
Answer the following question:
How would you convert aniline to iodobenzene?
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: Aniline has the chemical formula ${{{C}}_6}{{{H}}_5}{{N}}{{{H}}_2}$ and iodobenzene has the chemical formula ${{{C}}_6}{{{H}}_5}{{I}}$. During the conversion of aniline to iodobenzene, there is a formation of intermediate. This can be done using two methods.
Complete step by step answer:
Aniline is an example of an aromatic amine. Amine is a compound in which an amino group is attached to the benzene ring. The structure of aniline is given below:
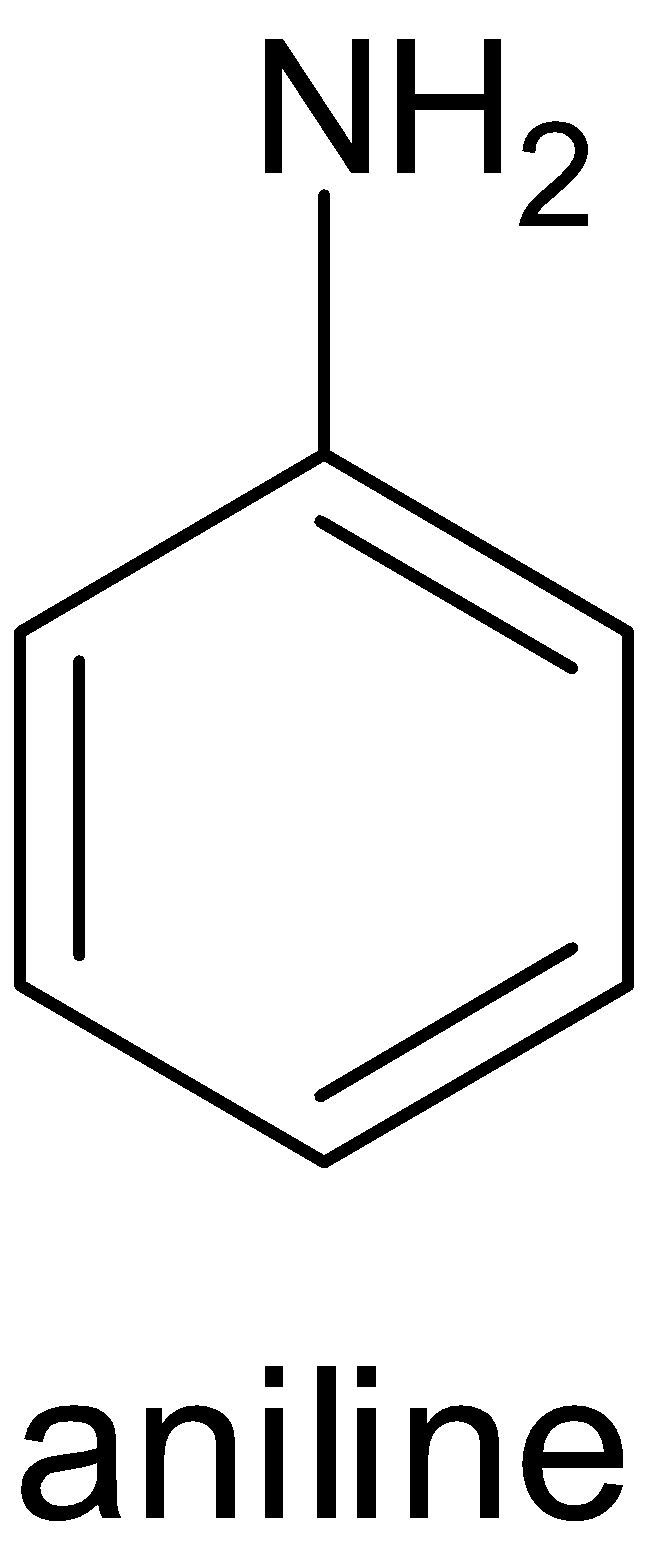
While iodobenzene is a compound in which an iodine atom is attached to the benzene ring. The structure of iodobenzene is given below:
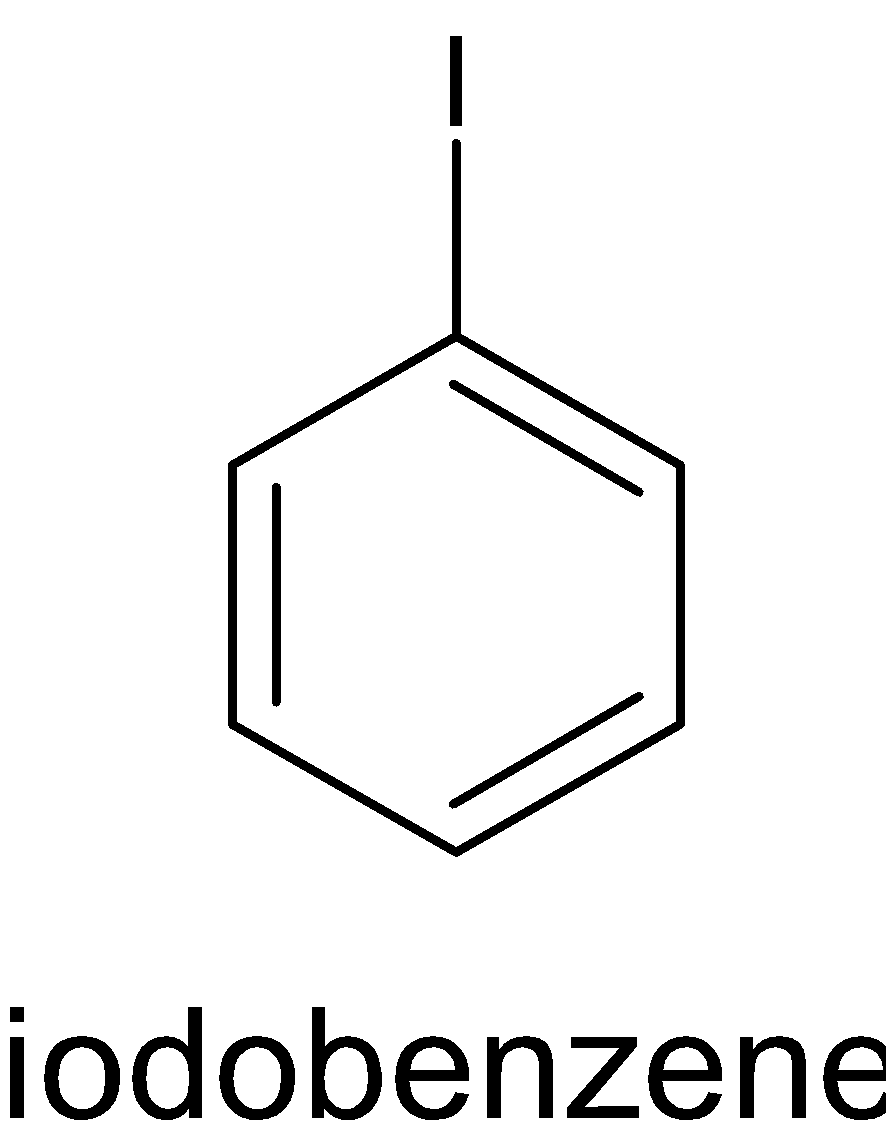
The conversion of aniline to iodobenzene undergoes several steps.
First step involves the conversion of aniline to benzene diazonium chloride. This is done by dissolving aniline in dilute hydrochloric acid with an aqueous solution of sodium nitrate. Now we get benzene diazonium chloride. This reaction occurs at $273{{K}} - 278{{K}}$. The chemical reaction is given below:
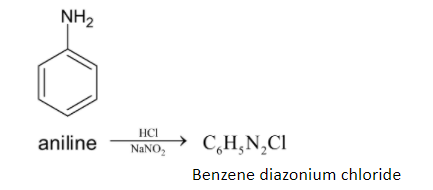
This process is called the Sandmeyer reaction. This benzene diazonium chloride is further converted to iodobenzene.
When benzene diazonium chloride is reacted with potassium iodide, it forms iodobenzene. Potassium iodide acts as a catalyst. The reaction is given below:
${{{C}}_6}{{{H}}_5}{{{N}}_2}{{Cl + KI}} \to {{{C}}_6}{{{H}}_5}{{I}}$ (Iodobenzene)
Additional information:
When sodium nitrite is reacted with hydrochloric acid, nitrous acid is formed. The chemical reaction is given below:
${{NaN}}{{{O}}_2} (Sodium\; nitrite) + {{HCl}} \to {{HONO}}$ (Nitrous acid)
When these are reacted together, two protonation steps occur and one water molecule is removed.
Note: This process of conversion of aniline to iodobenzene can also be done using Sandmeyer reaction. This reaction is the formation of aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts in the presence of some catalysts like copper salts.
Complete step by step answer:
Aniline is an example of an aromatic amine. Amine is a compound in which an amino group is attached to the benzene ring. The structure of aniline is given below:

