
Acid which contains both –OH and –COOH groups is:-
A.Phthalic acid
B.Adipic acid
C.Glutaric acid
D.Salicylic acid
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The –OH group individually the presence of an alcohol, and also known as alcohol group. It is found in phenol. The –COOH group indicates the carboxylic acid, mainly found in the benzoic acid. When 2 –COOH groups are present, it is called dicarboxylic acid. It is found in oxalic acid.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, let us look at the molecular formula and structure to find out the answer.
A. Phthalic acid has a molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ . The structure can be drawn as:
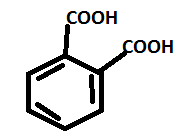 It is known as benzene-1, 2 dicarboxylic acid.
It is known as benzene-1, 2 dicarboxylic acid.
So, from the structure it is observed that it contains the presence of 2 –COOH groups.
B. Adipic acid has the chemical formula Hexanedioic acid. The structure can be drawn as:
So, we get to know that it is an aliphatic dicarboxylic acid.
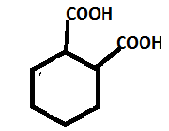
It also consists of 2 –COOH groups.
C. Glutaric acid is also known as pentanedioic acid. The chemical formula of glutaric acid is ${\text{HOOC - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ - COOH}}$. From the representation it is clear that it has presence of 2 –COOH groups.
D. Let us now check Salicylic acid. It is known as 2-hydroxy benzoic acid.
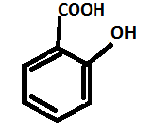
This means that on the ortho-position of Salicylic acid is a hydroxyl group and on para position is carboxylic group (-OH and –COOH group) respectively. Thus, Salicylic acid contains both OH and –COOH groups.
Hence, the correct answer is Option (D)
Note:
Molecular formula, IUPAC name and structure of these should be known inorder to answer this question. All the other options except option D indicates to be in the category of dicarboxylic acid due to the presence of 2 –COOH groups on the benzene ring. Another example is gallic acid. It consists of 2 -OH groups and 2 -COOH groups attached to a benzene ring.
Complete step by step answer:
Now, let us look at the molecular formula and structure to find out the answer.
A. Phthalic acid has a molecular formula ${{\text{C}}_{\text{8}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}$ . The structure can be drawn as:

So, from the structure it is observed that it contains the presence of 2 –COOH groups.
B. Adipic acid has the chemical formula Hexanedioic acid. The structure can be drawn as:
So, we get to know that it is an aliphatic dicarboxylic acid.

It also consists of 2 –COOH groups.
C. Glutaric acid is also known as pentanedioic acid. The chemical formula of glutaric acid is ${\text{HOOC - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ - C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{ - COOH}}$. From the representation it is clear that it has presence of 2 –COOH groups.
D. Let us now check Salicylic acid. It is known as 2-hydroxy benzoic acid.

This means that on the ortho-position of Salicylic acid is a hydroxyl group and on para position is carboxylic group (-OH and –COOH group) respectively. Thus, Salicylic acid contains both OH and –COOH groups.
Hence, the correct answer is Option (D)
Note:
Molecular formula, IUPAC name and structure of these should be known inorder to answer this question. All the other options except option D indicates to be in the category of dicarboxylic acid due to the presence of 2 –COOH groups on the benzene ring. Another example is gallic acid. It consists of 2 -OH groups and 2 -COOH groups attached to a benzene ring.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




