
What are structural isomers? List any four characteristics of isomers. Draw the possible structures of butane.
Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: In structural isomers the number of atoms present in the isomer of the chemical compound are the same but their arrangement is different in different isomers which influence their characteristics.
Complete step by step answer:
The isomers are defined as the molecules which have the same molecular formulas but different arrangements of atoms and groups are seen. Isomers are divided into conformational isomers, structural isomers, stereoisomers, geometric isomers, optical isomers.
The organic compounds which have similar molecular formula but differ in their structural arrangement are known as structural isomers.
Characteristics of isomers are shown below.
-The isomers of a chemical compound contain the same molecular formula but their structural arrangement are different.
-Even though the molecular formula of all the isomers of the chemical compound is the same but as the atoms and molecules are arranged differently in all isomers, therefore the chemical and physical properties of the all isomers differ from each other.
-In isomerism, the isomers of the chemical compound contain the same number of atoms.
-The isomerism takes place in only those compounds where four or more than four carbon atoms are present.
The given compound is butane. The molecular formula of butane is \[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}\]
In butane four carbon atoms are present which can either arrange themselves in a straight chain consisting of four carbon atoms or in a chain of three carbon atoms with a side group attached to one carbon atom. The two isomers of butane are n-butane and 2-methylpropane.
The structure of n-butane is shown below.
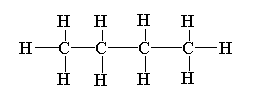
The structure of 2-methylpropane is shown below.
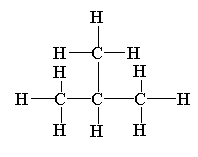
Note:
One of the isomers of butane that is 2-methyl propane is also known as isobutane which is a simplest alkane containing tertiary carbon atoms.
Complete step by step answer:
The isomers are defined as the molecules which have the same molecular formulas but different arrangements of atoms and groups are seen. Isomers are divided into conformational isomers, structural isomers, stereoisomers, geometric isomers, optical isomers.
The organic compounds which have similar molecular formula but differ in their structural arrangement are known as structural isomers.
Characteristics of isomers are shown below.
-The isomers of a chemical compound contain the same molecular formula but their structural arrangement are different.
-Even though the molecular formula of all the isomers of the chemical compound is the same but as the atoms and molecules are arranged differently in all isomers, therefore the chemical and physical properties of the all isomers differ from each other.
-In isomerism, the isomers of the chemical compound contain the same number of atoms.
-The isomerism takes place in only those compounds where four or more than four carbon atoms are present.
The given compound is butane. The molecular formula of butane is \[C{H_3}C{H_2}C{H_2}C{H_3}\]
In butane four carbon atoms are present which can either arrange themselves in a straight chain consisting of four carbon atoms or in a chain of three carbon atoms with a side group attached to one carbon atom. The two isomers of butane are n-butane and 2-methylpropane.
The structure of n-butane is shown below.

The structure of 2-methylpropane is shown below.

Note:
One of the isomers of butane that is 2-methyl propane is also known as isobutane which is a simplest alkane containing tertiary carbon atoms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




