
Addition of HCl to alkenes proceeds in two steps; the first step is the attack of ${{H}^{+}}$ ion to
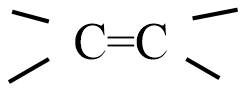 portion which can be shown as:
portion which can be shown as:
(A)
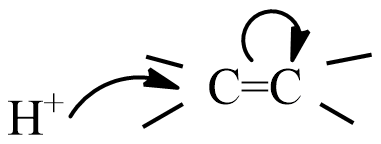
(B)
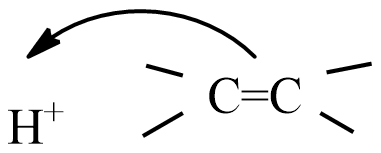
(C)
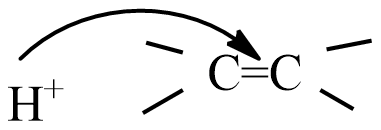
(D) all are possible
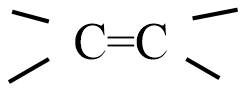
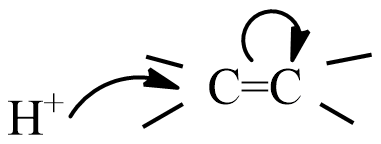


Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: Organic reactions are accompanied by breaking and the making of covalent bonds that involve the exchange of electrons. The functional groups of organic compounds also play a very important role in the exchange of electrons. Organic reactions are classified into four types of reactions which are addition reactions, substitution reactions, rearrangement reactions, and elimination reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
The chemical reactions undergone by organic compounds containing carbon are called organic reactions. Based on all fundamental considerations, organic reactions are classified into the following types:
(1) Addition reactions
(2) Substitution reactions
(3) Elimination reactions
(4) Rearrangement reactions
Addition reactions: Addition reactions are the reactions which the compounds are added to the carbon-carbon multiple bonds which are known as unsaturated compounds. These unsaturated compounds form by the addition of some reagent.
For example, $C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}+HCl\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl$.
Types of addition reactions: depending upon the nature of the attacking agent, the addition reactions are classified as follows:
(i) Electrophilic addition reactions
(ii) Nucleophilic addition reactions
(iii) Free radical addition reactions.
Given reaction is the addition of HCl to an alkene is a type of electrophilic addition reaction, which means the electrophile initiates the reaction and this slow step is the rate determining step.
The electrophile in HCl is ${{H}^{+}}$ an ion, and the mechanism of electrophilic addition is followed by two steps.
Step-1: formation of carbonium ion by the flow of electrons from the$\pi $ bond to electron-deficient ${{H}^{+}}$ion.
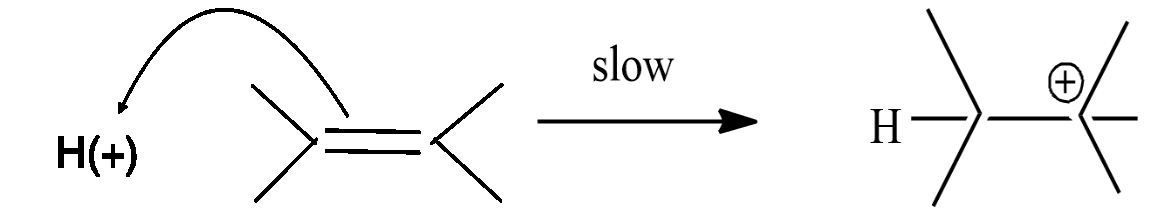
Step-2: the carbonium ion forms the final product with $C{{l}^{-}}$ ion
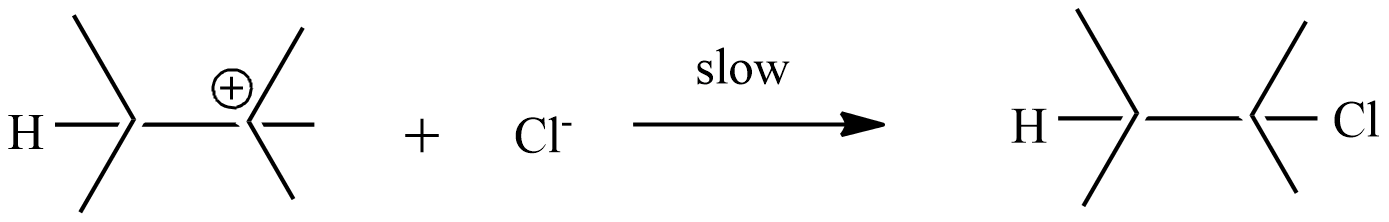
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: Positively charged or neutral species which are act as Lewis acid are electrophiles, negatively charged or Lewis bases are nucleophiles, and an atom or group of atoms having an unpaired electron that are produced from the homolytic fission of a covalent bond is called as free radical.
Complete step by step answer:
The chemical reactions undergone by organic compounds containing carbon are called organic reactions. Based on all fundamental considerations, organic reactions are classified into the following types:
(1) Addition reactions
(2) Substitution reactions
(3) Elimination reactions
(4) Rearrangement reactions
For example, $C{{H}_{2}}=C{{H}_{2}}+HCl\to C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}Cl$.
Types of addition reactions: depending upon the nature of the attacking agent, the addition reactions are classified as follows:
(i) Electrophilic addition reactions
(ii) Nucleophilic addition reactions
(iii) Free radical addition reactions.
Given reaction is the addition of HCl to an alkene is a type of electrophilic addition reaction, which means the electrophile initiates the reaction and this slow step is the rate determining step.
The electrophile in HCl is ${{H}^{+}}$ an ion, and the mechanism of electrophilic addition is followed by two steps.
Step-1: formation of carbonium ion by the flow of electrons from the$\pi $ bond to electron-deficient ${{H}^{+}}$ion.

Step-2: the carbonium ion forms the final product with $C{{l}^{-}}$ ion
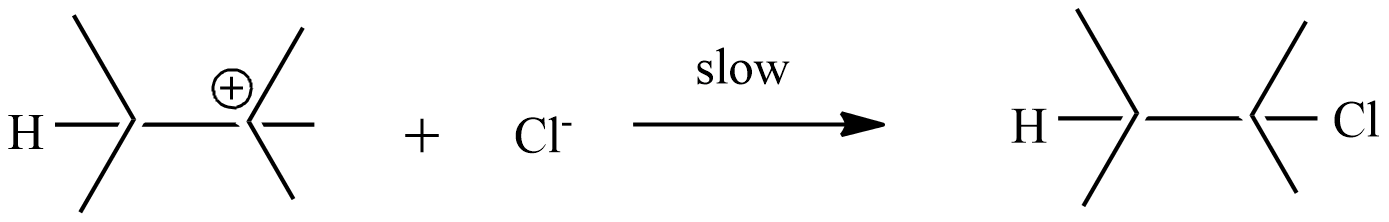
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: Positively charged or neutral species which are act as Lewis acid are electrophiles, negatively charged or Lewis bases are nucleophiles, and an atom or group of atoms having an unpaired electron that are produced from the homolytic fission of a covalent bond is called as free radical.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




