenchyma cells secrete cell wall enzymes to self-digest the center lamella, which holds the cell walls together at the abscission zone. This causes the cells of the abscission zone to interrupt apart and the leaf or other plant part to fall off.
Another way detachment occurs is through the imbibition of water. The plant cells at the abscission zone will absorb an outsized amount of water, swell, and eventually burst, making the organ fall off. Once detached, the protective layer of cork is going to be exposed.
Note: Researchers initially accepted abscisic acid is the hormone that stimulates abscission (for which the hormone was named), it had been later proven that it doesn't play a primary role. In fact, auxin, a plant hormone, and ethylene are implicated as prominent regulators of abscission signaling. The two compounds work in a synergistic fashion: because the auxin levels decrease, the flux of auxin to the abscission zone is reduced. The depletion of auxin makes the abscission zone sensitive to ethylene.
Complete answer:
Abscission is a process that initiates the removal/shedding of a region of the plant following the formation of a protective layer that protects the inner tissues from desiccation. Leaf abscission is quite a common phenomenon.
The protective layer and the region of separation, which is the abscission layer are collectively termed as the abscission zone. This zone initiates the method of abscission. The protective layer provides protection and acts as a defense against infections. The cells during this layer may become lignified.
During the method of abscission, walls of the cells forming the abscission layer undergo dissolution due to which the petiole remains attached to the stem only by the vascular elements. Thereafter, due to wind or the gravity pull, the leaf is separated from the parent plant. The abscission layer results in the formation of a protective layer across the area left by the abscission.
Additional Information:
Cells within the abscission zone divide and arrange a layer of cork cells. Layers of parenchyma cells are situated on each side of the abscission zone, which produces and injects suberin and lignin under the abscission zone into the new layer of cork cells. Suberin and lignin make a durable and waterproof layer for the plant once the organ is detached.
Detachment can occur when layers of parenchyma cells secrete cell wall enzymes to self-digest the center lamella, which holds the cell walls together at the abscission zone. This causes the cells of the abscission zone to interrupt apart and the leaf or other plant part to fall off.
Another way detachment occurs is through the imbibition of water. The plant cells at the abscission zone will absorb an outsized amount of water, swell, and eventually burst, making the organ fall off. Once detached, the protective layer of cork is going to be exposed.
Note: Researchers initially accepted abscisic acid is the hormone that stimulates abscission (for which the hormone was named), it had been later proven that it doesn't play a primary role. In fact, auxin, a plant hormone, and ethylene are implicated as prominent regulators of abscission signaling. The two compounds work in a synergistic fashion: because the auxin levels decrease, the flux of auxin to the abscission zone is reduced. The depletion of auxin makes the abscission zone sensitive to ethylene.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




