
What are guard cells? Explain their role in regulating transpiration
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: The mechanism of water passage through a plant and its evaporation from aerial components such as leaves, stems and flowers is transpiration. For plants, water is important, but for growth and digestion, only a limited amount of water taken up by the roots is used.
Complete Answer:
- Guard cells are the cells that cover each stomach. By opening and closing the stomata, they help to control the rate of transpiration.
- Role of Guard cells regulating transpiration: Guard cells are kidney-shaped cells that protect the stomach and are responsible for opening and closing the pore of the stomach. As potassium ions build up in the guard cells, they absorb water and become bloated or turgid. Owing to their turgidity, the stomatal pore is fully exposed and transpiration occurs. As they lose water due to external stimuli such as sunshine, temperature, etc., they become flaccid and close the stomatal opening and thereby avoid the transpiration.
- As epidermal cells, they play an essential role in the gas exchange in and out of plant leaves by controlling the opening and closure of pores known as the stoma. They are also the pathways by which the water is released from the leaves to the environment.
- As such, guard cells play a crucial role in photosynthesis by controlling the input of the materials required for the process. Apart from controlling the gas exchange, it has also been shown to include chloroplasts, which also allow them a photosynthesis site.
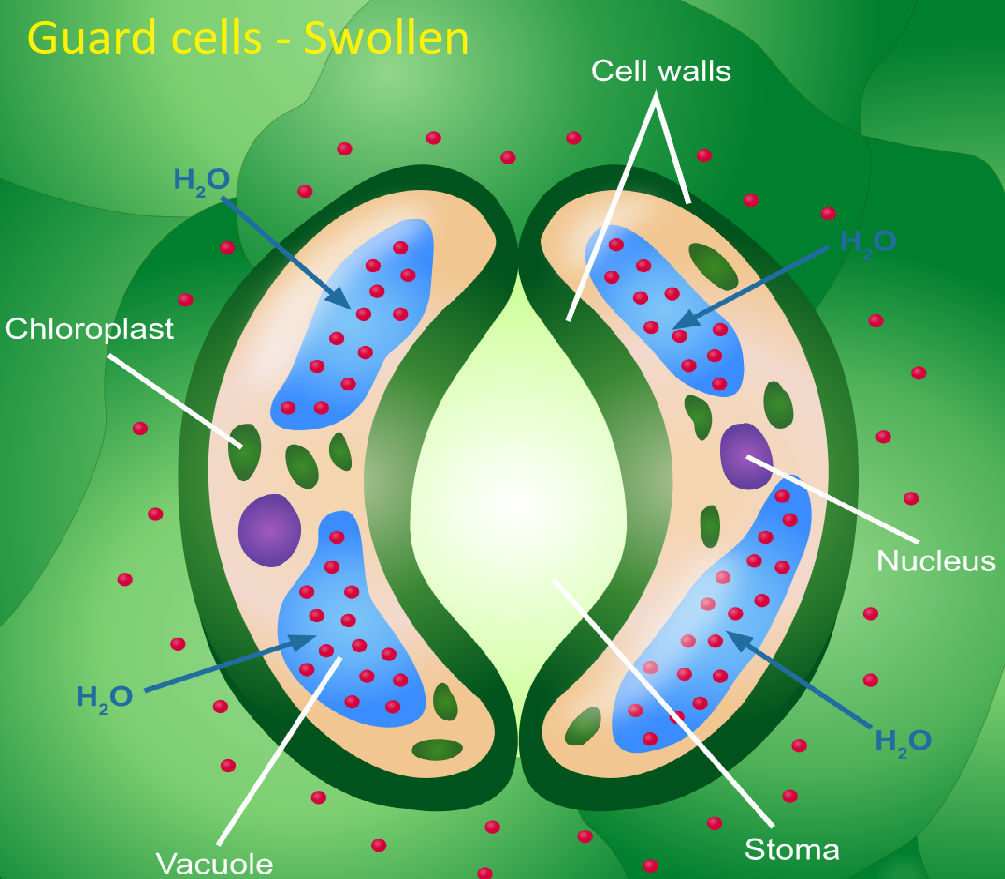
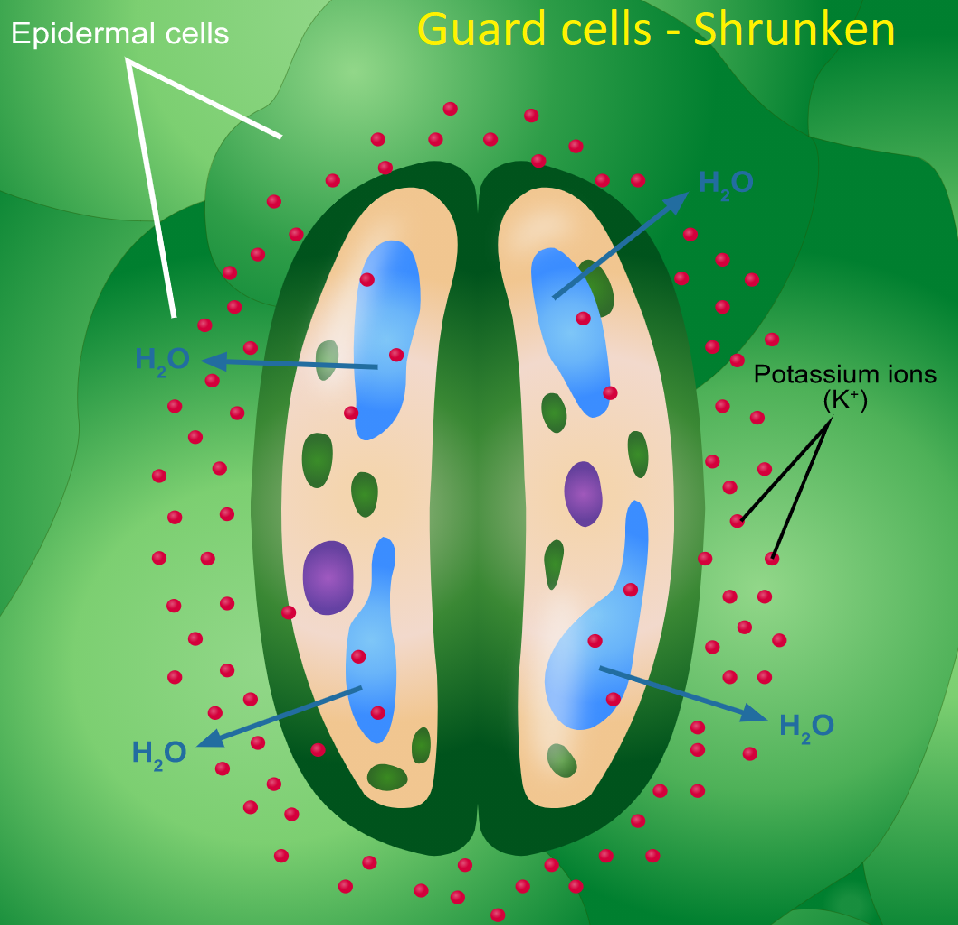
