
Allosteric enzymes have allosteric sites for
A. Both activation and inhibition
B. Inhibition only
C. Activation only
D. Reduction in activation energy
Answer
591k+ views
Hint: Allosteric enzymes are unique compared to other enzymes as they have an additional site, as well as the active site. These allosteric sites are unique in the way that they have the ability to respond to multiple different conditions in their immediate environment.
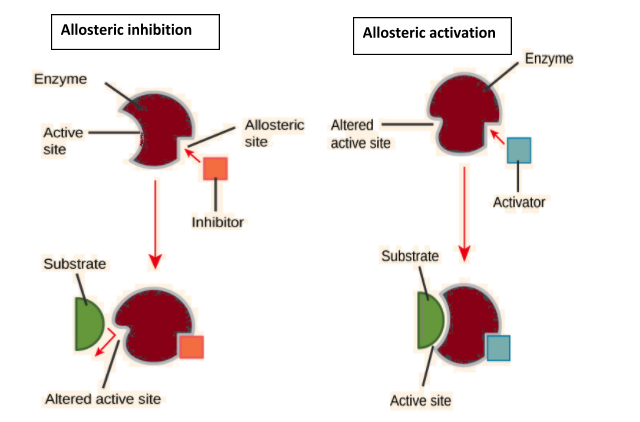
Complete answer: Enzymes sometimes act as their own regulators. Such enzymes are known as allosteric enzymes. Allosteric enzymes have separate areas for different types of modulators that alter the conformation of the active site to make it effective or ineffective. These areas are called allosteric sites. The substances which cause a change in allosteric sites are called modulators, allosteric substances or effectors. The latter may be of two types, activators and inhibitors. Allosteric activators bind with allosteric sites in such a way that they make active sites operational. On the other hand, allosteric inhibitors bring about such a change in the active sites that they become unable to combine with substrate molecules.
So, the correct answer is option A.
Additional information:
Allosteric enzymes are more complex than non-allosteric enzymes. In most of the allosteric enzymes, the substrate binding site and the effector binding site are on different subunits.
The substrate binding site is on the catalytic subunit which is referred to as the C subunit. The effector binding site is on the regulatory subunit and is referred to as the R subunit.
When an effector molecule exists at one binding site and causes a conformational change in that subunit, then a conformational change is also caused in the other subunits in the protein. This means that a huge part of the binding energy of the effector is used to change the conformation of the whole protein complex.
Allosteric enzymes can also ‘switch’ between their inactive form and active form. This can play a huge role in biological functions. Once the effector dissociates from the binding site of the enzyme, the enzyme can then revert back to its inactive or less active form. It is known as cooperative binding.
Note: Some enzymes that are allosterically regulated contain a set of specific properties which make them apart. These enzymes, which include some of the key metabolic regulators, are often given the name of allosteric enzymes.
Complete answer: Enzymes sometimes act as their own regulators. Such enzymes are known as allosteric enzymes. Allosteric enzymes have separate areas for different types of modulators that alter the conformation of the active site to make it effective or ineffective. These areas are called allosteric sites. The substances which cause a change in allosteric sites are called modulators, allosteric substances or effectors. The latter may be of two types, activators and inhibitors. Allosteric activators bind with allosteric sites in such a way that they make active sites operational. On the other hand, allosteric inhibitors bring about such a change in the active sites that they become unable to combine with substrate molecules.

So, the correct answer is option A.
Additional information:
Allosteric enzymes are more complex than non-allosteric enzymes. In most of the allosteric enzymes, the substrate binding site and the effector binding site are on different subunits.
The substrate binding site is on the catalytic subunit which is referred to as the C subunit. The effector binding site is on the regulatory subunit and is referred to as the R subunit.
When an effector molecule exists at one binding site and causes a conformational change in that subunit, then a conformational change is also caused in the other subunits in the protein. This means that a huge part of the binding energy of the effector is used to change the conformation of the whole protein complex.
Allosteric enzymes can also ‘switch’ between their inactive form and active form. This can play a huge role in biological functions. Once the effector dissociates from the binding site of the enzyme, the enzyme can then revert back to its inactive or less active form. It is known as cooperative binding.
Note: Some enzymes that are allosterically regulated contain a set of specific properties which make them apart. These enzymes, which include some of the key metabolic regulators, are often given the name of allosteric enzymes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




