
Active transport occurs
(a)Against concentration gradient and requires ATP
(b)Against concentration gradient but does not require ATP
(c)Along concentration gradient but requires ATP
(d)Along concentration gradient but does not require ATP
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Opposite to diffusion is active transport. To attain its process it needs cellular energy. They need carrier protein assistance for their process to occur. The taking of glucose in the intestines is an example of active transport in human physiology.
Complete answer:
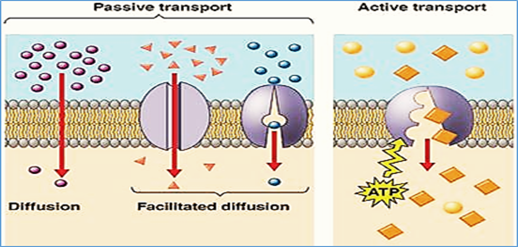
Active transport is the movement of molecules against gradient through a cell membrane from a region of their lower concentration to a region of their higher concentration. This type of movement requires ATP generated energy.
Provided that molecules travel against their gradients of concentration, active transport can not take place without assistance. In this phase often a carrier protein is needed. A protein in the membrane carries the molecules across the membrane-like facilitated diffusion, except this protein pushes the molecules from low concentration to high concentration. These proteins are also called "pumps," because they move the molecules across the membrane using energy.
One example of an active transport pump is the sodium-potassium pump. The sodium-potassium pump uses ATP to transfer three sodium ions and two potassium ions. Sodium ions pass out of the cell, and ions of potassium pass in the cell.
Additional Information:
There are two forms of active transportation namely primary and secondary active transport. Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) is used in primary active transport, and an electrochemical gradient is used for secondary active transport.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Against concentration gradient and requires ATP’.
Note:
In general, active transport occurs through the cell membrane. One thousand proteins are found in the lipid bilayer of the cell. These proteins do much of the effectively transporting function. They are placed to cross the membrane so that there is one part within the cell and one part outside. They are able to move molecules and ions in and out of the cell only when they cross the bilayer. The proteins are very unique to the membrane. Calcium ions won't move one protein that carries glucose. In many cells of your body, there are hundreds of forms of such membrane proteins.
Complete answer:
Active transport is the movement of molecules against gradient through a cell membrane from a region of their lower concentration to a region of their higher concentration. This type of movement requires ATP generated energy.
Provided that molecules travel against their gradients of concentration, active transport can not take place without assistance. In this phase often a carrier protein is needed. A protein in the membrane carries the molecules across the membrane-like facilitated diffusion, except this protein pushes the molecules from low concentration to high concentration. These proteins are also called "pumps," because they move the molecules across the membrane using energy.
One example of an active transport pump is the sodium-potassium pump. The sodium-potassium pump uses ATP to transfer three sodium ions and two potassium ions. Sodium ions pass out of the cell, and ions of potassium pass in the cell.
Additional Information:
There are two forms of active transportation namely primary and secondary active transport. Adenosine triphosphate ( ATP) is used in primary active transport, and an electrochemical gradient is used for secondary active transport.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Against concentration gradient and requires ATP’.
Note:
In general, active transport occurs through the cell membrane. One thousand proteins are found in the lipid bilayer of the cell. These proteins do much of the effectively transporting function. They are placed to cross the membrane so that there is one part within the cell and one part outside. They are able to move molecules and ions in and out of the cell only when they cross the bilayer. The proteins are very unique to the membrane. Calcium ions won't move one protein that carries glucose. In many cells of your body, there are hundreds of forms of such membrane proteins.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




