
Aluminium oxide is soluble in water. State true or false.
(A) True
(B) False
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: $A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$ (Aluminium oxide) or alumina exists as a hexagonal crystal lattice. It is a ceramic compound. So it’s structure is not as simple as sodium oxide or magnesium oxide. It has a giant ionic lattice structure with a high degree of covalent bonding.
Complete answer:
- Aluminium oxide exists in various forms. It is an amphoteric oxide that is, it can react with both acids and bases to give salts. It is also known as corundum (crystalline form).
- Aluminium oxide does not react with water at room temperature because of its hexagonal close packing (hcp) structure. The oxide ions are too strongly held together in the crystal lattice to react with water. It simply settles down when dissolved in water.
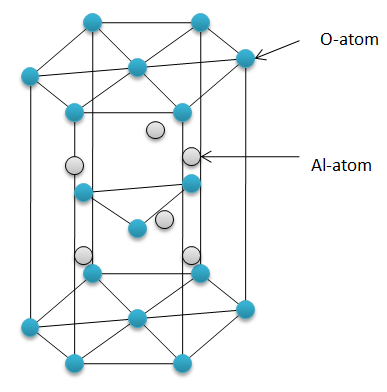
- Aluminium is a metal and oxygen is a non-metal. Metal and non-metal forms an ionic compound. So, aluminium oxide is an ionic compound. Still, it is insoluble in water.
- The reason is \[Al\] has smaller ionic size as compared to the other elements of that group due to its half-filled stable valence shell configuration. Now hydration energy is inversely proportional to the square of the cationic size and lattice energy is directly proportional to the charges of the ions and inversely proportional to the radius of the ion. From the above relations, we can derive that lattice energy is more than hydration energy in this case. So, $A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$ remains insoluble in water.
So, the correct option is B.
Note:
Hexagonal close packing (HCP) structure – the repetitive layer of structure when a hexagon on the top and the bottom sandwiches a triangle in between.
Hydration energy – the amount of energy involved when something dissolves in water.
Lattice energy - the amount of energy required to bind a crystal lattice.
When hydration energy is more than lattice energy, a compound becomes soluble in water.
Complete answer:
- Aluminium oxide exists in various forms. It is an amphoteric oxide that is, it can react with both acids and bases to give salts. It is also known as corundum (crystalline form).
- Aluminium oxide does not react with water at room temperature because of its hexagonal close packing (hcp) structure. The oxide ions are too strongly held together in the crystal lattice to react with water. It simply settles down when dissolved in water.

- Aluminium is a metal and oxygen is a non-metal. Metal and non-metal forms an ionic compound. So, aluminium oxide is an ionic compound. Still, it is insoluble in water.
- The reason is \[Al\] has smaller ionic size as compared to the other elements of that group due to its half-filled stable valence shell configuration. Now hydration energy is inversely proportional to the square of the cationic size and lattice energy is directly proportional to the charges of the ions and inversely proportional to the radius of the ion. From the above relations, we can derive that lattice energy is more than hydration energy in this case. So, $A{{l}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$ remains insoluble in water.
So, the correct option is B.
Note:
Hexagonal close packing (HCP) structure – the repetitive layer of structure when a hexagon on the top and the bottom sandwiches a triangle in between.
Hydration energy – the amount of energy involved when something dissolves in water.
Lattice energy - the amount of energy required to bind a crystal lattice.
When hydration energy is more than lattice energy, a compound becomes soluble in water.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




