
An aggregate fruit is the one which develops from,
(A) Multicarpellary apocarpous gynoecium
(B) Complete inflorescence
(C) Multicarpellary superior ovary
(D) Multicarpellary syncarpous gynoecium
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: An aggregate fruit is the one which develops from the flower which has many carpels present in it, and the carpels are freely present which means that carpels are not fused. Ripened ovaries are borne together on a common receptacle.
Complete step by step answer:
An aggregate fruit is the one that develops from Multicarpellary apocarpous gynoecium which means that there are many fused carpels present in the flower of that fruit. Examples of aggregate fruit are strawberries and blackberries.
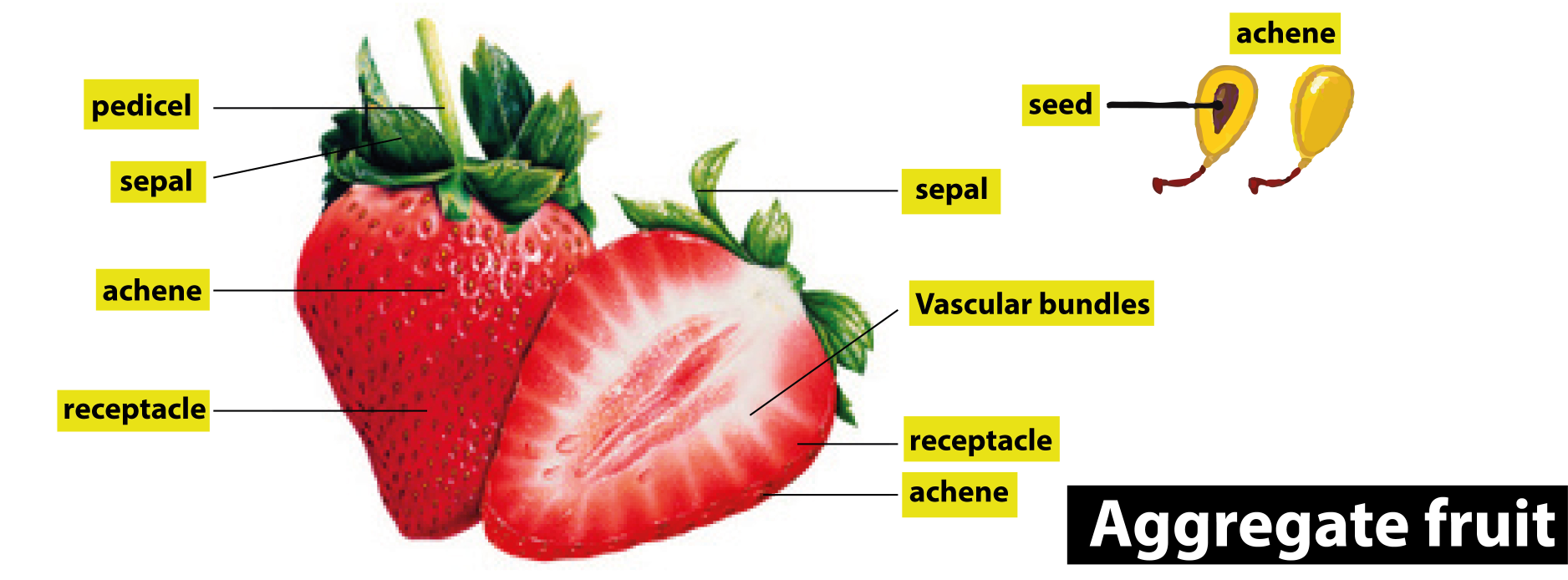
So, the correct answer is ‘Multicarpellary apocarpous gynoecium’.
Additional information: The fruit is the edible fleshy part of the plant that is consumed and obtained from the ripened ovary. The fruit is a fleshy or dried but ripened ovary of a flowering plant which encloses single or multiple seeds. The outer edible part in normal fruits is made from pericarp which was formed by the ovary and this fleshy part only surrounds the seed. The pericarp consists of three layers. The names of these layers from outer to inner are- the epicarp, mesocarp, and endocarp.
Not all fruits have seeds present in them. Seedless fruits are also present in nature. Parthenocarpy is the process of the natural or artificial production of fruit without fertilization of ovules. For example, seedless bananas and grapes are very common.
Note: The carpel is the female reproductive organ of a flower that consists of an ovary, stigma, and a style. If the gynoecium of the flower has a single carpel, it is known as a monocarpous. Carpel consists of the innermost whorl of the flower.
Complete step by step answer:
An aggregate fruit is the one that develops from Multicarpellary apocarpous gynoecium which means that there are many fused carpels present in the flower of that fruit. Examples of aggregate fruit are strawberries and blackberries.

So, the correct answer is ‘Multicarpellary apocarpous gynoecium’.
Additional information: The fruit is the edible fleshy part of the plant that is consumed and obtained from the ripened ovary. The fruit is a fleshy or dried but ripened ovary of a flowering plant which encloses single or multiple seeds. The outer edible part in normal fruits is made from pericarp which was formed by the ovary and this fleshy part only surrounds the seed. The pericarp consists of three layers. The names of these layers from outer to inner are- the epicarp, mesocarp, and endocarp.
Not all fruits have seeds present in them. Seedless fruits are also present in nature. Parthenocarpy is the process of the natural or artificial production of fruit without fertilization of ovules. For example, seedless bananas and grapes are very common.
Note: The carpel is the female reproductive organ of a flower that consists of an ovary, stigma, and a style. If the gynoecium of the flower has a single carpel, it is known as a monocarpous. Carpel consists of the innermost whorl of the flower.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




