
Why are enantiomers optically active?
Answer
491.7k+ views
Hint: The rotation of the orientation of the plane of polarisation about the optical axis of linearly polarised light as it travels through certain materials is known as optical rotation, polarisation rotation, or circular birefringence. Optical activity manifests itself as circular birefringence and circular dichroism.
Complete answer:
Enantiomers are molecules that exist in two forms that are mirror copies of one another but cannot be overlaid.
Enantiomers are chemically similar in every other way. The direction in which enantiomers twist polarised light when dissolved in solution, either dextro (d or +) or levo (l or -), is what distinguishes them as optical isomers. When two enantiomers are present in equal quantities, they form a racemic mixture, which does not spin polarised light because the optical activity of one enantiomer cancels out the optical activity of the other.
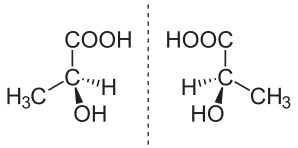
Optical isomers, also known as enantiomers, have the same atomic and bond sequence but differ in their 3D form. The most often stated example of two enantiomers is human hands, which are nonsuperimposable mirror copies of one another (i.e., chiral). Despite the fact that our left hand is a mirror copy of our right, our left thumb cannot be put over our right thumb if our palms are facing the same direction and positioned over one another. Optical isomers also lack an axis of symmetry, which means there is no line that divides the compound into two halves, with the left half mirroring the right.
Chiral molecules rotate polarised light in a plane, and a compound that spins polarised light in a plane is said to be optically active.
Note:
In the following illustration, we can observe that the light remains the same when we employ a pair of enantiomers in a 50:50 ratio (the sum of the rotations cancels out).
They rotate the light to the same degree but in opposing directions since they are non-superimposable mirror copies, causing external compensation and the light to appear to not have rotated.
Complete answer:
Enantiomers are molecules that exist in two forms that are mirror copies of one another but cannot be overlaid.
Enantiomers are chemically similar in every other way. The direction in which enantiomers twist polarised light when dissolved in solution, either dextro (d or +) or levo (l or -), is what distinguishes them as optical isomers. When two enantiomers are present in equal quantities, they form a racemic mixture, which does not spin polarised light because the optical activity of one enantiomer cancels out the optical activity of the other.
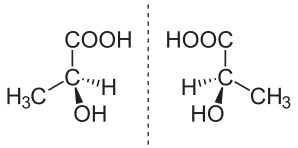
Optical isomers, also known as enantiomers, have the same atomic and bond sequence but differ in their 3D form. The most often stated example of two enantiomers is human hands, which are nonsuperimposable mirror copies of one another (i.e., chiral). Despite the fact that our left hand is a mirror copy of our right, our left thumb cannot be put over our right thumb if our palms are facing the same direction and positioned over one another. Optical isomers also lack an axis of symmetry, which means there is no line that divides the compound into two halves, with the left half mirroring the right.
Chiral molecules rotate polarised light in a plane, and a compound that spins polarised light in a plane is said to be optically active.
Note:
In the following illustration, we can observe that the light remains the same when we employ a pair of enantiomers in a 50:50 ratio (the sum of the rotations cancels out).
They rotate the light to the same degree but in opposing directions since they are non-superimposable mirror copies, causing external compensation and the light to appear to not have rotated.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




