
When alkyl halide reacts with silver acetate, the product formed is a/an:
A.Ether
B.Ester
C.Hydrocarbon
D.Alcohol
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: We know that the alkyl halides are the compounds in which one hydrogen atom of an alkane is replaced by any halogen atom such as fluorine, chlorine, bromine etc. The classification of alkyl halides is done in three types, primary, secondary and tertiary.
Complete step by step solution:
Now, we understand the reaction alkyl halide with silver acetate. When alkyl halide reacts with silver acetate, formation of ester and silver halide takes place. The reaction is,
${\rm{R}} - {\rm{X}} + {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOAg}} \to {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOR}} + {\rm{AgX}}$
Here, R is any alkyl group and X is any halogen. The above reaction shows that the alkyl group of the alkyl halide replaces the silver ion from the silver acetate. And the silver ion and halogen ion form a compound.
So, the correct answer is ester.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Additional Information:
There are three types of alkyl halides, primary, secondary and tertiary. In primary alkyl halides, only one carbon atom is bonded to the carbon atom bearing the halogen atom . For example,
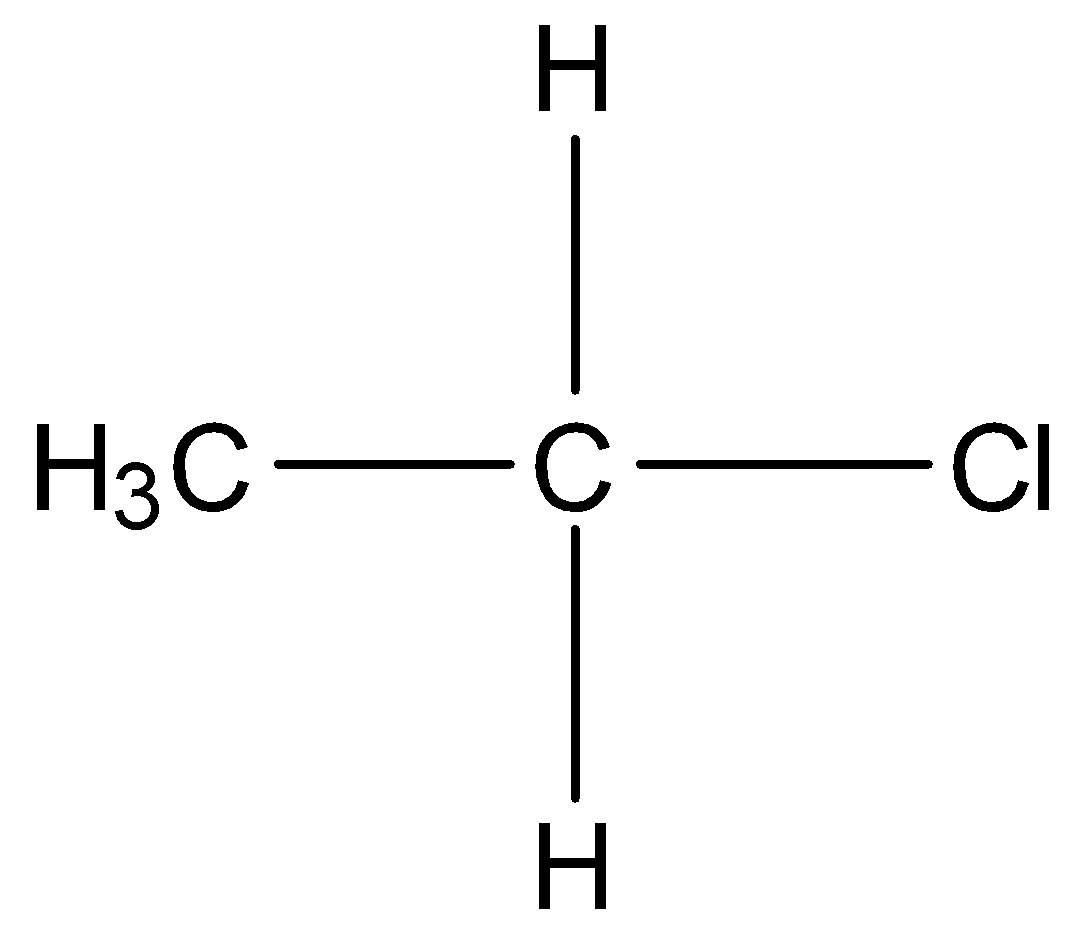
In secondary alkyl halides, two other carbon atoms are bonded to the carbon atom bearing the halogen atom. For example,
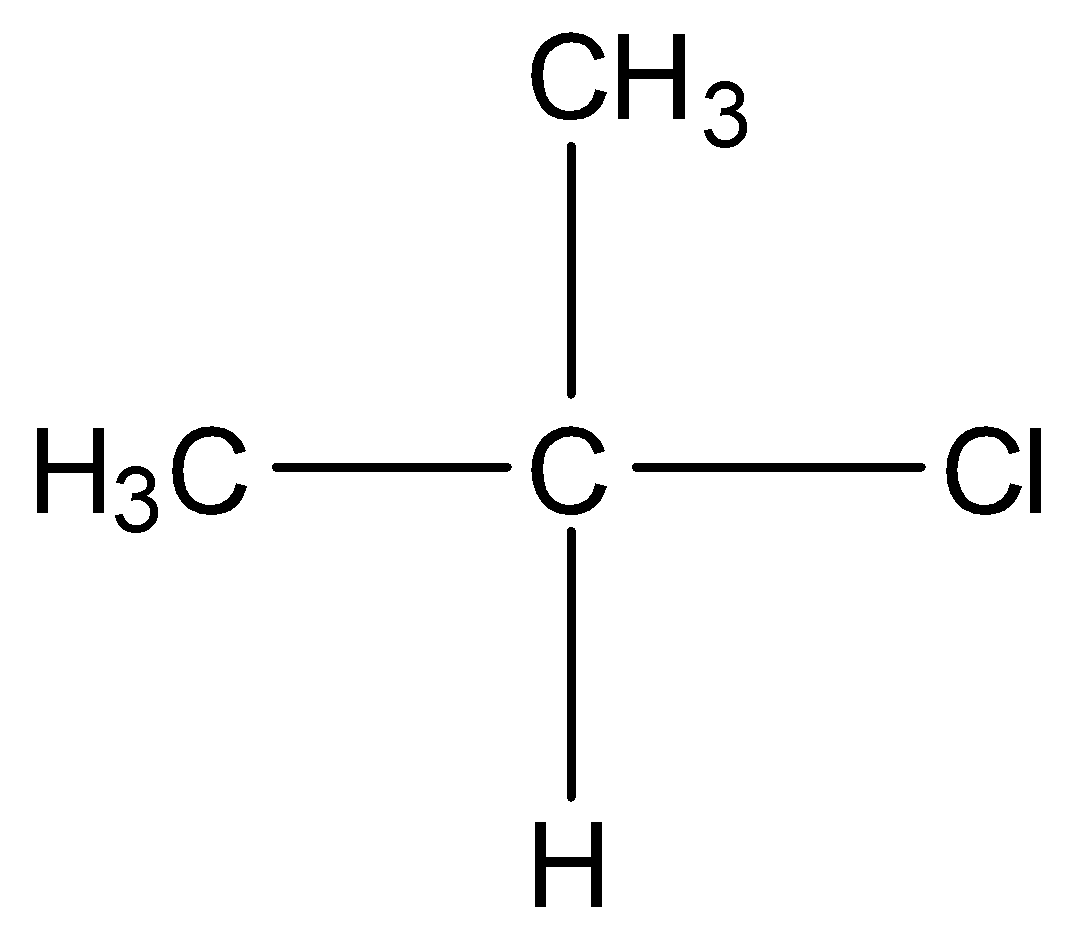
In tertiary alkyl halides, the carbon that is bonded to the halogen atom is bonded to other three carbon atoms. For example,
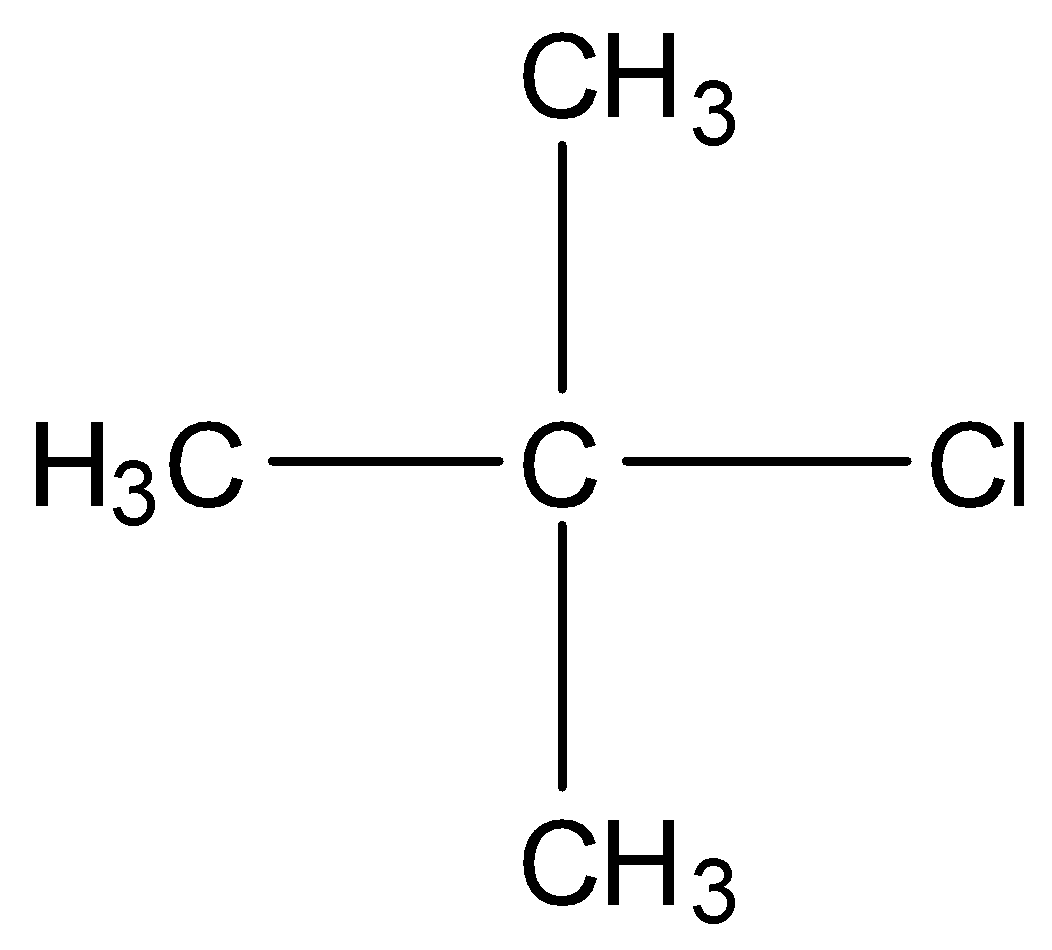
Note: There is a class of compounds containing $s{p^3}{\rm{C}} - {\rm{X}}$ bond (X=Cl, F, I, Br)
1) Alkyl halides: In this class, the halogen atom is bonded to an alkyl group. The structural formula of homologous series of alkyl halides is ${{\rm{C}}_n}{{\rm{H}}_{2n + 1}}{\rm{X}}$.
