
All plastids essentially have the same structure because
(a)They have to perform the same function
(b)They are localised in the aerial parts of the plant
(c)One of the plastid can differentiate into another type of plastid depending upon the cell requirements
(d)All plastids have to store starch, lipids and proteins
Answer
590.1k+ views
Hint: Plastids are double membranous, semi-autonomous organelles which means they can control much of their functioning and contain DNA and ribosomes. They appear from colorless precursors, proplastids.
Complete answer:
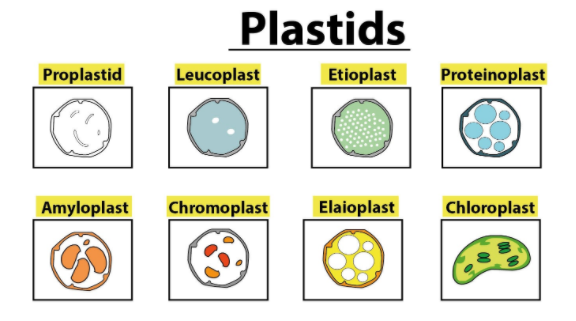
All plastids have the same structure because they can divide into another type of plastid depending upon the cell requirements. The precursors of plastids known as proplastids can divide and differentiate into various types of plastids.
Additional Information: -The plastids are differentiated into 4 types based on their special function they perform:
-Chloroplasts: These are biconvex cell organelle found within the mesophyll of the plant cell and are the site for photosynthesis.
-Chromoplasts: These have carotenoid pigments that impart color to flowers and fruits. The main reason for expressing different colors is for attracting pollinators.
- Gerontoplasts: These are aged chloroplasts. Gerontoplasts are formed during leaf senescence when the leaf is no longer using photosynthesis usually in an autumn month.
-Leucoplasts: These are the non-pigmented colorless organelles. Leucoplasts are usually found in most of the non-photosynthetic parts of the plant like roots and stores starches (Amyloplasts), lipids (Elaioplast), and proteins (Proteinoplasts), depending on the need of the plants.
So, the correct answer is, ‘One of the plastids can differentiate into another type of plastid depending upon the cell requirements.’
Note: -All proplastids are undifferentiated plastids and are derived from the meristematic regions of the plant. Proplastids can divide by binary fission, but more mature chloroplasts can also divide in this manner.
-Plastids are found in the cells of plants and algae and can manufacture and store food in plants. Pigments are present in these organelles that are used in photosynthesis and can change the color of the cell.
Complete answer:
All plastids have the same structure because they can divide into another type of plastid depending upon the cell requirements. The precursors of plastids known as proplastids can divide and differentiate into various types of plastids.
Additional Information: -The plastids are differentiated into 4 types based on their special function they perform:
-Chloroplasts: These are biconvex cell organelle found within the mesophyll of the plant cell and are the site for photosynthesis.
-Chromoplasts: These have carotenoid pigments that impart color to flowers and fruits. The main reason for expressing different colors is for attracting pollinators.
- Gerontoplasts: These are aged chloroplasts. Gerontoplasts are formed during leaf senescence when the leaf is no longer using photosynthesis usually in an autumn month.
-Leucoplasts: These are the non-pigmented colorless organelles. Leucoplasts are usually found in most of the non-photosynthetic parts of the plant like roots and stores starches (Amyloplasts), lipids (Elaioplast), and proteins (Proteinoplasts), depending on the need of the plants.
So, the correct answer is, ‘One of the plastids can differentiate into another type of plastid depending upon the cell requirements.’
Note: -All proplastids are undifferentiated plastids and are derived from the meristematic regions of the plant. Proplastids can divide by binary fission, but more mature chloroplasts can also divide in this manner.
-Plastids are found in the cells of plants and algae and can manufacture and store food in plants. Pigments are present in these organelles that are used in photosynthesis and can change the color of the cell.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




