
Among the following, the dissociation constant is highest for:
A: $ {C_6}{H_5}OH $
B: $ C{H_3}OH $
C: $ C{H_3}C \equiv CH $
D: $ C{H_3}N{H_3}^ + C{l^ - } $
Answer
539.1k+ views
Hint :Atoms can either gain or lose electrons to form ions in a phenomenon known as ionization and compounds that are formed in this manner are known as ionic compounds). When these ionic compounds are dissolved in water, they yield ions in a process known as dissociation.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
If the compound has an ability to lose a proton easily in water (i.e. hydrogen can be easily removed), then that compound will possess a low dissociation constant. Now, let us look at the different compounds given in the options one by one:
Option A: $ {C_6}{H_5}OH $
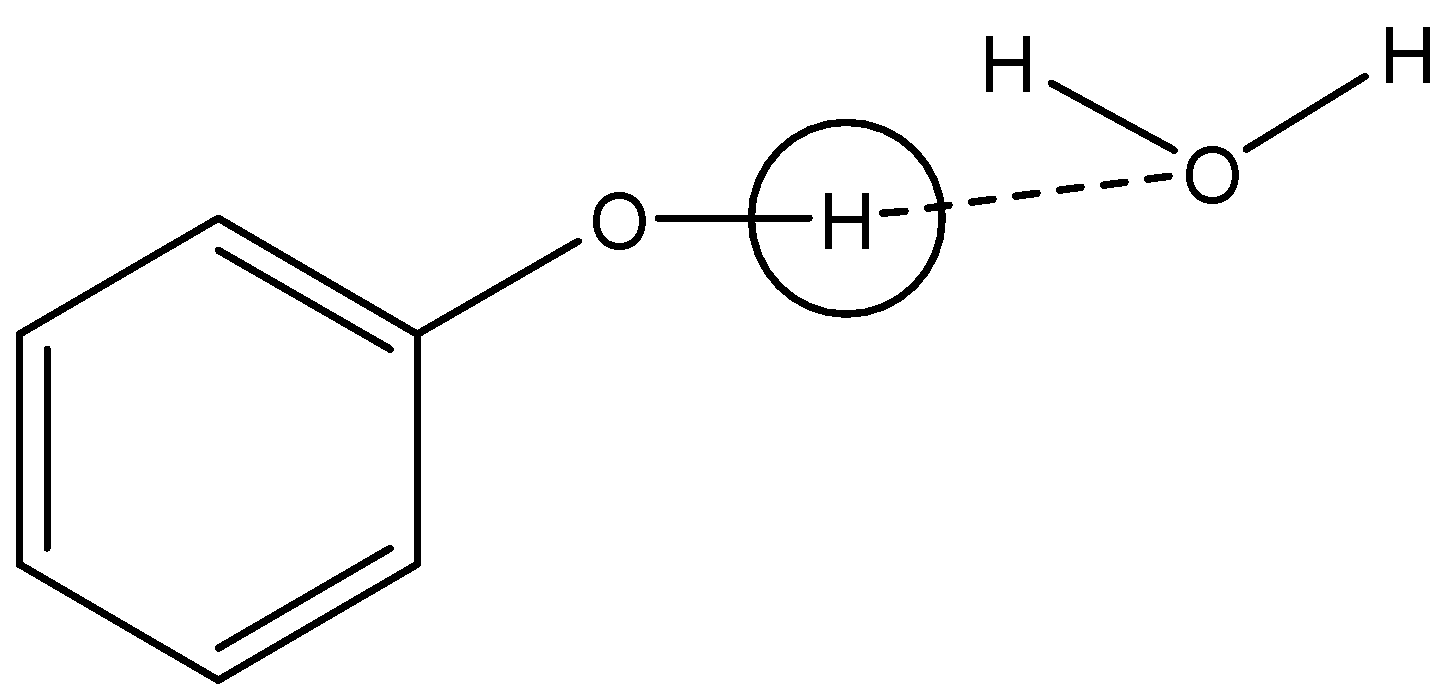
As clear from the figure, H atom of hydroxyl group will create hydrogen bonds with water molecules and thus in $ {C_6}{H_5}OH $ hydrogen can be easily removed. Hence, dissociation constant will be low in this case.
