
What are lone pairs and how are they represented in a Lewis dot diagram?
Answer
544.5k+ views
Hint: The Lewis dot structure is generally defined as the graphic representation of the electrons which have been distributed around the atom. The main reason for learning the Lewis dot structure is that it helps us to predict the number of the bonds as well as the types of bonds that can be formed around the atom. It also helps in predicting the geometry of the molecule..
Complete step-by-step answer:
The lone pairs are defined as those pairs of electrons which have been left in the outermost valence shell without participating in the formation of covalent bonds. Generally it is the valence electrons which have not been exchanged with other atoms often known as unshared pairs or the non bonding pairs. When the unshared pair of electrons are being absolutely shared by the other atom or the ion around the atom in the centre of the molecule it is called lone pair effect. The polar covalent compounds generally show the lone pair effect such as HCl. In the Lewis dot structure the lone pairs are represented as a dot in the structure.
Now let us see the Lewis dot structure of the \[N{O_3}^ - \]. The steps for drawing a Lewis dot structure is the following:
First we need to know the number of the valence electrons in the molecule. so the number of valence electrons in a nitrogen atom is 5. As we have 3 atoms of oxygen and we know the number of valence electrons in oxygen is 6 so in 3 atoms it will be 18. There is the presence of a negative charge (1)in the molecule. So the total number of valence electrons in the molecule will be 5+18+1= 24.
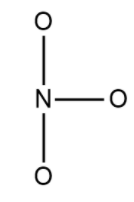
Now in the next step we would draw the skeleton of the molecule in which we would see the central atom connecting the ball to other atoms using a single bond. The structure is:
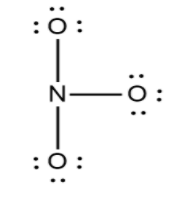
Now in the next step out of the 24 electrons we have used the 6 electrons in the formation of the skeleton. Now we have 18 electrons to fill their octet. So to fill the octet we always fill the octet of the most electronegative atom then the electropositive atom. So here is the structure.
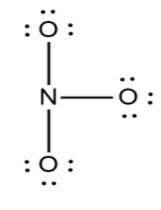
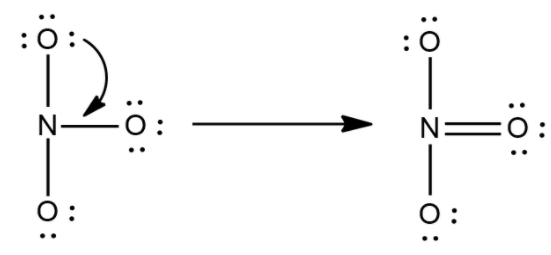
Now in the next step check whether the octets are filled or not if yes then make the multiple bonds.
Now these dots are the lone pairs.
Note: Always remember that the total vapour pressure over the solution is related to the mole fraction of any one component and it varies linearly with the mole fraction of the second component. Also, the total vapour pressure increases or decreases according to the increase in the mole fraction of the second component.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The lone pairs are defined as those pairs of electrons which have been left in the outermost valence shell without participating in the formation of covalent bonds. Generally it is the valence electrons which have not been exchanged with other atoms often known as unshared pairs or the non bonding pairs. When the unshared pair of electrons are being absolutely shared by the other atom or the ion around the atom in the centre of the molecule it is called lone pair effect. The polar covalent compounds generally show the lone pair effect such as HCl. In the Lewis dot structure the lone pairs are represented as a dot in the structure.
Now let us see the Lewis dot structure of the \[N{O_3}^ - \]. The steps for drawing a Lewis dot structure is the following:
First we need to know the number of the valence electrons in the molecule. so the number of valence electrons in a nitrogen atom is 5. As we have 3 atoms of oxygen and we know the number of valence electrons in oxygen is 6 so in 3 atoms it will be 18. There is the presence of a negative charge (1)in the molecule. So the total number of valence electrons in the molecule will be 5+18+1= 24.

Now in the next step we would draw the skeleton of the molecule in which we would see the central atom connecting the ball to other atoms using a single bond. The structure is:

Now in the next step out of the 24 electrons we have used the 6 electrons in the formation of the skeleton. Now we have 18 electrons to fill their octet. So to fill the octet we always fill the octet of the most electronegative atom then the electropositive atom. So here is the structure.

Now in the next step check whether the octets are filled or not if yes then make the multiple bonds.
Now these dots are the lone pairs.

Note: Always remember that the total vapour pressure over the solution is related to the mole fraction of any one component and it varies linearly with the mole fraction of the second component. Also, the total vapour pressure increases or decreases according to the increase in the mole fraction of the second component.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




