
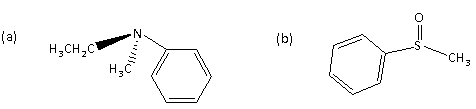
Among the following the optically inactive compound is

Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint: To show the optical activity compounds should be chiral. The chirality indicates the presence of the chiral center in the molecule. The chiral center is the atom which is attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms. Such an atom that is attached to four different groups is the asymmetric atom.
Complete solution:
The substance or compound which rotates the plane of plane polarised light is known as an optically active compound and one which fails to rotate the plane of plane polarised light is optically inactive. The compounds containing atoms C, N, S, P attached to four different atoms are chiral and possess optical activity.
If the compound contains one lone pair of electrons then also it can show the optical activity but in the case of the nitrogen-containing compounds, inversion is taking place which leads to optical inactivity.
Now we can see that the name of the compound (a) is N-ethyl-N-methyl benzenamine having one lone pair of the electron along with ethyl, methyl, and phenyl groups attached to the N atom.
Because of the presence of the lone pair, it shows the inversion.
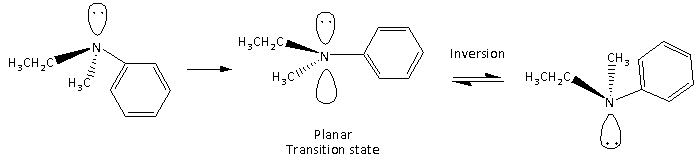
Here, we can see that the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$ hybridized N containing compound form transition state which is planar and again form ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$ geometry with the opposite configuration of the initial molecule. Therefore, one molecule rotates the plane of plane polarised light in one direction while the molecule with the opposite configuration rotates the plane of plane polarised light in the opposite direction. It results in optical inactivity of the compound containing nitrogen having lone pairs.
Hence, the correct answer to the question is an option (a).
In case of the compound (b) sulfur atom is present having a lone pair of electrons on it but does not show the inversion like the nitrogen atom.
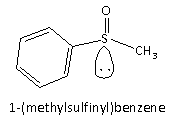
Here, we can see that as no inversion in the compound it exists in only one configuration, and hence, the compound is optically active.
Thus, option (A) is the correct answer to the question.
Note:Inversion of the molecule is shown by the compound which easily undergoes change from ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$geometry to planar ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ geometry and again forms ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$ hybridized molecule with a configuration change. When the same compound shows both the configuration one which rotates the plane of plane polarised light in one direction and another rotate the plane of plane polarised light to opposite direction are optically inactive.
Complete solution:
The substance or compound which rotates the plane of plane polarised light is known as an optically active compound and one which fails to rotate the plane of plane polarised light is optically inactive. The compounds containing atoms C, N, S, P attached to four different atoms are chiral and possess optical activity.
If the compound contains one lone pair of electrons then also it can show the optical activity but in the case of the nitrogen-containing compounds, inversion is taking place which leads to optical inactivity.
Now we can see that the name of the compound (a) is N-ethyl-N-methyl benzenamine having one lone pair of the electron along with ethyl, methyl, and phenyl groups attached to the N atom.
Because of the presence of the lone pair, it shows the inversion.

Here, we can see that the ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$ hybridized N containing compound form transition state which is planar and again form ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$ geometry with the opposite configuration of the initial molecule. Therefore, one molecule rotates the plane of plane polarised light in one direction while the molecule with the opposite configuration rotates the plane of plane polarised light in the opposite direction. It results in optical inactivity of the compound containing nitrogen having lone pairs.
Hence, the correct answer to the question is an option (a).
In case of the compound (b) sulfur atom is present having a lone pair of electrons on it but does not show the inversion like the nitrogen atom.

Here, we can see that as no inversion in the compound it exists in only one configuration, and hence, the compound is optically active.
Thus, option (A) is the correct answer to the question.
Note:Inversion of the molecule is shown by the compound which easily undergoes change from ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$geometry to planar ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{2}}}$ geometry and again forms ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}$ hybridized molecule with a configuration change. When the same compound shows both the configuration one which rotates the plane of plane polarised light in one direction and another rotate the plane of plane polarised light to opposite direction are optically inactive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




