
Acetone and Propanal are:
A .functional isomers
B. position isomers
C .geometrical isomers
D .optical isomers
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: Molecular formula for Acetone is $\,{C_3}{H_6}O\,$ and molecular formula for propanal is $\,{C_3}{H_6}O\,$ which means they have the same molecular formula. But one is from the ketone family whereas another from the aldehyde family.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly what is the definition of an isomer?
The term isomer means each of two or more compounds with the same formula but a different arrangement of atoms in the molecule and different properties.
Isomers can be split into two broad groups – structural (or constitutional) isomers and stereoisomers and structural isomer classified into three groups, chain isomer , position isomer and functional isomer
Now let us see all options with detailed information
A.functional isomers
Occurs when the same molecular formula but differs in the functional group.
Examples:
A.Acetone
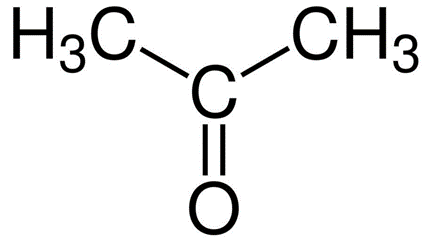
-Propanal( Propanaldehyde)
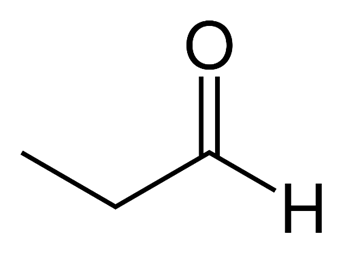
So from this we can conclude Acetone and Propanal are functional isomers hence option A is the correct answer.
B.Position isomers:
Occurs when the functional group is in a different position on the same carbon chain.
Example:
$\,1 - \,$ chloropropane
$\,2 - \,$ chloropropane
C.Geometrical isomers:
Two or more compounds differ from each other in the arrangement but same in the structure
Example:
cis - but $\, - 2 - \,$ ene
trans - but $\, - 2 - \,$ ene
D.Optical isomers:
Optical isomers are compounds that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. ... If the arrangement in space makes the two isomers non-superimposable mirror images of each other, we call them optical isomers or enantiomers. An example is the amino acid alanine.
So, the correct answer to this is option A.
Note: In geometrical isomerism the arrangement is differ from double bond or ring and non-superimposable mirror images forms. Non- superimposable mirror images are the ones in which we can distinguish the left and right side of the object. Examples like “MOM” are the same in its mirror image too.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly what is the definition of an isomer?
The term isomer means each of two or more compounds with the same formula but a different arrangement of atoms in the molecule and different properties.
Isomers can be split into two broad groups – structural (or constitutional) isomers and stereoisomers and structural isomer classified into three groups, chain isomer , position isomer and functional isomer
Now let us see all options with detailed information
A.functional isomers
Occurs when the same molecular formula but differs in the functional group.
Examples:
A.Acetone

-Propanal( Propanaldehyde)

So from this we can conclude Acetone and Propanal are functional isomers hence option A is the correct answer.
B.Position isomers:
Occurs when the functional group is in a different position on the same carbon chain.
Example:
$\,1 - \,$ chloropropane
$\,2 - \,$ chloropropane
C.Geometrical isomers:
Two or more compounds differ from each other in the arrangement but same in the structure
Example:
cis - but $\, - 2 - \,$ ene
trans - but $\, - 2 - \,$ ene
D.Optical isomers:
Optical isomers are compounds that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. ... If the arrangement in space makes the two isomers non-superimposable mirror images of each other, we call them optical isomers or enantiomers. An example is the amino acid alanine.
So, the correct answer to this is option A.
Note: In geometrical isomerism the arrangement is differ from double bond or ring and non-superimposable mirror images forms. Non- superimposable mirror images are the ones in which we can distinguish the left and right side of the object. Examples like “MOM” are the same in its mirror image too.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




