
Among the isomeric alkanes of molecular formula ${C_5}{H_{12}}$.Identify the one that on photochemical chlorination yields:
A) A single monochloride
B) Three isomeric monochlorides
C) Four isomeric monochlorides
Answer
559.8k+ views
Hint:Photochemical chlorination is a chlorination method that takes place in presence of light. In this process usually $C - H$ bond is converted into $C - Cl$. The photochemical chlorination of alkanes takes place by free radical mechanism.
Complete answer:
Photochemical chlorination follows a free radical mechanism where the free radical is formed by homolytic bond fission or homolysis. Homolysis or homolytic bond fission is mainly a bond dissociation process of a molecule where each fragment is able to retain one of the originally bonded electrons. In case of the homolytic fission of a neutral molecule having even number of electrons, two free radicals will be generated.
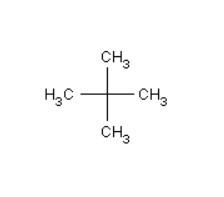
1) In order to have a single monochloride then there should be only a single $H - atom$ in the isomer of the alkane of molecular formula ${C_5}{H_{12}}$. The reason for this is because, the replacement of any $H - atom$ will result in the formation of the same product itself. Therefore, the isomer is neopentane.
2) In order to have three mono -chlorides, the isomer should have three different types of $H - atom$. Therefore, the isomer is normal-pentane (n-pentane).
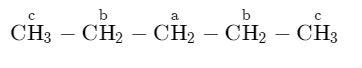
3) In order to have four mono -chlorides, the isomer should have four different types of $H - atom$. Therefore, the isomer is 2-methyl butane.
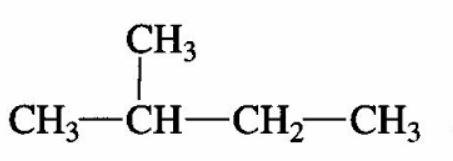
Additional Information:Photochlorination is an exothermic reaction and it proceeds in the form of a chain reaction initiated by homolytic cleavage of molecular chlorine into smaller units of chlorine radicals by means of ultraviolet radiation.
Note:Homolytic fission is the principle responsible for photochlorination and the energy associated with it is called bond dissociation energy. At high temperature in the absence of oxygen homolytic cleavage takes place in carbon compounds.
Complete answer:
Photochemical chlorination follows a free radical mechanism where the free radical is formed by homolytic bond fission or homolysis. Homolysis or homolytic bond fission is mainly a bond dissociation process of a molecule where each fragment is able to retain one of the originally bonded electrons. In case of the homolytic fission of a neutral molecule having even number of electrons, two free radicals will be generated.
1) In order to have a single monochloride then there should be only a single $H - atom$ in the isomer of the alkane of molecular formula ${C_5}{H_{12}}$. The reason for this is because, the replacement of any $H - atom$ will result in the formation of the same product itself. Therefore, the isomer is neopentane.

2) In order to have three mono -chlorides, the isomer should have three different types of $H - atom$. Therefore, the isomer is normal-pentane (n-pentane).
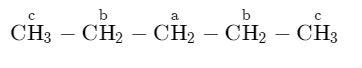
3) In order to have four mono -chlorides, the isomer should have four different types of $H - atom$. Therefore, the isomer is 2-methyl butane.
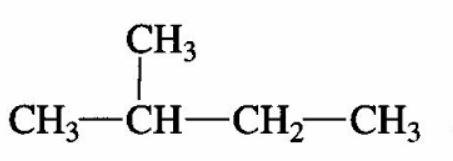
Additional Information:Photochlorination is an exothermic reaction and it proceeds in the form of a chain reaction initiated by homolytic cleavage of molecular chlorine into smaller units of chlorine radicals by means of ultraviolet radiation.
Note:Homolytic fission is the principle responsible for photochlorination and the energy associated with it is called bond dissociation energy. At high temperature in the absence of oxygen homolytic cleavage takes place in carbon compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




