
What are primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols? Give one example of each.
Answer
502.8k+ views
Hint: Alcohols have –OH group attached to the alkyl groups. The three types of alcohols, primary, secondary, and tertiary are determined by the position of the hydroxyl functional group attached to the alkyl group. Just write the definition of all the three types and give one example each.
Complete answer:
Alcohol is any class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (―OH) groups attached to a carbon atom of an alkyl group (hydrocarbon chain).
Based upon the presence of hydroxyl group attached to the alkyl group and the location of this hydroxyl group the alcohols are differentiated into primary, secondary, and tertiary.
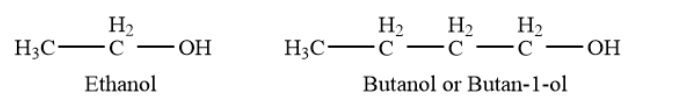
Primary alcohols- In a primary \[\left( {1^\circ } \right)\]alcohol, the carbon atom that carries the -OH group is only attached to one alkyl group. Example- ethanol, butanol or butan-\[1\]- etc.
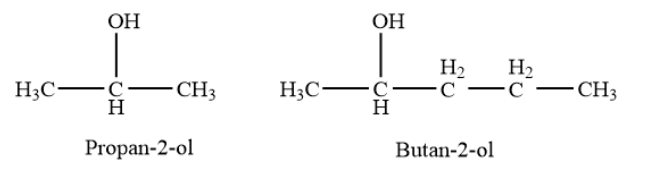
Secondary alcohols- In a secondary \[\left( {2^\circ } \right)\]alcohol, the carbon atom with the -OH group attached is joined directly to two alkyl groups, which may be the same or different. Examples- propan-\[2\]-ol, butan-\[2\]-ol etc.
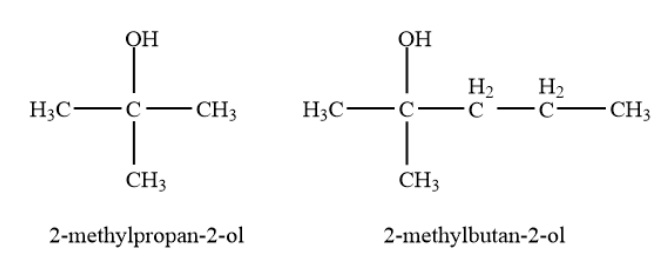
Tertiary alcohols-In a tertiary \[\left( {3^\circ } \right)\]alcohol, the carbon atom holding the -OH group is attached directly to three alkyl groups, which may be any combination of the same or different groups. Example- \[2\]-methylpropan-\[2\]-ol, \[2\]-methylbutan-\[2\]-ol etc.
Note:
Alcohols can also have multiple hydroxyl groups instead of one. If an alcohol has two hydroxyl groups then it is called diols, if it has three hydroxyl groups then it is triols, and so on. Alcohols are an important class of compounds. Alcohols may be considered as organic derivatives of water \[\left( {{H_2}O} \right)\] in which one of the hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an alkyl group, typically represented by R in organic structures.
Complete answer:
Alcohol is any class of organic compounds characterized by the presence of one or more hydroxyl (―OH) groups attached to a carbon atom of an alkyl group (hydrocarbon chain).
Based upon the presence of hydroxyl group attached to the alkyl group and the location of this hydroxyl group the alcohols are differentiated into primary, secondary, and tertiary.
Primary alcohols- In a primary \[\left( {1^\circ } \right)\]alcohol, the carbon atom that carries the -OH group is only attached to one alkyl group. Example- ethanol, butanol or butan-\[1\]- etc.

Secondary alcohols- In a secondary \[\left( {2^\circ } \right)\]alcohol, the carbon atom with the -OH group attached is joined directly to two alkyl groups, which may be the same or different. Examples- propan-\[2\]-ol, butan-\[2\]-ol etc.

Tertiary alcohols-In a tertiary \[\left( {3^\circ } \right)\]alcohol, the carbon atom holding the -OH group is attached directly to three alkyl groups, which may be any combination of the same or different groups. Example- \[2\]-methylpropan-\[2\]-ol, \[2\]-methylbutan-\[2\]-ol etc.

Note:
Alcohols can also have multiple hydroxyl groups instead of one. If an alcohol has two hydroxyl groups then it is called diols, if it has three hydroxyl groups then it is triols, and so on. Alcohols are an important class of compounds. Alcohols may be considered as organic derivatives of water \[\left( {{H_2}O} \right)\] in which one of the hydrogen atoms has been replaced by an alkyl group, typically represented by R in organic structures.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




