
According to which theory/theories ammonia is a base?
(A) Arrhenius, Bronsted
(B) Bronsted, Lewis
(C) Arrhenius, Lewis
(D) Both (B) and (C)
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: In the theories of acids and bases as given, in which the tendency of the molecule to release proton or hydroxide ion in solution (in Arrhenius theory) or tendency to accept or donate protons (in Bronsted theory) or the tendency to accept or donate the electrons (in Lewis theory) helps us to decide the nature of the molecule as an acid or base.
Complete step by step solution:
In the ammonia molecule, which is made up of nitrogen and hydrogen atoms with a lone pair of electrons present on the nitrogen atom.
The ammonia on reaction with water, it dissociates to produce ammonium ion and hydroxide ion in the solution. This is because of the tendency of the ammonia molecule to accept a proton $({{H}^{+}})$ through the lone pair of electrons present in the $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised orbital of the nitrogen.
The reaction is as follows: $N{{H}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\rightleftharpoons N{{H}_{4}}^{+}+O{{H}^{-}}$.
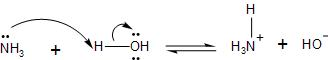
Now, according to the Bronsted theory of acid and bases, which takes into account the tendency of the base to accept a proton is seen. Also, the Lewis theory according to which the base donates its electrons is fulfilled. Therefore, it proves that ammonia is a base.
Thus, according to option (B)- Bronsted and Lewis theories, ammonia is a base.
Note: The ammonia as a base, is not explained by to the Arrhenius theory of acids and bases, because on dissolving in water, the ammonia does not dissociate in the solution to give hydroxide ions due to the absence of O-H bond in the ammonia molecule. Though, in the reaction, it accepts a proton from water molecules and favours the formation of hydroxide ions in the solution. It is a limitation to the Arrhenius theory.
Complete step by step solution:
In the ammonia molecule, which is made up of nitrogen and hydrogen atoms with a lone pair of electrons present on the nitrogen atom.
The ammonia on reaction with water, it dissociates to produce ammonium ion and hydroxide ion in the solution. This is because of the tendency of the ammonia molecule to accept a proton $({{H}^{+}})$ through the lone pair of electrons present in the $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridised orbital of the nitrogen.
The reaction is as follows: $N{{H}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\rightleftharpoons N{{H}_{4}}^{+}+O{{H}^{-}}$.
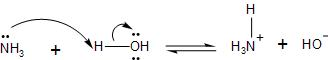
Now, according to the Bronsted theory of acid and bases, which takes into account the tendency of the base to accept a proton is seen. Also, the Lewis theory according to which the base donates its electrons is fulfilled. Therefore, it proves that ammonia is a base.
Thus, according to option (B)- Bronsted and Lewis theories, ammonia is a base.
Note: The ammonia as a base, is not explained by to the Arrhenius theory of acids and bases, because on dissolving in water, the ammonia does not dissociate in the solution to give hydroxide ions due to the absence of O-H bond in the ammonia molecule. Though, in the reaction, it accepts a proton from water molecules and favours the formation of hydroxide ions in the solution. It is a limitation to the Arrhenius theory.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




