
An element is placed in ${2^{nd}}$ group and ${3^{rd}}$ period of periodic table, it burns in the presence of Oxygen to form basic oxide.
(a) Identify the element.
(b) Write the electronic configuration.
(c) Write the balanced equation when it burns in presence of air.
(d) Write the balanced equation when this oxide is dissolved in water.
(e) Draw the electron dot structure for the formula of this oxide.
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint:We know that elements of ${2^{nd}}$ group are known as Alkaline earth. Elements of group $2$ are $Be,Mg,Ca,Ba,Sr$. As it is mentioned in the question that the element lies in the ${3^{rd}}$ period it means that the outermost shell would be $3$i.e. either $3s,3p$ or $3d$. It is also mentioned that the element lies in the ${2^{nd}}$ group, so it will have two electrons in the ${3^{rd}}$ shell.
Complete step-by-step answer:(a) The identified element is Magnesium with the Atomic number $12$.
(b) Electronic configuration: With the help of Aufbau principle which states that electrons will occupy the lowest-energy orbital first before filling higher-energy orbitals.
So, the electronic configuration = $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}$
(c) Balanced equation of Magnesium when it burns in the presence of air:
Here Magnesium will react with oxygen and will form Magnesium oxide.
$2Mg\left( s \right) + {O_2}\left( g \right) \to 2MgO(s)$
(d) Balanced equation of Magnesium oxide when it is dissolved in water: -
Here, Magnesium oxide will react with water will form Magnesium hydroxide
We will write the equation as:
$MgO(s) + {H_2}O(l) \to Mg{(OH)_2}(aq)$
(e) Electron dot structure of Magnesium oxide:
$Mg$ contains two valence electrons so the valency of Magnesium is $M{g^{2 + }}$
$O$ contains six valence electrons so the valency of Oxygen is ${O^{2 - }}$
We will now draw the structure:
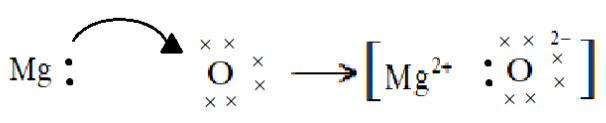
Here we see that Magnesium gives its two valence electrons to Oxygen in order to complete its octane and since Oxygen needs only two electrons to complete its octet and gain stability it accepts two electrons of Magnesium and forms Magnesium oxide.
Note:While drawing the electron dot structure we are following the octet rule which states that atoms combine and form bonds either by transferring electrons to form ions or by sharing electrons in covalent bonds until each atom is surrounded by eight valence electrons. Hence here the type of bond formed is an ionic bond as the electrons are being transferred from magnesium to oxygen.
Complete step-by-step answer:(a) The identified element is Magnesium with the Atomic number $12$.
(b) Electronic configuration: With the help of Aufbau principle which states that electrons will occupy the lowest-energy orbital first before filling higher-energy orbitals.
So, the electronic configuration = $1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^6}3{s^2}$
(c) Balanced equation of Magnesium when it burns in the presence of air:
Here Magnesium will react with oxygen and will form Magnesium oxide.
$2Mg\left( s \right) + {O_2}\left( g \right) \to 2MgO(s)$
(d) Balanced equation of Magnesium oxide when it is dissolved in water: -
Here, Magnesium oxide will react with water will form Magnesium hydroxide
We will write the equation as:
$MgO(s) + {H_2}O(l) \to Mg{(OH)_2}(aq)$
(e) Electron dot structure of Magnesium oxide:
$Mg$ contains two valence electrons so the valency of Magnesium is $M{g^{2 + }}$
$O$ contains six valence electrons so the valency of Oxygen is ${O^{2 - }}$
We will now draw the structure:
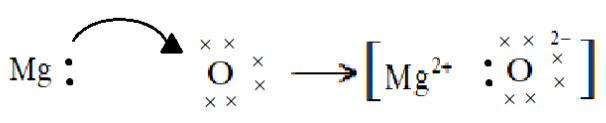
Here we see that Magnesium gives its two valence electrons to Oxygen in order to complete its octane and since Oxygen needs only two electrons to complete its octet and gain stability it accepts two electrons of Magnesium and forms Magnesium oxide.
Note:While drawing the electron dot structure we are following the octet rule which states that atoms combine and form bonds either by transferring electrons to form ions or by sharing electrons in covalent bonds until each atom is surrounded by eight valence electrons. Hence here the type of bond formed is an ionic bond as the electrons are being transferred from magnesium to oxygen.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




