
An example of pyrosilicate is:
A) Thortveitite
B) Willemite
C) Spodumene
D) Kaolinite
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: The silicate is formed by fusing an alkali with the$\text{ Si}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$. It exists in various allotropes like Orthosilicate, pyrosilicate, cyclic silicate, chain silicate, etc. The pyrosilicate consists of the $\text{ S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}_{\text{7}}^{\text{6-}}$ anions which are joined together by the removal of oxygen. The thortveitite is an example of silicate, it is scandium yttrium silicate. $\text{ (Sc,Y}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
The $\text{ Si}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ fuses with the alkali oxides to give silicates. This is discrete tetrahedral units. Since silicon is \[\text{ s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}\] hybridized. The various units are linked in several patterns and classified as follows,
1) Orthosilicate: Orthosilicate contains the separated $\text{ Si}{{\text{O}}_{4}}$units. This is linked together by various patterns. An example is Willemite$\text{ (ZrSi}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{)}$.
2) Pyrosilicate: In pyrosilicate, the two units are linked together by the oxygen atom. The simplest ion is\[\text{ S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}\] . Example is Thortveitite\[\text{ S}{{\text{c}}_{\text{2}}}\left[ \text{S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}} \right]\]
3) Cyclic silicates: this allotrope shares the two oxygen atoms. The example is Beryl - \[\text{ B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{3}}}\text{A}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{18}}}\]
4) Chain silicates: these are formed by the linking of units to form a chain silicate. They are of two types:
i) Metasilicates
ii) Amphiboles
Now, we will discuss pyrosilicate. A pyrosilicate is a chemical compound that contains the phyllosilicate anion $\text{ S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}_{\text{7}}^{\text{6-}}$ with the hexavalent group \[\text{ }-({{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{Si-O-Si}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}})-\] .
Pyrosilicate is formed by joining the two tetrahedral units$\text{ S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}_{4}^{4-}$.this units joined together by the removal of oxygen and two units then join at the corners of oxygen atoms.
The structure of pyrosilicate is as follows:
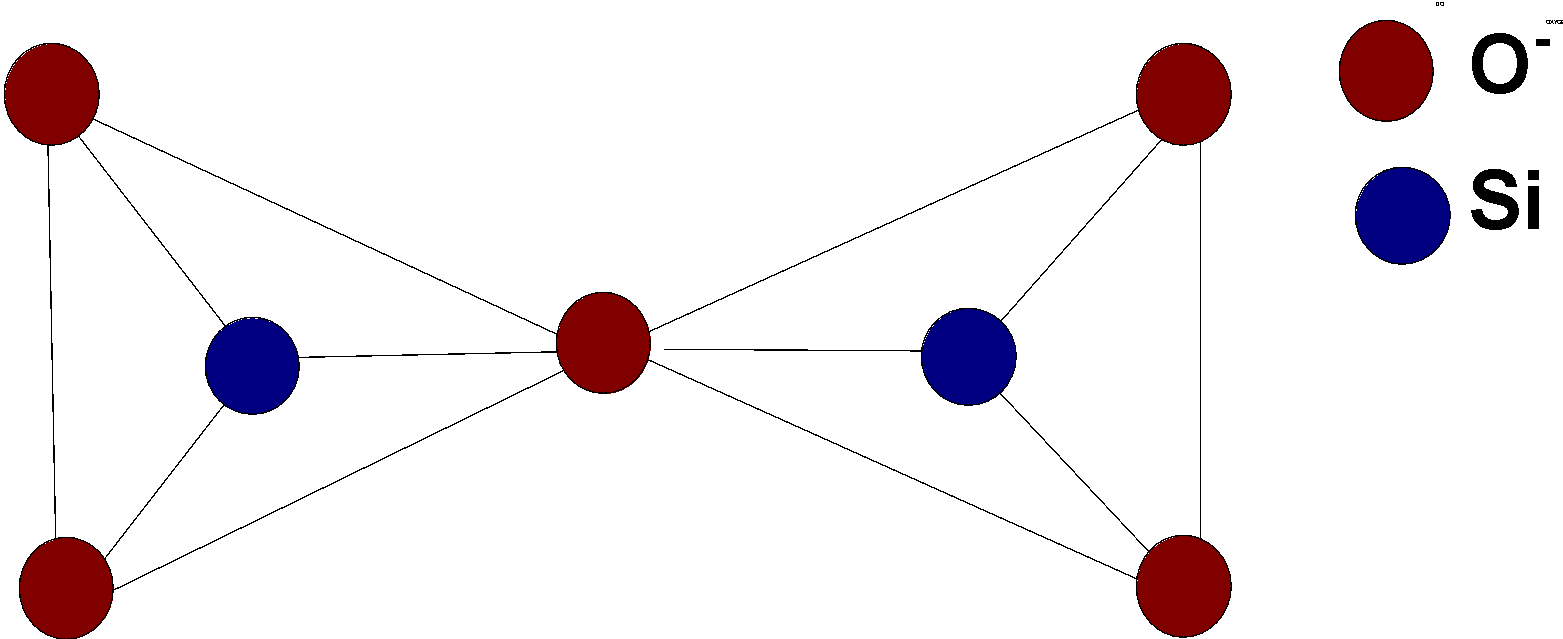
One of the common examples of pyrosilicate is thortveitite. It is a scandium silicate yttrium silicate$\text{ (Sc,Y}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$. It is a primary source of scandium.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Note: The silicon is a group 14 element and shows the allotropic properties. The
silicates have the silicon-oxide linkage but exist in a different structure. Students should remember the formulas for the silicates.
Complete step by step answer:
The $\text{ Si}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}$ fuses with the alkali oxides to give silicates. This is discrete tetrahedral units. Since silicon is \[\text{ s}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}\] hybridized. The various units are linked in several patterns and classified as follows,
1) Orthosilicate: Orthosilicate contains the separated $\text{ Si}{{\text{O}}_{4}}$units. This is linked together by various patterns. An example is Willemite$\text{ (ZrSi}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\text{)}$.
2) Pyrosilicate: In pyrosilicate, the two units are linked together by the oxygen atom. The simplest ion is\[\text{ S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}\] . Example is Thortveitite\[\text{ S}{{\text{c}}_{\text{2}}}\left[ \text{S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}} \right]\]
3) Cyclic silicates: this allotrope shares the two oxygen atoms. The example is Beryl - \[\text{ B}{{\text{e}}_{\text{3}}}\text{A}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{6}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{18}}}\]
4) Chain silicates: these are formed by the linking of units to form a chain silicate. They are of two types:
i) Metasilicates
ii) Amphiboles
Now, we will discuss pyrosilicate. A pyrosilicate is a chemical compound that contains the phyllosilicate anion $\text{ S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}_{\text{7}}^{\text{6-}}$ with the hexavalent group \[\text{ }-({{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\text{Si-O-Si}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}})-\] .
Pyrosilicate is formed by joining the two tetrahedral units$\text{ S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}\text{O}_{4}^{4-}$.this units joined together by the removal of oxygen and two units then join at the corners of oxygen atoms.
The structure of pyrosilicate is as follows:

One of the common examples of pyrosilicate is thortveitite. It is a scandium silicate yttrium silicate$\text{ (Sc,Y}{{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}\text{S}{{\text{i}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{7}}}$. It is a primary source of scandium.
Hence, (A) is the correct option.
Note: The silicon is a group 14 element and shows the allotropic properties. The
silicates have the silicon-oxide linkage but exist in a different structure. Students should remember the formulas for the silicates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




