
All living organisms are made up of ___
Answer
574.5k+ views
Hint: All living organisms are made up of the basic membrane-bound unit or the structures that contain the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed.
Complete answer:
All living organisms are made up of cells. The cell is defined in easy words as the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known organisms. A cell is known to be the smallest unit of life. Cells are often known to be the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is commonly known as cell biology, cellular biology, or cytology.
Additional Information: Cells are mainly classified into two types: eukaryotic, which contain a nucleus, and prokaryotic, which don't. Prokaryotes are known as single-celled organisms, while eukaryotes are often either single-celled or multicellular.
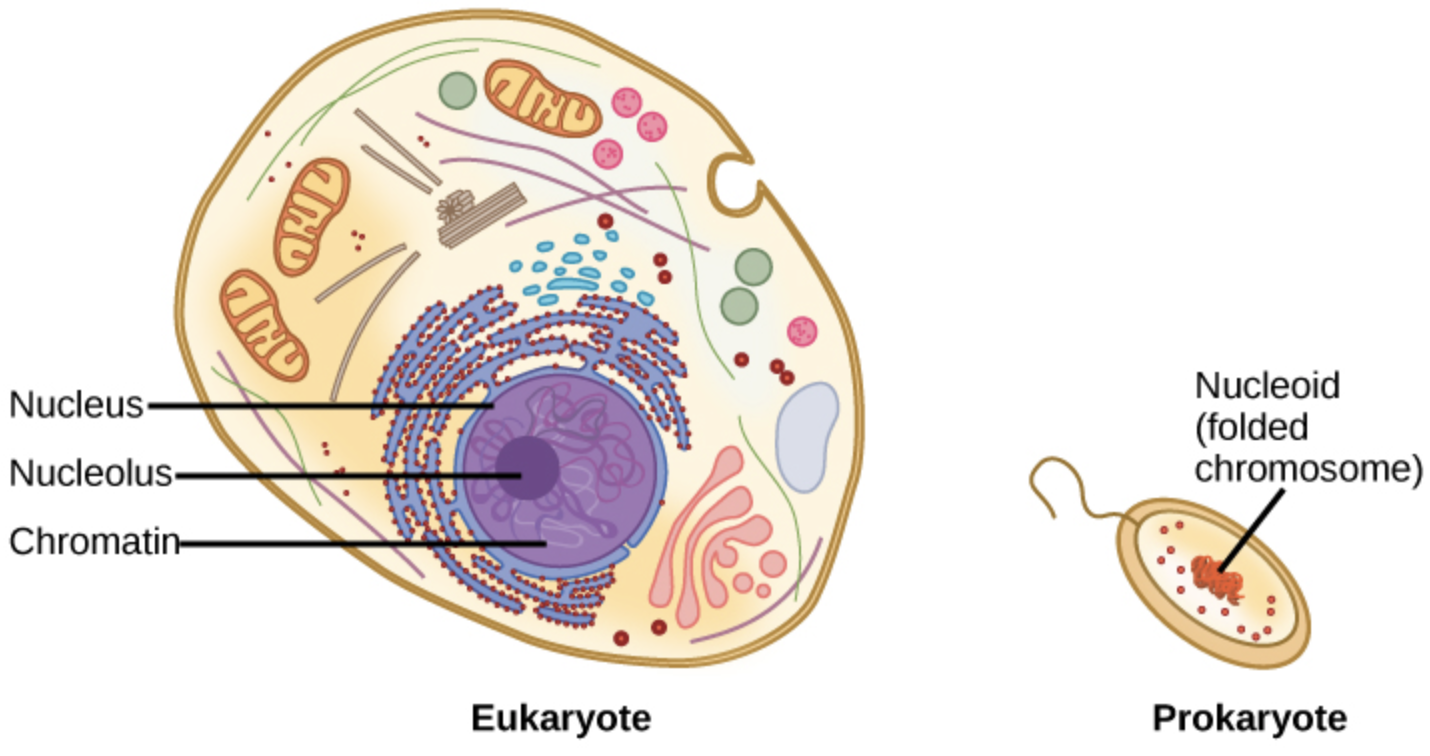
Prokaryotic cell: Prokaryotic organisms include bacteria and archaea, two of the three domains of life. These organisms or cells were the first kind of life seen on the Earth, characterized by having vital biological processes including cell signaling. They're simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells, and lack a nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotic Cell: Plants, animals, fungi, are some examples of eukaryotic organisms. These cells of eukaryotes are wider than prokaryotes at around fifteen times while its volume is greater at around a thousand times. The most different feature of the eukaryotic organisms as compared to prokaryotes is compartmentalization: the presence of membrane-bound organelles (compartments) during which specific activities occur. Most significant among these is a nucleus, an organelle that houses the cell's DNA.
Note: There are many theories about the origin of small molecules that led to life on the early Earth. It is thought that they are carried to Earth on meteorites, created at deep-sea vents, or synthesized by lightning in a very reducing atmosphere (explained by Miller–Urey experiment).
Complete answer:
All living organisms are made up of cells. The cell is defined in easy words as the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known organisms. A cell is known to be the smallest unit of life. Cells are often known to be the "building blocks of life". The study of cells is commonly known as cell biology, cellular biology, or cytology.
Additional Information: Cells are mainly classified into two types: eukaryotic, which contain a nucleus, and prokaryotic, which don't. Prokaryotes are known as single-celled organisms, while eukaryotes are often either single-celled or multicellular.

Prokaryotic cell: Prokaryotic organisms include bacteria and archaea, two of the three domains of life. These organisms or cells were the first kind of life seen on the Earth, characterized by having vital biological processes including cell signaling. They're simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells, and lack a nucleus, and other membrane-bound organelles.
Eukaryotic Cell: Plants, animals, fungi, are some examples of eukaryotic organisms. These cells of eukaryotes are wider than prokaryotes at around fifteen times while its volume is greater at around a thousand times. The most different feature of the eukaryotic organisms as compared to prokaryotes is compartmentalization: the presence of membrane-bound organelles (compartments) during which specific activities occur. Most significant among these is a nucleus, an organelle that houses the cell's DNA.
Note: There are many theories about the origin of small molecules that led to life on the early Earth. It is thought that they are carried to Earth on meteorites, created at deep-sea vents, or synthesized by lightning in a very reducing atmosphere (explained by Miller–Urey experiment).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




