
An ammeter is always connected in parallel with the circuit in which the current is to be measured
(A). True
(B). False
Answer
605.4k+ views
Hint: The same amount of current flows in the same branch. If the ammeter is connected in series the same amount of current will flow through the ammeter as well as in device or wire with which it is connected. If the ammeter is connected in parallel different amounts of current will flow through the ammeter and into the device or wire with which it is connected.
Complete Step By Step Solution:
Ammeter is a device which measures the current passing through it. It consists of a galvanometer and a small resistance connected in parallel with the galvanometer. Galvanometer is a simple device which measures a small amount of current passing through it. An ammeter is always connected in series with the circuit. This allows the same amount of current to flow in circuit and ammeter.
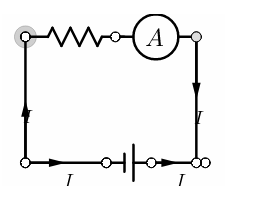
When the current enters the ammeter it gets divided, some part of it enters the galvanometer while other passes through small resistance in parallel. This resistance is attached to make the total resistance of the ammeter very less. This is because the net resistance of two resistors connected in parallel is always less than individual resistance of both resistors. So that the ammeter does not change current flowing in the entire circuit.
If an ammeter had been attached in parallel instead it would have measured the current passing through its branch not the branch where measurement of current is intended.
Hence the correct option is B. False
Note: Someone can think that we can use ammeter is parallel and use the fact that current get divided in inverse ratio of resistance, to get the current flowing through the main branch. But the problem with such an approach is that we do not know the resistance of the device with which we are connecting the ammeter, so this method cannot be used.
Complete Step By Step Solution:
Ammeter is a device which measures the current passing through it. It consists of a galvanometer and a small resistance connected in parallel with the galvanometer. Galvanometer is a simple device which measures a small amount of current passing through it. An ammeter is always connected in series with the circuit. This allows the same amount of current to flow in circuit and ammeter.

When the current enters the ammeter it gets divided, some part of it enters the galvanometer while other passes through small resistance in parallel. This resistance is attached to make the total resistance of the ammeter very less. This is because the net resistance of two resistors connected in parallel is always less than individual resistance of both resistors. So that the ammeter does not change current flowing in the entire circuit.
If an ammeter had been attached in parallel instead it would have measured the current passing through its branch not the branch where measurement of current is intended.
Hence the correct option is B. False
Note: Someone can think that we can use ammeter is parallel and use the fact that current get divided in inverse ratio of resistance, to get the current flowing through the main branch. But the problem with such an approach is that we do not know the resistance of the device with which we are connecting the ammeter, so this method cannot be used.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




