
Among the following compounds, which compound is polar as well as exhibit \[s{p^2}\] hybridization by the central atom?
A ) \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]
B ) \[{\text{Si}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}\]
C ) \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\]
D ) \[{\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]
Answer
565.2k+ views
Hint: First determine the hybridization of the central atom in each compound. For this, determine the number of bonding domains and the number of lone pairs of electrons around central atom. Then determine if the individual bond dipoles cancels each other or not based on the molecular geometry.
Complete step by step answer:
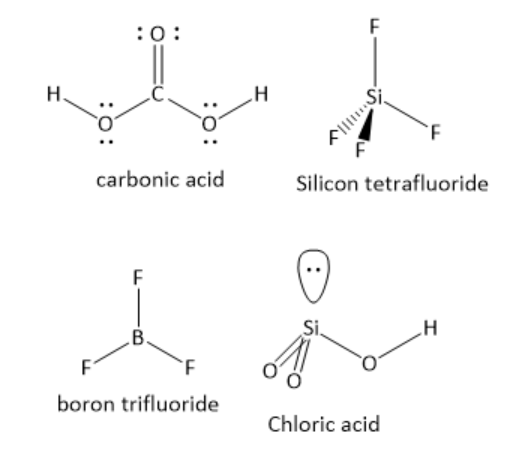
In \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]the central carbon atom has one carbon -oxygen double bond and two carbon-oxygen single bonds. The number of lone pair of electrons is zero. The central carbon atom has three bonding domains and zero lone pairs of electrons. Hence, the carbon atom is \[s{p^2}\] hybridized. The geometry around the carbon atom is trigonal planar. The individual bond dipoles do not cancel each other. Hence, it is a polar molecule.
In \[{\text{Si}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}\]the central silicon atom has four silicon-fluorine single bonds. The number of lone pair of electrons is zero. The central silicon atom has four bonding domains and zero lone pairs of electrons. Hence, the silicon atom is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized. The geometry around silicon atom is tetrahedral. The individual bond dipoles cancel each other. Hence, it is a non-polar molecule.
In \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\]the central boron atom has three boron-fluorine single bonds. The number of lone pair of electrons is zero. The central boron atom has three bonding domains and zero lone pairs of electrons. Hence, the boron atom is \[s{p^2}\] hybridized. The geometry around the boron atom is trigonal planar. The individual bond dipoles cancel each other. Hence, it is a non-polar molecule.
In \[{\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]the central chlorine atom has two chlorine-oxygen double bonds and one chlorine-oxygen single bond. The number of lone pairs of electrons is one. The central chlorine atom has three bonding domains and one lone pair of electrons. Hence, the chlorine atom is \[s{p^3}\] hybridised. The geometry around the chlorine atom is tetrahedral. The individual bond dipoles do not cancel each other. Hence, it is a polar molecule.
Hence, the option A ) \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] carbonic acid is the correct answer.
Additional information: Steric number five is associated with \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization and trigonal bipyramidal shape, when five bond pairs of electrons and zero lone pair of electrons are present. When four bond pairs of electrons and zero lone pair of electrons are present, the shape is see-saw.
Steric number seven is associated with \[s{p^3}{d^3}\] hybridization and pentagonal bipyramidal shape
Note:
When n number of atomic orbitals undergo hybridization, n number of degenerate hybrid orbitals are obtained. Some of these hybrid orbitals are occupied by the bond pairs of electrons and the remaining hybrid orbitals are occupied by the lone pair of electrons. By counting the number of bond pairs of electrons and the number of lone pairs of electrons, the number of hybrid orbitals and the type of hybridization can be determined.
Complete step by step answer:

In \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]the central carbon atom has one carbon -oxygen double bond and two carbon-oxygen single bonds. The number of lone pair of electrons is zero. The central carbon atom has three bonding domains and zero lone pairs of electrons. Hence, the carbon atom is \[s{p^2}\] hybridized. The geometry around the carbon atom is trigonal planar. The individual bond dipoles do not cancel each other. Hence, it is a polar molecule.
In \[{\text{Si}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{4}}}\]the central silicon atom has four silicon-fluorine single bonds. The number of lone pair of electrons is zero. The central silicon atom has four bonding domains and zero lone pairs of electrons. Hence, the silicon atom is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized. The geometry around silicon atom is tetrahedral. The individual bond dipoles cancel each other. Hence, it is a non-polar molecule.
In \[{\text{B}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{3}}}\]the central boron atom has three boron-fluorine single bonds. The number of lone pair of electrons is zero. The central boron atom has three bonding domains and zero lone pairs of electrons. Hence, the boron atom is \[s{p^2}\] hybridized. The geometry around the boron atom is trigonal planar. The individual bond dipoles cancel each other. Hence, it is a non-polar molecule.
In \[{\text{HCl}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\]the central chlorine atom has two chlorine-oxygen double bonds and one chlorine-oxygen single bond. The number of lone pairs of electrons is one. The central chlorine atom has three bonding domains and one lone pair of electrons. Hence, the chlorine atom is \[s{p^3}\] hybridised. The geometry around the chlorine atom is tetrahedral. The individual bond dipoles do not cancel each other. Hence, it is a polar molecule.
Hence, the option A ) \[{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\] carbonic acid is the correct answer.
Additional information: Steric number five is associated with \[s{p^3}d\] hybridization and trigonal bipyramidal shape, when five bond pairs of electrons and zero lone pair of electrons are present. When four bond pairs of electrons and zero lone pair of electrons are present, the shape is see-saw.
Steric number seven is associated with \[s{p^3}{d^3}\] hybridization and pentagonal bipyramidal shape
Note:
When n number of atomic orbitals undergo hybridization, n number of degenerate hybrid orbitals are obtained. Some of these hybrid orbitals are occupied by the bond pairs of electrons and the remaining hybrid orbitals are occupied by the lone pair of electrons. By counting the number of bond pairs of electrons and the number of lone pairs of electrons, the number of hybrid orbitals and the type of hybridization can be determined.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