2) Allylic halides: In this class of compounds, the bonding of halogen atom is to a $s{p^3}$
hybridized carbon next to C=C bond. For example,
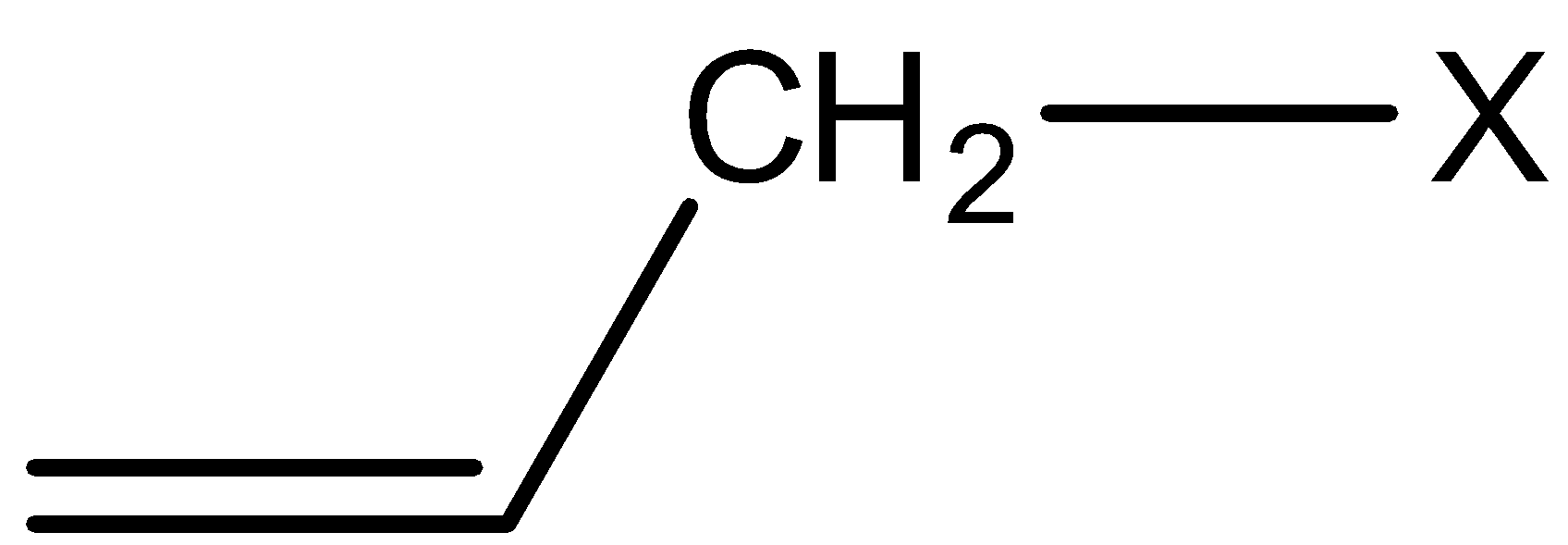
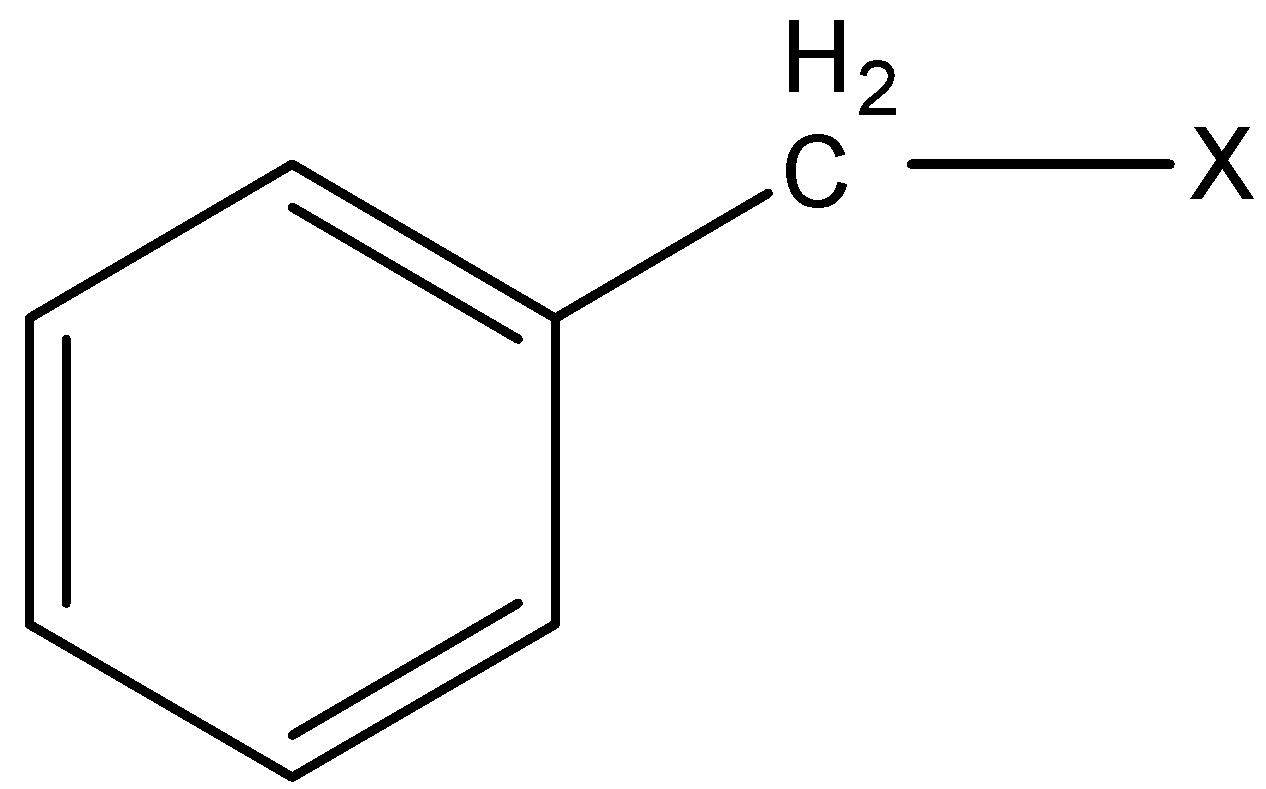
3) Benzylic halides: In this class of compounds, the bonding of halogen is to the carbon atom next to the benzene ring.
Complete step by step solution:
Now, we understand the reaction alkyl halide with silver acetate. When alkyl halide reacts with silver acetate, formation of ester and silver halide takes place. The reaction is,
${\rm{R}} - {\rm{X}} + {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOAg}} \to {\rm{C}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{COOR}} + {\rm{AgX}}$
Here, R is any alkyl group and X is any halogen. The above reaction shows that the alkyl group of the alkyl halide replaces the silver ion from the silver acetate. And the silver ion and halogen ion form a compound.
So, the correct answer is ester.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Additional Information:
There are three types of alkyl halides, primary, secondary and tertiary. In primary alkyl halides, only one carbon atom is bonded to the carbon atom bearing the halogen atom . For example,

In secondary alkyl halides, two other carbon atoms are bonded to the carbon atom bearing the halogen atom. For example,

In tertiary alkyl halides, the carbon that is bonded to the halogen atom is bonded to other three carbon atoms. For example,

Note: There is a class of compounds containing $s{p^3}{\rm{C}} - {\rm{X}}$ bond (X=Cl, F, I, Br)
1) Alkyl halides: In this class, the halogen atom is bonded to an alkyl group. The structural formula of homologous series of alkyl halides is ${{\rm{C}}_n}{{\rm{H}}_{2n + 1}}{\rm{X}}$.
2) Allylic halides: In this class of compounds, the bonding of halogen atom is to a $s{p^3}$
hybridized carbon next to C=C bond. For example,

3) Benzylic halides: In this class of compounds, the bonding of halogen is to the carbon atom next to the benzene ring.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