While iodobenzene is a compound in which an iodine atom is attached to the benzene ring. The structure of iodobenzene is given below:

The conversion of aniline to iodobenzene undergoes several steps.
First step involves the conversion of aniline to benzene diazonium chloride. This is done by dissolving aniline in dilute hydrochloric acid with an aqueous solution of sodium nitrate. Now we get benzene diazonium chloride. This reaction occurs at $273{{K}} - 278{{K}}$. The chemical reaction is given below:

This process is called the Sandmeyer reaction. This benzene diazonium chloride is further converted to iodobenzene.
When benzene diazonium chloride is reacted with potassium iodide, it forms iodobenzene. Potassium iodide acts as a catalyst. The reaction is given below:
${{{C}}_6}{{{H}}_5}{{{N}}_2}{{Cl + KI}} \to {{{C}}_6}{{{H}}_5}{{I}}$ (Iodobenzene)
Additional information:
When sodium nitrite is reacted with hydrochloric acid, nitrous acid is formed. The chemical reaction is given below:
${{NaN}}{{{O}}_2} (Sodium\; nitrite) + {{HCl}} \to {{HONO}}$ (Nitrous acid)
When these are reacted together, two protonation steps occur and one water molecule is removed.
Note: This process of conversion of aniline to iodobenzene can also be done using Sandmeyer reaction. This reaction is the formation of aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts in the presence of some catalysts like copper salts.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