Note: Some of the variables that affect guard cell behaviour are: humidity, temperature, sun, carbon dioxide, potassium ions, hormones. While stomata are commonly found in the leaves of plants, it can also be found in the stems.
Complete Answer:
- Guard cells are the cells that cover each stomach. By opening and closing the stomata, they help to control the rate of transpiration.
- Role of Guard cells regulating transpiration: Guard cells are kidney-shaped cells that protect the stomach and are responsible for opening and closing the pore of the stomach. As potassium ions build up in the guard cells, they absorb water and become bloated or turgid. Owing to their turgidity, the stomatal pore is fully exposed and transpiration occurs. As they lose water due to external stimuli such as sunshine, temperature, etc., they become flaccid and close the stomatal opening and thereby avoid the transpiration.
- As epidermal cells, they play an essential role in the gas exchange in and out of plant leaves by controlling the opening and closure of pores known as the stoma. They are also the pathways by which the water is released from the leaves to the environment.
- As such, guard cells play a crucial role in photosynthesis by controlling the input of the materials required for the process. Apart from controlling the gas exchange, it has also been shown to include chloroplasts, which also allow them a photosynthesis site.


Note: Some of the variables that affect guard cell behaviour are: humidity, temperature, sun, carbon dioxide, potassium ions, hormones. While stomata are commonly found in the leaves of plants, it can also be found in the stems.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




