
Alpha helices and beta sheets are examples of----- protein organization.
A.Primary structure
B.Secondary structure
C.Tertiary structure
D.Quaternary structure
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: Proteins are the large biomolecules, which consists of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform different functions like metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, transporting molecules. etc based on their shapes. The proteins get the final shape based on the four levels of protein structure.
Complete answer:
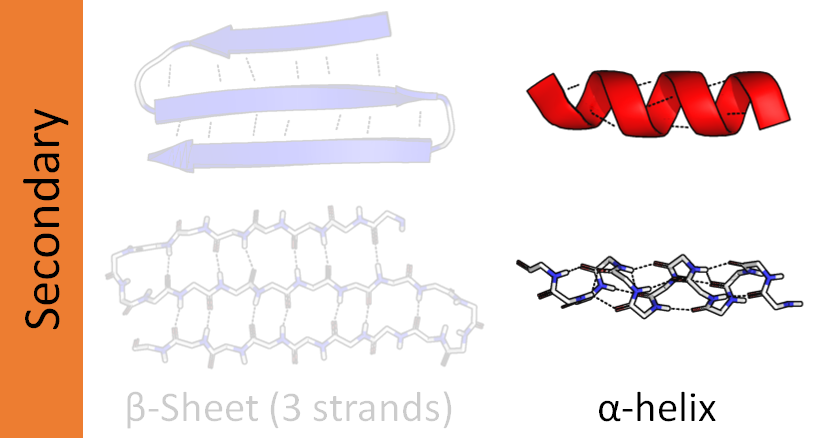
Here, the distinct structures of protein organisation have been classified into- primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure. The secondary structure, which forms within a polypeptide due to interaction between atoms of the backbone and that usually refers to local folded structures.
The most common type of secondary structure here is Alpha helix and beta-pleated sheet. They are held in a shape by hydrogen bonds. They form between the carbonyl O of one amino acid and the amino H of another. In Alpha helix, the carbonyl of one amino acid is hydrogen bonded to the amino H of an amino acid.
The pattern of bonding of the Alpha helix resembles a curled ribbon like structure. In the Beta pleated sheet, when two or more segments of polypeptides chain line up next to each other, they form a sheet-like structure by holding the hydrogen bonds together. The strands present here may be parallel(pointing the same direction) or anti-parallel (pointing opposite direction).
Hence the correct answer is OPTION(B)
Note: Many proteins contain both Alpha helices and Beta sheets, even though some contain just one type of secondary structure. If the temperature of a protein environment is changed or when it is exposed to chemicals, they denatured. They will lose their three-dimensional structure and they are non-functional.
Complete answer:
Here, the distinct structures of protein organisation have been classified into- primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure. The secondary structure, which forms within a polypeptide due to interaction between atoms of the backbone and that usually refers to local folded structures.
The most common type of secondary structure here is Alpha helix and beta-pleated sheet. They are held in a shape by hydrogen bonds. They form between the carbonyl O of one amino acid and the amino H of another. In Alpha helix, the carbonyl of one amino acid is hydrogen bonded to the amino H of an amino acid.
The pattern of bonding of the Alpha helix resembles a curled ribbon like structure. In the Beta pleated sheet, when two or more segments of polypeptides chain line up next to each other, they form a sheet-like structure by holding the hydrogen bonds together. The strands present here may be parallel(pointing the same direction) or anti-parallel (pointing opposite direction).

Hence the correct answer is OPTION(B)
Note: Many proteins contain both Alpha helices and Beta sheets, even though some contain just one type of secondary structure. If the temperature of a protein environment is changed or when it is exposed to chemicals, they denatured. They will lose their three-dimensional structure and they are non-functional.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




