
An organic compound gives an orange precipitate with 2,4-DNPH. What is the functional group in the compound?
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint:
The full form of 2,4-DNPH is 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. It has a nucleophilic nitrogen atom which can attack the electrophilic atom. It is also called Brady’s reagent.
Complete step by step solution:
We first need to know what 2,4-DNPH is in order to find and solve this question.
- 2,4-DNPH stands for 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. It is red to orange coloured powder. It is slightly soluble in water.
- 2,4-DNPH is used to identify the functional group present in the compound. So, it is used in organic qualitative analysis.
- 2,4-DNPH is used to identify the aldehydes and ketone, functional groups. It is also called Brady’s reagent. The reaction of 2,4-DNPH with aldehydes or ketones can be given as below with mechanism.
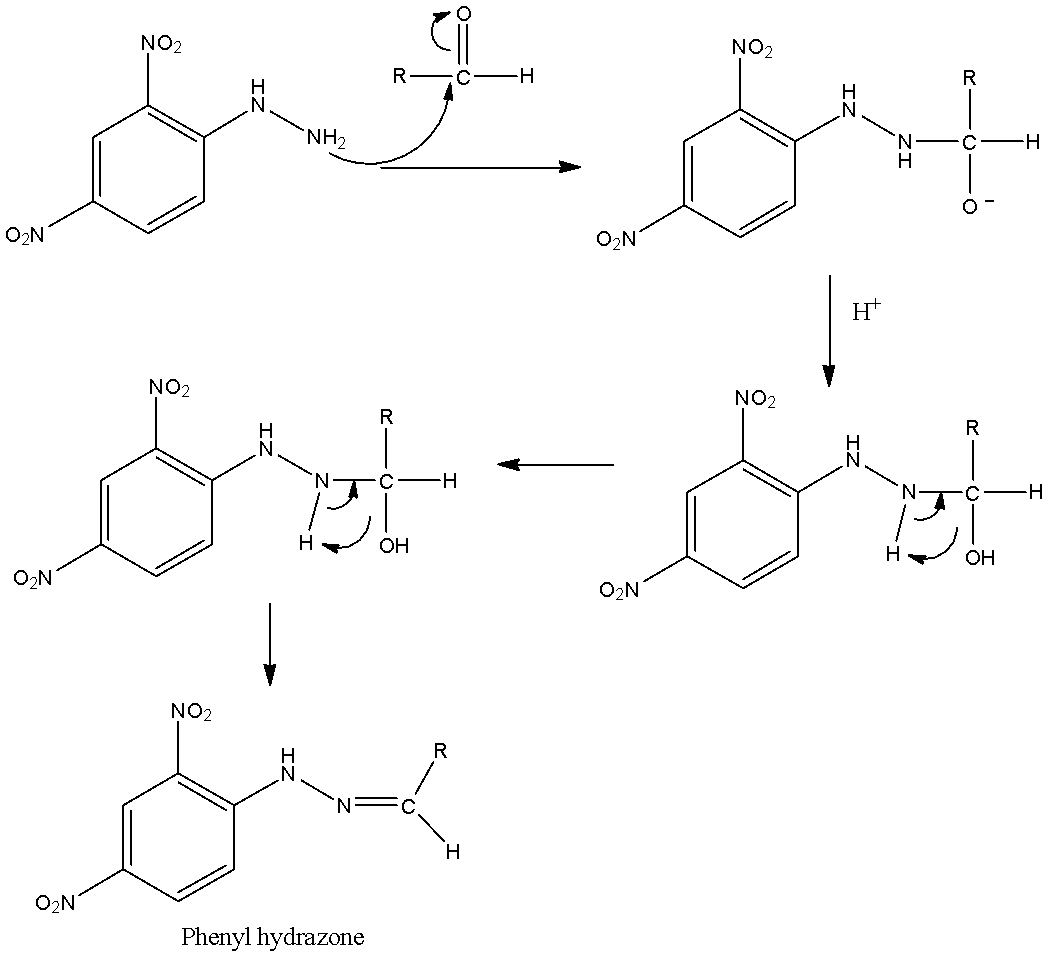
- We can see that the nucleophilic nitrogen atom of 2,4-DNPH attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon and C-O double bond is cleaved. Then the loss of the water molecule gives phenyl hydrazone as a final product which is orange in colour. This reaction can be considered as a condensation reaction.
- Thus, the derivative obtained can be checked for the melting point and we can confirm the organic compound from this test.
- So, we can conclude that 2,4-DNPH is used to identify aldehyde and ketones.
Note: Remember that this reagent cannot give orange precipitates with other functional groups that have carbonyl groups like esters, acids, etc. This happens because they are romance stabilized and hence do not give these types of additional reactions easily.
The full form of 2,4-DNPH is 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. It has a nucleophilic nitrogen atom which can attack the electrophilic atom. It is also called Brady’s reagent.
Complete step by step solution:
We first need to know what 2,4-DNPH is in order to find and solve this question.
- 2,4-DNPH stands for 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine. It is red to orange coloured powder. It is slightly soluble in water.
- 2,4-DNPH is used to identify the functional group present in the compound. So, it is used in organic qualitative analysis.
- 2,4-DNPH is used to identify the aldehydes and ketone, functional groups. It is also called Brady’s reagent. The reaction of 2,4-DNPH with aldehydes or ketones can be given as below with mechanism.

- We can see that the nucleophilic nitrogen atom of 2,4-DNPH attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon and C-O double bond is cleaved. Then the loss of the water molecule gives phenyl hydrazone as a final product which is orange in colour. This reaction can be considered as a condensation reaction.
- Thus, the derivative obtained can be checked for the melting point and we can confirm the organic compound from this test.
- So, we can conclude that 2,4-DNPH is used to identify aldehyde and ketones.
Note: Remember that this reagent cannot give orange precipitates with other functional groups that have carbonyl groups like esters, acids, etc. This happens because they are romance stabilized and hence do not give these types of additional reactions easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