Option B: $ C{H_3}OH $
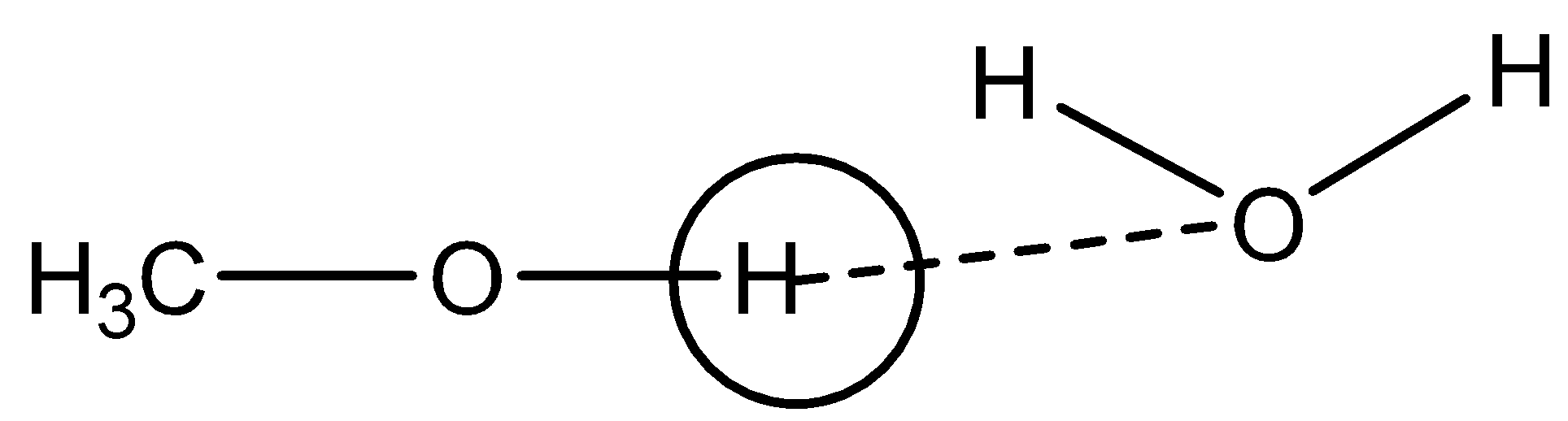
As clear from the figure, H atom of hydroxyl group will create hydrogen bonds with water molecules and thus in $ C{H_3}OH $ hydrogen can be easily removed. Hence, dissociation constant will be low in this case.
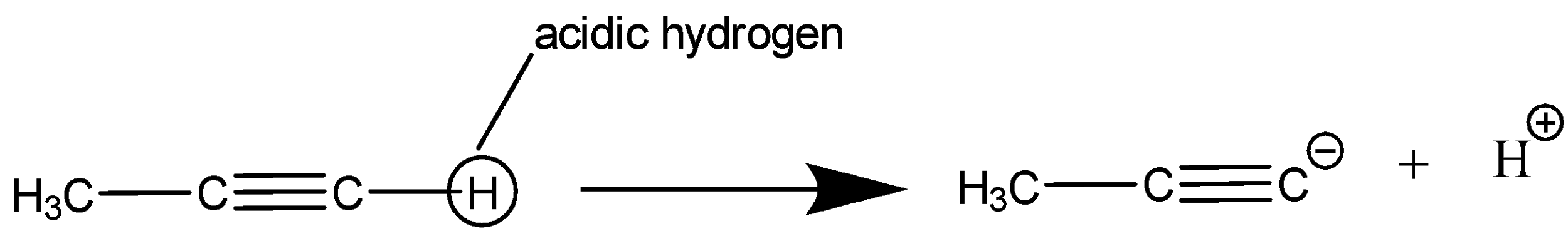
Option C: $ C{H_3}C \equiv CH $
As we know, alkyne possesses acidic hydrogen which can easily be removed as shown in figure. Hence, dissociation constant will be low in this case.
