
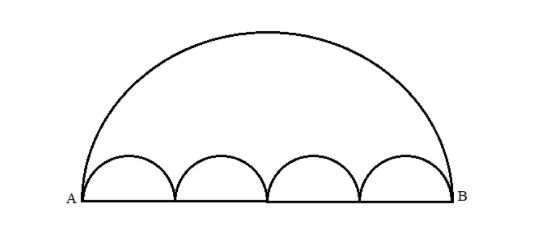
All the arcs in the following diagram are semi-circles. This diagram shows two paths connecting A to B. Path \[1\] is the single large semi-circle and path \[2\] consists of the chain of small semi-circles. Then
A. Path \[1\] is longer than path \[2\]
B. Path \[1\] is of the same length as path \[2\]
C. Path \[1\] is shorter than path \[2\]
D. Path \[1\] is of the same length as path \[2\] , only if the number of semi-circles is not more than \[4\] .

Answer
517.8k+ views
Hint: Some of the thing we need to know before solving this question:
Half of the circle is known as a semi-circle. Therefore, the area of the semi-circle will be half of the area of the circle.
Area of a circle is \[\pi {r^2}\] then, area of a semicircle is \[\dfrac{{\pi {r^2}}}{2}\] where \[r\] is the radius of circle or radius of semi-circle. Perimeter of a semicircle is given by, \[\pi r + 2r\] where \[r\] is the radius of the semi-circle.
Complete step by step answer:
The given diagram consists of one large semi-circle and four small semi-circles. Thus, we have two paths to reach B from A.
It is given that the path \[1\] from A to B is the large semi-circle that is the arc length of that semi-circle. That is the perimeter of a semi-circle minus its diameter, since this path doesn’t include the diameter. And it is given by \[\pi r + 2r - d\] where \[r\] is the radius of the semi-circle and \[d\] is the diameter of the semi-circle.
We know that diameter is nothing but twice the radius that is, \[d = 2r\] . Thus, we get, \[\pi r + 2r + 2r\] .
On simplifying this we get, \[\pi r\] . Thus, Path \[1 = \] \[\pi r\] .
Let’s calculate the path \[2\] . It is given that path \[2\] is the way along the small four semi-circles. That is nothing but the perimeter of those four semicircles minus their diameters, since the path doesn’t cover its diameters. Since all four semi-circles are equal, we get, \[4 \times (\pi r)\] . Thus, Path \[2 = \] \[4\pi r\] .
On comparing both parts we get, Path \[1 < \] Path \[2\] . Since, \[\pi r < 4\pi \] is obvious.
Therefore, Path \[1\] is smaller than Path \[2\] .
Let us see the options, option (a) Path \[1\] is longer than path \[2\] this cannot be a correct answer since Path \[1\] is smaller than Path \[2\] .
Option (b) Path \[1\] is of the same length as path \[2\] , also this cannot be the correct answer since Path \[1\] is smaller than Path \[2\] .
Option (c) Path \[1\] is shorter than path \[2\] , this is the correct answer since Path \[1\] is smaller than Path \[2\] .
Option (d) Path \[1\] is of the same length as path \[2\] , only if the number of semi-circles is not more than \[4\] , this cannot be the correct answer since Path \[1\] is smaller than Path \[2\] .
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Since the path is from A to B, we cannot walk through the diameter of the semicircle clearly, they said that we need to walk through the arc. Thus, the path is the perimeter of the semi-circle except the diameter thus we neglected the diameter from the formula. Same idea is applied for those four semicircles.
Half of the circle is known as a semi-circle. Therefore, the area of the semi-circle will be half of the area of the circle.
Area of a circle is \[\pi {r^2}\] then, area of a semicircle is \[\dfrac{{\pi {r^2}}}{2}\] where \[r\] is the radius of circle or radius of semi-circle. Perimeter of a semicircle is given by, \[\pi r + 2r\] where \[r\] is the radius of the semi-circle.
Complete step by step answer:
The given diagram consists of one large semi-circle and four small semi-circles. Thus, we have two paths to reach B from A.
It is given that the path \[1\] from A to B is the large semi-circle that is the arc length of that semi-circle. That is the perimeter of a semi-circle minus its diameter, since this path doesn’t include the diameter. And it is given by \[\pi r + 2r - d\] where \[r\] is the radius of the semi-circle and \[d\] is the diameter of the semi-circle.
We know that diameter is nothing but twice the radius that is, \[d = 2r\] . Thus, we get, \[\pi r + 2r + 2r\] .
On simplifying this we get, \[\pi r\] . Thus, Path \[1 = \] \[\pi r\] .
Let’s calculate the path \[2\] . It is given that path \[2\] is the way along the small four semi-circles. That is nothing but the perimeter of those four semicircles minus their diameters, since the path doesn’t cover its diameters. Since all four semi-circles are equal, we get, \[4 \times (\pi r)\] . Thus, Path \[2 = \] \[4\pi r\] .
On comparing both parts we get, Path \[1 < \] Path \[2\] . Since, \[\pi r < 4\pi \] is obvious.
Therefore, Path \[1\] is smaller than Path \[2\] .
Let us see the options, option (a) Path \[1\] is longer than path \[2\] this cannot be a correct answer since Path \[1\] is smaller than Path \[2\] .
Option (b) Path \[1\] is of the same length as path \[2\] , also this cannot be the correct answer since Path \[1\] is smaller than Path \[2\] .
Option (c) Path \[1\] is shorter than path \[2\] , this is the correct answer since Path \[1\] is smaller than Path \[2\] .
Option (d) Path \[1\] is of the same length as path \[2\] , only if the number of semi-circles is not more than \[4\] , this cannot be the correct answer since Path \[1\] is smaller than Path \[2\] .
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Since the path is from A to B, we cannot walk through the diameter of the semicircle clearly, they said that we need to walk through the arc. Thus, the path is the perimeter of the semi-circle except the diameter thus we neglected the diameter from the formula. Same idea is applied for those four semicircles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




