
What are interstitial compounds? Why are such compounds well known for transition metals?
Answer
528.4k+ views
Hint: We know that transition metals are the elements present in the d-block of the periodic table. Some of the examples of transition metals are cobalt, nickel, iron etc.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Those compounds which form when very small atoms, such as hydrogen, nitrogen and carbon get trapped inside the crystal lattices of metals are termed as interstitial compounds. These compounds are generally not ionic or covalent and non-stoichiometric.
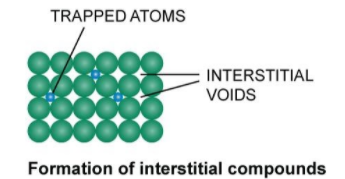
From the above diagram, we clearly see that the trapped atoms in the interstitial sites form interstitial compounds.
The transition metals are well known for the formation of interstitial compounds because of its closed structure with voids in them. The atomic size of transition metals is very large, so they have large voids where small atoms are occupied. Some examples of interstitial compounds are ${\rm{TiC}}$, ${\rm{M}}{{\rm{n}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{N}}$etc.
Additional information:
1) Interstitial compounds do not obey rules of valency.
2) These compounds are extremely hard, of metallic nature and possess high boiling and melting points.
3) ${\rm{F}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}$is an interstitial compound of steel that governs many properties of steel.
4) The hardness of interstitial compounds is used in hardening of alloys and high speed cutting tool tips.
5) They are generally more reactive than the compounds.
6) They maintain metallic conductivity.
Note:
There are three most common interactive alloy phases present, they are intermetallic compounds, interstitial compounds and electron compounds. Intermetallic compounds are generally formed between metals which are chemically not similar and electron compounds formed in alloys of copper, gold, iron with the metals of calcium, magnesium, etc.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Those compounds which form when very small atoms, such as hydrogen, nitrogen and carbon get trapped inside the crystal lattices of metals are termed as interstitial compounds. These compounds are generally not ionic or covalent and non-stoichiometric.

From the above diagram, we clearly see that the trapped atoms in the interstitial sites form interstitial compounds.
The transition metals are well known for the formation of interstitial compounds because of its closed structure with voids in them. The atomic size of transition metals is very large, so they have large voids where small atoms are occupied. Some examples of interstitial compounds are ${\rm{TiC}}$, ${\rm{M}}{{\rm{n}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{N}}$etc.
Additional information:
1) Interstitial compounds do not obey rules of valency.
2) These compounds are extremely hard, of metallic nature and possess high boiling and melting points.
3) ${\rm{F}}{{\rm{e}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{C}}$is an interstitial compound of steel that governs many properties of steel.
4) The hardness of interstitial compounds is used in hardening of alloys and high speed cutting tool tips.
5) They are generally more reactive than the compounds.
6) They maintain metallic conductivity.
Note:
There are three most common interactive alloy phases present, they are intermetallic compounds, interstitial compounds and electron compounds. Intermetallic compounds are generally formed between metals which are chemically not similar and electron compounds formed in alloys of copper, gold, iron with the metals of calcium, magnesium, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




