
Among the following metal carbonyls the $C - O$ bond order is lowest in
A. $[Mn{\left( {CO{)_6}} \right]^ + }$
B. $\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)}_5}} \right]$
C. $\left[ {Cr{{\left( {CO} \right)}_6}} \right]$
D. ${\left[ {V\left( {CO} \right)6} \right]^ - }$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: We know that higher the strength of metal carbonyl, weaker the $C - O$ bond will be. We also know that $CO$ is a strong field ligand and this gives a lot of stability to the complexes.
Complete step by step answer:
(a) For $[Mn{\left( {CO{)_6}} \right]^ + }$ we know that the charge for Carbon monoxide $(CO)$ is zero.
Therefore, the charge for $Mn$ will be +1.
The electron configuration of $M{n^ + }$ will be $3{d^5}4{s^1}$
But in the presence of $CO$ the effective configuration will be $3{d^6}4{s^0}$. This gives us three lone pairs for back bonding with a vacant orbital of $C$ In $CO$.
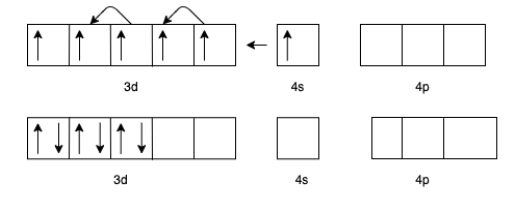
(b) For $\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)}_5}} \right]$ the charge of $Fe$ is zero.
The electron configuration of $Fe$ will be $3{d^6}4{s^2}$
But in presence of $CO$ the effective configuration will be $3{d^8}$. This gives us 4 lone pairs for backing bonding with a vacant orbital of $C$ In $CO$.
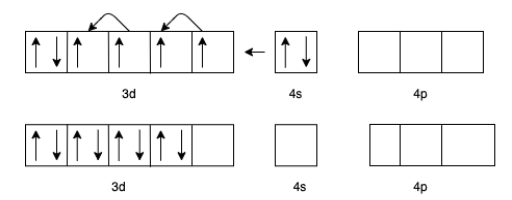
(c) For $\left[ {Cr{{\left( {CO} \right)}_6}} \right]$ the charge of $Cr$ is zero.
The electron configuration of $Cr$ will be $3{d^5}4{s^1}$
But in presence of $CO$ the effective configuration will be $3{d^6}$. This gives us 3 lone pair for backing bonding with a vacant orbital of $C$ In $CO$.
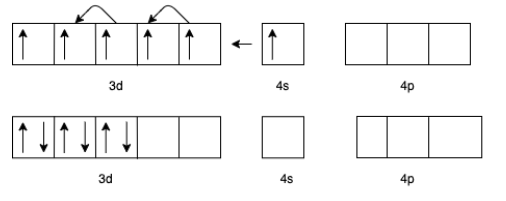
(d) For ${\left[ {V\left( {CO} \right)6} \right]^ - }$ we know that the charge for Carbon monoxide $(CO)$ is zero.
Therefore, the charge for $V$ will be -1.
The electron configuration of ${V^ - }$ will be $3{d^4}4{s^2}$
But in presence of $CO$ the effective configuration will be $3{d^6}$. This gives us 3 lone pair for backing bonding with a vacant orbital of $C$ In $CO$.
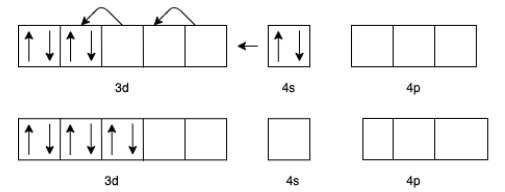
From this we can observe that the $\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)}_5}} \right]$ is having the maximum back bonding, hence the bond order will also be lowest for $\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)}_5}} \right]$.
Note:
For solving this problem, we can use a shortcut also.
As we said that higher the strength of metal carbonyl, weaker the $C - O$ bond will be. From the options we can see that all of them has a coordination number of 6 except $\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)}_5}} \right]$. In $\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)}_5}} \right]$ we can see that the bond between $Fe$ and carbonyl group is distributed among 5 carbonyl group whereas the rest of them Is distributed among 6 carbonyl group. So the per bond strength of the $Fe$ will be greatest, which implies that $C - O$ bond will be weaker
Complete step by step answer:
(a) For $[Mn{\left( {CO{)_6}} \right]^ + }$ we know that the charge for Carbon monoxide $(CO)$ is zero.
Therefore, the charge for $Mn$ will be +1.
The electron configuration of $M{n^ + }$ will be $3{d^5}4{s^1}$
But in the presence of $CO$ the effective configuration will be $3{d^6}4{s^0}$. This gives us three lone pairs for back bonding with a vacant orbital of $C$ In $CO$.

(b) For $\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)}_5}} \right]$ the charge of $Fe$ is zero.
The electron configuration of $Fe$ will be $3{d^6}4{s^2}$
But in presence of $CO$ the effective configuration will be $3{d^8}$. This gives us 4 lone pairs for backing bonding with a vacant orbital of $C$ In $CO$.

(c) For $\left[ {Cr{{\left( {CO} \right)}_6}} \right]$ the charge of $Cr$ is zero.
The electron configuration of $Cr$ will be $3{d^5}4{s^1}$
But in presence of $CO$ the effective configuration will be $3{d^6}$. This gives us 3 lone pair for backing bonding with a vacant orbital of $C$ In $CO$.

(d) For ${\left[ {V\left( {CO} \right)6} \right]^ - }$ we know that the charge for Carbon monoxide $(CO)$ is zero.
Therefore, the charge for $V$ will be -1.
The electron configuration of ${V^ - }$ will be $3{d^4}4{s^2}$
But in presence of $CO$ the effective configuration will be $3{d^6}$. This gives us 3 lone pair for backing bonding with a vacant orbital of $C$ In $CO$.

From this we can observe that the $\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)}_5}} \right]$ is having the maximum back bonding, hence the bond order will also be lowest for $\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)}_5}} \right]$.
Note:
For solving this problem, we can use a shortcut also.
As we said that higher the strength of metal carbonyl, weaker the $C - O$ bond will be. From the options we can see that all of them has a coordination number of 6 except $\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)}_5}} \right]$. In $\left[ {{\text{Fe}}{{\left( {{\text{CO}}} \right)}_5}} \right]$ we can see that the bond between $Fe$ and carbonyl group is distributed among 5 carbonyl group whereas the rest of them Is distributed among 6 carbonyl group. So the per bond strength of the $Fe$ will be greatest, which implies that $C - O$ bond will be weaker
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




