
How do action-reaction pairs keep a book sitting on a table in equilibrium?
Answer
549.6k+ views
Hint:The action reaction pairs working here are the gravitational force by the Earth on the book and the normal reaction force by the table on the book. However, they are not the action reaction pairs as prescribed in Newton’s third law of motion. We are treating them like an action-reaction pair because they are equal and acting in completely opposite directions.
Complete step by step solution:
The gravitational force, ${{F}_{g}}$ acting on a body if expressed as
${{F}_{g}}=mg$
Where,
$m=$ mass of the body
$g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}$ is the acceleration due to gravity acting on the body.
The normal force, ${{F}_{N}}$ acting on a body is exerted by the surface on which the body is kept is represented as
${{F}_{N}}=N$
We shall now analyze the forces acting on the book kept on the table.
We observe that the gravitational force pulls the book in the downward direction and tends to cause deformations in the book, hence it can be called as the deforming force.
Now, we see that the table exerts a normal reaction force on the book in the upward direction.
Thus, we understand that the gravitational force and the normal are in completely opposite directions.
Although the prominent force of gravity does not let the book fly in the air. The normal reaction force exerted by the table acts like a restoring force on the book against the deforming force of gravity.
This means that the force of gravity is being balanced by the normal force exerted by the table on the book.
Hence,${{F}_{g}}={{F}_{N}}$
$\Rightarrow mg=N$
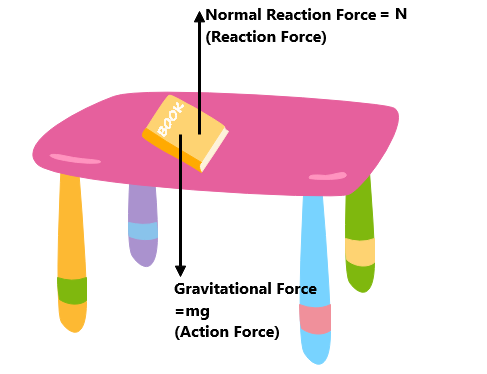
In this way, the forces continue to support each other and balance each other out in order to keep the book sitting on the table.
Hence, we conclude that here,
the gravitational force = action force
normal reaction force = reaction force
Therefore, in this way the gravitational force and normal force act as action-reaction pairs and keep a book sitting on a table in equilibrium.
Note:
According to Newton’s third of motion, to every action there is an equal and opposite reaction, that is, the forces of two bodies on each other are always equal and are directed in opposite directions. The action-reaction pair of forces are equal and in opposite directions. The important point is that if the action force is acting on a body then the reaction force must be exerted by that particular body only.
Complete step by step solution:
The gravitational force, ${{F}_{g}}$ acting on a body if expressed as
${{F}_{g}}=mg$
Where,
$m=$ mass of the body
$g=9.8m{{s}^{-2}}$ is the acceleration due to gravity acting on the body.
The normal force, ${{F}_{N}}$ acting on a body is exerted by the surface on which the body is kept is represented as
${{F}_{N}}=N$
We shall now analyze the forces acting on the book kept on the table.
We observe that the gravitational force pulls the book in the downward direction and tends to cause deformations in the book, hence it can be called as the deforming force.
Now, we see that the table exerts a normal reaction force on the book in the upward direction.
Thus, we understand that the gravitational force and the normal are in completely opposite directions.
Although the prominent force of gravity does not let the book fly in the air. The normal reaction force exerted by the table acts like a restoring force on the book against the deforming force of gravity.
This means that the force of gravity is being balanced by the normal force exerted by the table on the book.
Hence,${{F}_{g}}={{F}_{N}}$
$\Rightarrow mg=N$

In this way, the forces continue to support each other and balance each other out in order to keep the book sitting on the table.
Hence, we conclude that here,
the gravitational force = action force
normal reaction force = reaction force
Therefore, in this way the gravitational force and normal force act as action-reaction pairs and keep a book sitting on a table in equilibrium.
Note:
According to Newton’s third of motion, to every action there is an equal and opposite reaction, that is, the forces of two bodies on each other are always equal and are directed in opposite directions. The action-reaction pair of forces are equal and in opposite directions. The important point is that if the action force is acting on a body then the reaction force must be exerted by that particular body only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




