
When an adduct is formed from Diels Alder reaction of maleic anhydride and furan, what does the adduct decompose to at its melting point?
Answer
487.5k+ views
Hint: We know that the $ 4\pi $ electrons system of aromatic compounds refers to mainly diene structure of compound whereas the $ 2\pi $ electrons system of aromatic compounds refer to dienophile structure. With the help of the mechanism of these structures we can find the product of decomposition of adducts so formed.
Complete answer:
In Diels Alder reaction basically we have substituted alkene and a conjugated diene. The substituted alkene refers to dienophile. The reaction is basically a pericyclic reaction in which all bond breaking and bond making takes place in a single step only. The result of the reaction will be a new formation of rings from the reactants. Here diene is furan and dienophile is maleic anhydride. It follows the concentrated mechanism.
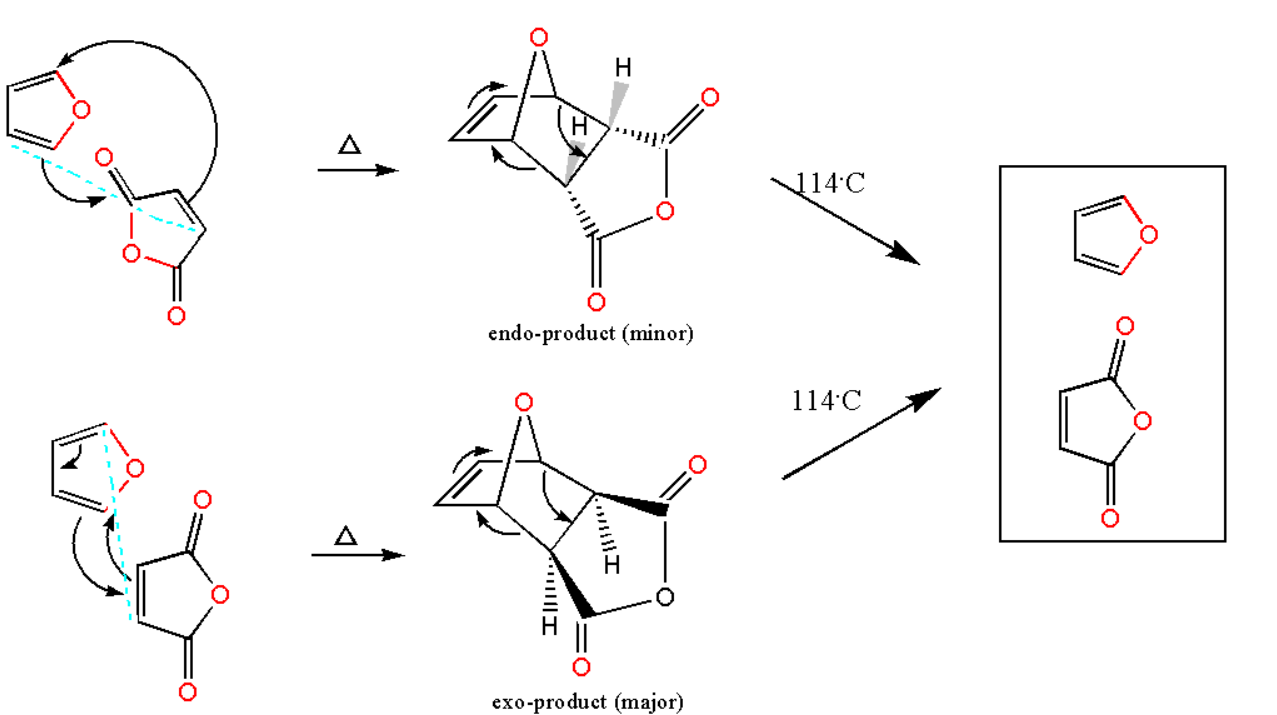
The decomposition of this compound at its melting point will take place at approximately $ 114{{\text{ }}^ \circ }C $ . The products formed after its decomposition will be its original products. This is known as the retro Diels-Alder reaction. Therefore the product above is formed below its melting point. The Diels-Alder reaction creates a more stable substance or product since sigma bonds are formed which are stronger than pi bonds. Pi bonds break easily while sigma bonds are stronger.
Note:
It must be noted that a diene is an organic compound which contains only two double bonds in its structure while dienophile is an organic compound which reacts with the diene. The reaction has a high degree of region-selectivity and stereo-selectivity which makes it a more very effective reaction. Furan will act as diene whereas maleic anhydride will be acting as dienophile.
Complete answer:
In Diels Alder reaction basically we have substituted alkene and a conjugated diene. The substituted alkene refers to dienophile. The reaction is basically a pericyclic reaction in which all bond breaking and bond making takes place in a single step only. The result of the reaction will be a new formation of rings from the reactants. Here diene is furan and dienophile is maleic anhydride. It follows the concentrated mechanism.

The decomposition of this compound at its melting point will take place at approximately $ 114{{\text{ }}^ \circ }C $ . The products formed after its decomposition will be its original products. This is known as the retro Diels-Alder reaction. Therefore the product above is formed below its melting point. The Diels-Alder reaction creates a more stable substance or product since sigma bonds are formed which are stronger than pi bonds. Pi bonds break easily while sigma bonds are stronger.
Note:
It must be noted that a diene is an organic compound which contains only two double bonds in its structure while dienophile is an organic compound which reacts with the diene. The reaction has a high degree of region-selectivity and stereo-selectivity which makes it a more very effective reaction. Furan will act as diene whereas maleic anhydride will be acting as dienophile.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