Option D: $ C{H_3}N{H_3}^ + C{l^ - } $
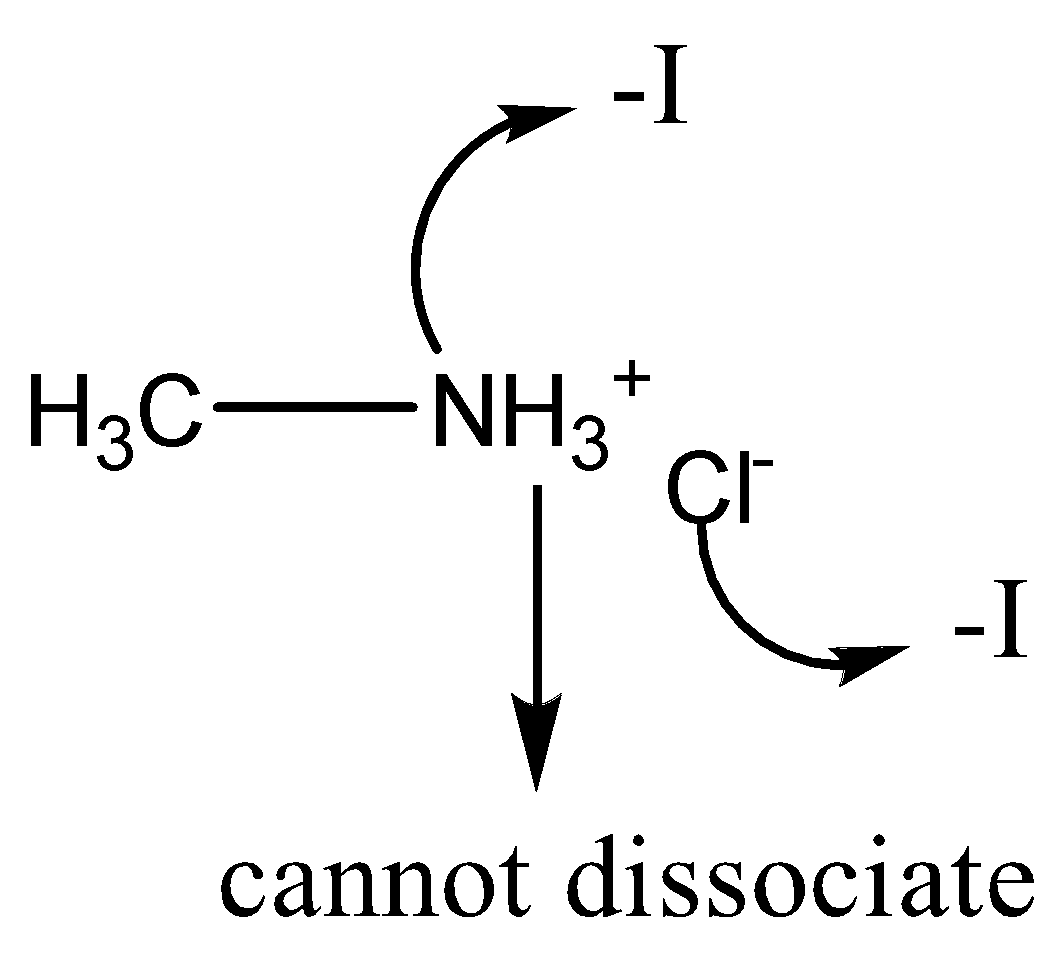
As clear from the above figure, nitrogen and chlorine induces the inductive effect ( $ - I $ ) and attracts hydrogen towards themselves due to which hydrogen cannot be removed easily. Hence, in this case the dissociation constant will be very high.
As a result, the correct answer is Option D.
Note :
For a generalised chemical reaction taking place in a solution:
$ aA + bB \rightleftharpoons cC + dD\; $
The equilibrium constant can be expressed as follows:
$ K = \dfrac{{{{[C]}^c}{{[D]}^d}}}{{{{[A]}^a}{{[B]}^b}}} $
where [A], [B], [C] and [D] refer to the molar concentration of species A, B, C, D respectively at equilibrium. The coefficients like a, b, c, and d in the generalised chemical equation become exponents as seen in the above expression. $ {K_a} $ is acid dissociation constant and $ {K_b} $ is base dissociation constant.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
If the compound has an ability to lose a proton easily in water (i.e. hydrogen can be easily removed), then that compound will possess a low dissociation constant. Now, let us look at the different compounds given in the options one by one:
Option A: $ {C_6}{H_5}OH $

As clear from the figure, H atom of hydroxyl group will create hydrogen bonds with water molecules and thus in $ {C_6}{H_5}OH $ hydrogen can be easily removed. Hence, dissociation constant will be low in this case.
Option B: $ C{H_3}OH $

As clear from the figure, H atom of hydroxyl group will create hydrogen bonds with water molecules and thus in $ C{H_3}OH $ hydrogen can be easily removed. Hence, dissociation constant will be low in this case.
Option C: $ C{H_3}C \equiv CH $
As we know, alkyne possesses acidic hydrogen which can easily be removed as shown in figure. Hence, dissociation constant will be low in this case.

Option D: $ C{H_3}N{H_3}^ + C{l^ - } $

As clear from the above figure, nitrogen and chlorine induces the inductive effect ( $ - I $ ) and attracts hydrogen towards themselves due to which hydrogen cannot be removed easily. Hence, in this case the dissociation constant will be very high.
As a result, the correct answer is Option D.
Note :
For a generalised chemical reaction taking place in a solution:
$ aA + bB \rightleftharpoons cC + dD\; $
The equilibrium constant can be expressed as follows:
$ K = \dfrac{{{{[C]}^c}{{[D]}^d}}}{{{{[A]}^a}{{[B]}^b}}} $
where [A], [B], [C] and [D] refer to the molar concentration of species A, B, C, D respectively at equilibrium. The coefficients like a, b, c, and d in the generalised chemical equation become exponents as seen in the above expression. $ {K_a} $ is acid dissociation constant and $ {K_b} $ is base dissociation constant.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




