
Alexander Von Humboldt described for the first time?
A. Ecological Diversity
B. Laws of limiting factor
C. Species Area Relationship
D. Population growth equation
Answer
608.7k+ views
Hint: Alexander Von Humboldt observed something related to the richness in organisms while he was exploring the South American wilderness.
Complete answer:
Alexander Von Humboldt during his exploration found out that species richness increased with the increase in explored area, but it was up to a certain limit. He later saw that the relationship between species richness and area turned out to be a rectangular hyperbola for a wide variety of organisms like birds, bats, fishes, and flowering plants.
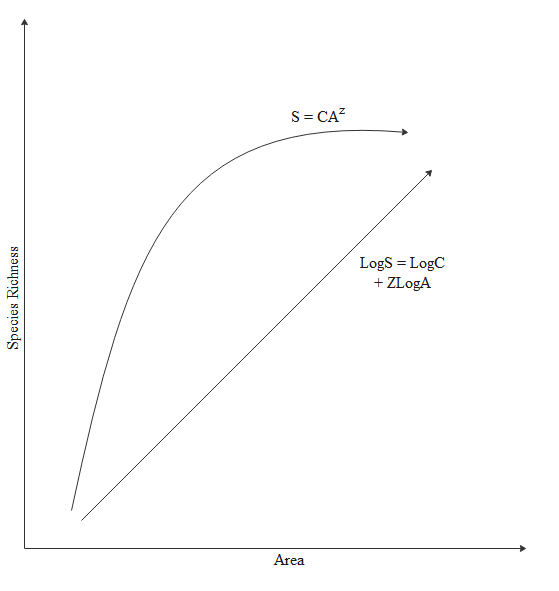
Species area relationship becomes linear in the logarithmic scale as shown in the above diagram.
The parameters of the graph are as follows:
S represents species richness, Z is the regression coefficient, C is the Y-intercept and A is the area.
Additional Information:
- The regression coefficient Z has a value of 0.1-0.2 regardless of the taxonomic group or area.
- For extremely large areas like an entire continent the value of Z ranges from 0.6-1.2.
- For the mammals of tropical forests of different continents, the value of the regression coefficient or Z is around 1.15.
- Species diversity is the variety in the number of species in a region and the species richness in an area.
- Species evenness is represented by the number of individuals of different species.
- Species richness is the number of species per unit area.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Alexander Von Humboldt described for the first time the Species Area Relationship’
Note: It should be remembered that the species-area relationship is related to species richness and explored area and not species evenness. The value of the regression coefficient increases when the area explored is very large, which means the slope is steeper. The relationship of species richness and area is normally a hyperbola but becomes a straight line in the logarithmic scale.
Complete answer:
Alexander Von Humboldt during his exploration found out that species richness increased with the increase in explored area, but it was up to a certain limit. He later saw that the relationship between species richness and area turned out to be a rectangular hyperbola for a wide variety of organisms like birds, bats, fishes, and flowering plants.

Species area relationship becomes linear in the logarithmic scale as shown in the above diagram.
The parameters of the graph are as follows:
S represents species richness, Z is the regression coefficient, C is the Y-intercept and A is the area.
Additional Information:
- The regression coefficient Z has a value of 0.1-0.2 regardless of the taxonomic group or area.
- For extremely large areas like an entire continent the value of Z ranges from 0.6-1.2.
- For the mammals of tropical forests of different continents, the value of the regression coefficient or Z is around 1.15.
- Species diversity is the variety in the number of species in a region and the species richness in an area.
- Species evenness is represented by the number of individuals of different species.
- Species richness is the number of species per unit area.
So, the correct answer is, ‘Alexander Von Humboldt described for the first time the Species Area Relationship’
Note: It should be remembered that the species-area relationship is related to species richness and explored area and not species evenness. The value of the regression coefficient increases when the area explored is very large, which means the slope is steeper. The relationship of species richness and area is normally a hyperbola but becomes a straight line in the logarithmic scale.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




