
An AC voltage source of variable angular frequency $\omega $and fixed amplitude ${{V}_{0}}$ is connected in series with a capacitance C and an electric bulb of resistance R (inductance zero). When $\omega $ is increased
A. the bulb glows dimmer
B. the bulb glows brighter
C. total impedance of the circuit is unchanged
D. total impedance of the circuit increases.
Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: The voltage across the resistance is equal to ${{V}_{R}}=iR$ and the voltage across the capacitor is equal to ${{V}_{C}}=i{{X}_{C}}$. Use the formula ${{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$ and find what happens to the current when $\omega $ is increased. Power $P={{i}^{2}}R$. Power tells whether the bulb is glowing brighter or dimmer.
Formula Used:
${{V}_{R}}=iR$
${{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$
${{V}_{C}}=i{{X}_{C}}$
$P={{i}^{2}}R$
Complete step-by-step answer:
In an AC circuit the amplitudes of the voltages across the components and the current in the circuit are treated as vectors. The phase difference between the voltage and current is the angle between these vectors.
Let the amplitude of the current flowing in the circuit be i. Then the magnitude of the voltage vector of the resistance is ${{V}_{R}}=iR$ ……. (i).
Since the voltage across the resistance and the current are always in phase, the vectors of voltage of resistance (${{V}_{R}}$) and current (i) are parallel.
In an AC circuit, capacitance acts as resistance to the flow of circuit called the reactance of the circuit (${{X}_{c}}$). The value of the capacitive reactance is ${{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$ ….. (ii).
where, $\omega $ is the angular frequency of the source and C is the capacitance.
The magnitude of the voltage vector of the capacitance is ${{V}_{C}}=i{{X}_{C}}$ ……(iii).
There is a phase difference of $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ between the capacitor voltage and the current. That is the capacitor voltage lags behind the current by a phase of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Therefore, the vector of capacitor voltage (${{V}_{c}}$) is at an angle of $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ from the current vector.
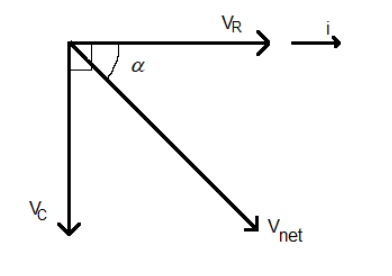
Therefore, the resultant or the net voltage in the circuit is equal to ${{V}_{net}}={{V}_{R}}+{{V}_{C}}$.
(Note that here, ${{V}_{R}}$ and ${{V}_{C}}$ are vectors and thus ${{V}_{net}}$ is also a vector.)
Therefore, magnitude of net voltage is ${{V}_{net}}=\sqrt{V_{R}^{2}+V_{C}^{2}}$
Substitute the value of ${{V}_{R}}$ and ${{V}_{C}}$ from equations (i) and (iii).
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{\left( iR \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( i{{X}_{C}} \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{net}}=i\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{{{\omega }^{2}}{{C}^{2}}}}$.
$\Rightarrow i=\dfrac{{{V}_{net}}}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{{{\omega }^{2}}{{C}^{2}}}}}$
Here ${{V}_{net}}={{V}_{0}}$.
$\Rightarrow i=\dfrac{{{V}_{0}}}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{{{\omega }^{2}}{{C}^{2}}}}}$
This means that if the value of $\omega $ is increased, then the value of the current (i) will increase.
Power dissipated through the resistance is given as $P={{i}^{2}}R$. Therefore, the power in the circuit will also increase.
If the power of the bubs increases, it will glow brighter.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:Here, $\left( \sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+X_{C}^{2}} \right)=Z$ and Z is called the impedance of the circuit. It is similar to resistance of a DC circuit. When the value of the angular frequency is increased, since ${{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$, the value of ${{X}_{C}}$ will decrease. Hence, the value of the impedance (Z) will also decrease.
Formula Used:
${{V}_{R}}=iR$
${{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$
${{V}_{C}}=i{{X}_{C}}$
$P={{i}^{2}}R$
Complete step-by-step answer:
In an AC circuit the amplitudes of the voltages across the components and the current in the circuit are treated as vectors. The phase difference between the voltage and current is the angle between these vectors.
Let the amplitude of the current flowing in the circuit be i. Then the magnitude of the voltage vector of the resistance is ${{V}_{R}}=iR$ ……. (i).
Since the voltage across the resistance and the current are always in phase, the vectors of voltage of resistance (${{V}_{R}}$) and current (i) are parallel.
In an AC circuit, capacitance acts as resistance to the flow of circuit called the reactance of the circuit (${{X}_{c}}$). The value of the capacitive reactance is ${{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$ ….. (ii).
where, $\omega $ is the angular frequency of the source and C is the capacitance.
The magnitude of the voltage vector of the capacitance is ${{V}_{C}}=i{{X}_{C}}$ ……(iii).
There is a phase difference of $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ between the capacitor voltage and the current. That is the capacitor voltage lags behind the current by a phase of $\dfrac{\pi }{2}$.
Therefore, the vector of capacitor voltage (${{V}_{c}}$) is at an angle of $-\dfrac{\pi }{2}$ from the current vector.

Therefore, the resultant or the net voltage in the circuit is equal to ${{V}_{net}}={{V}_{R}}+{{V}_{C}}$.
(Note that here, ${{V}_{R}}$ and ${{V}_{C}}$ are vectors and thus ${{V}_{net}}$ is also a vector.)
Therefore, magnitude of net voltage is ${{V}_{net}}=\sqrt{V_{R}^{2}+V_{C}^{2}}$
Substitute the value of ${{V}_{R}}$ and ${{V}_{C}}$ from equations (i) and (iii).
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{net}}=\sqrt{{{\left( iR \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( i{{X}_{C}} \right)}^{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow {{V}_{net}}=i\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{{{\omega }^{2}}{{C}^{2}}}}$.
$\Rightarrow i=\dfrac{{{V}_{net}}}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{{{\omega }^{2}}{{C}^{2}}}}}$
Here ${{V}_{net}}={{V}_{0}}$.
$\Rightarrow i=\dfrac{{{V}_{0}}}{\sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{{{\omega }^{2}}{{C}^{2}}}}}$
This means that if the value of $\omega $ is increased, then the value of the current (i) will increase.
Power dissipated through the resistance is given as $P={{i}^{2}}R$. Therefore, the power in the circuit will also increase.
If the power of the bubs increases, it will glow brighter.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:Here, $\left( \sqrt{{{R}^{2}}+X_{C}^{2}} \right)=Z$ and Z is called the impedance of the circuit. It is similar to resistance of a DC circuit. When the value of the angular frequency is increased, since ${{X}_{C}}=\dfrac{1}{\omega C}$, the value of ${{X}_{C}}$ will decrease. Hence, the value of the impedance (Z) will also decrease.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




