
Action of hydrogen iodide on anisole gives
A ) phenol and iodomethane
B) iodobenzene and methanol
C) phenol and methanol
D) Iodobenzene and iodomethane
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Consider which of the two bonds attached to the oxygen atom of anisole breaks, upon reaction with hydrogen iodide. Anisole contains one aromatic carbon-oxygen bond and one aliphatic carbon-oxygen bond. Cleavage of aliphatic carbon-oxygen bond is much easier compared to aromatic carbon-oxygen bond.
Hydrogen iodide is an acid and dissociates to give protons and iodide ions. Proton is accepted by the oxygen atom of anisole. Iodide ion attacks the aliphatic C atom of carbon-oxygen bond.
Complete answer:
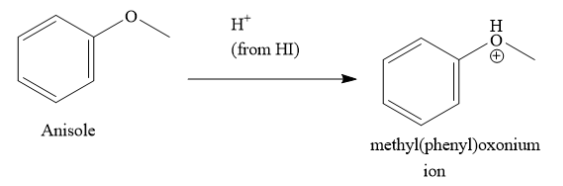
Anisole is methoxy benzene. Anisole reacts with protons from hydroiodic acid to form methyl(phenyl) oxonium ion.
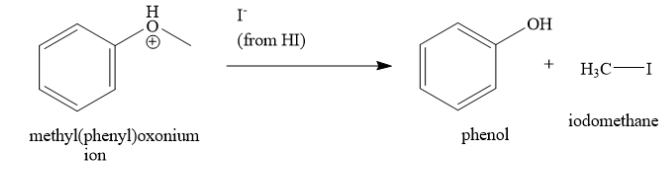
This methyl(phenyl)oxonium ion then accepts a iodide ion to form phenol and iodomethane. The iodide ion can attack either the carbon atom of methyl group or aromatic carbon atom of benzene ring. If iodide ion attacks the carbon atom of the methyl group, then the products are phenol and iodomethane. But if the iodide ion attacks aromatic carbon atom, then the products are methanol and iodobenzene.
In the methyl(phenyl)oxonium ion, the oxygen atom has positive charge. This positive charge is delocalized through resonance with the benzene ring. Due to this, the bond between the oxygen atom and the aromatic carbon atom of benzene has partial double bond character. This bond is difficult to break. Hence, iodide ion does not attack the aromatic carbon atom of benzene ring. On the other hand, the bond between the oxygen atom and the carbon atom of the methyl group is a single bond. This bond can be easily broken. Hence, iodide ion attacks the carbon atom of the methyl group to form phenol and iodomethane.
Hence, the correct answer is option A ) phenol and iodomethane.
Note: When alkyl aryl ethers are reacted with hydrogen iodide, phenol and alkyl iodide are formed. This is because the bond between oxygen atom and aromatic carbon atom is difficult to break due to the presence of partial double bond character.
Hydrogen iodide is an acid and dissociates to give protons and iodide ions. Proton is accepted by the oxygen atom of anisole. Iodide ion attacks the aliphatic C atom of carbon-oxygen bond.
Complete answer:
Anisole is methoxy benzene. Anisole reacts with protons from hydroiodic acid to form methyl(phenyl) oxonium ion.
This methyl(phenyl)oxonium ion then accepts a iodide ion to form phenol and iodomethane. The iodide ion can attack either the carbon atom of methyl group or aromatic carbon atom of benzene ring. If iodide ion attacks the carbon atom of the methyl group, then the products are phenol and iodomethane. But if the iodide ion attacks aromatic carbon atom, then the products are methanol and iodobenzene.
In the methyl(phenyl)oxonium ion, the oxygen atom has positive charge. This positive charge is delocalized through resonance with the benzene ring. Due to this, the bond between the oxygen atom and the aromatic carbon atom of benzene has partial double bond character. This bond is difficult to break. Hence, iodide ion does not attack the aromatic carbon atom of benzene ring. On the other hand, the bond between the oxygen atom and the carbon atom of the methyl group is a single bond. This bond can be easily broken. Hence, iodide ion attacks the carbon atom of the methyl group to form phenol and iodomethane.


Hence, the correct answer is option A ) phenol and iodomethane.
Note: When alkyl aryl ethers are reacted with hydrogen iodide, phenol and alkyl iodide are formed. This is because the bond between oxygen atom and aromatic carbon atom is difficult to break due to the presence of partial double bond character.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




