
What are the 3 layers that make up the wall of the eyeball?
Answer
490.2k+ views
Hint: The eyeball is a spherical organ found in all vertebrates and a major structure of an eye. The eyeball contains vision sense receptors and is built similarly to a basic camera. The eye's primary purpose is to detect visual stimuli (photoreception) and transmit that information to the brain via the optic nerve.
Complete answer:
A circular, bilateral organ that contains the vision-related components, an eyeball is located in the bone orbit, a bony cavity within the structure of a face skeleton. The fibrous, vascular, and interior layers of the eyeball can be classified anatomically into three divisions. Here we'll look at the anatomy of the eyeball and its clinical implications in depth.
The eyeball is made up of three layers in general, which are as follows:
1. The Outer Layer: The sclera or the outer layer is a firm, white, opaque membrane that lines the inside of the eye (the white of the eye). The cornea is a clear, thin, dome-shaped tissue that bulges slightly in the sclera at the front of the eye.
2. The Middle Layer: Also known as the choroid. The iris, the coloured component of the eye, sits in front of the choroid. The pupil is a circular hole or opening in the centre of the iris.
3. The Inner Layer: The inner layer also popularly known as the retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back two-thirds of the eyeball. The sensory retina, which contains nerve cells that process visual information and convey it to the brain, and the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), which lies between the sensory retina and the eye wall, are the two layers that make up the retina.
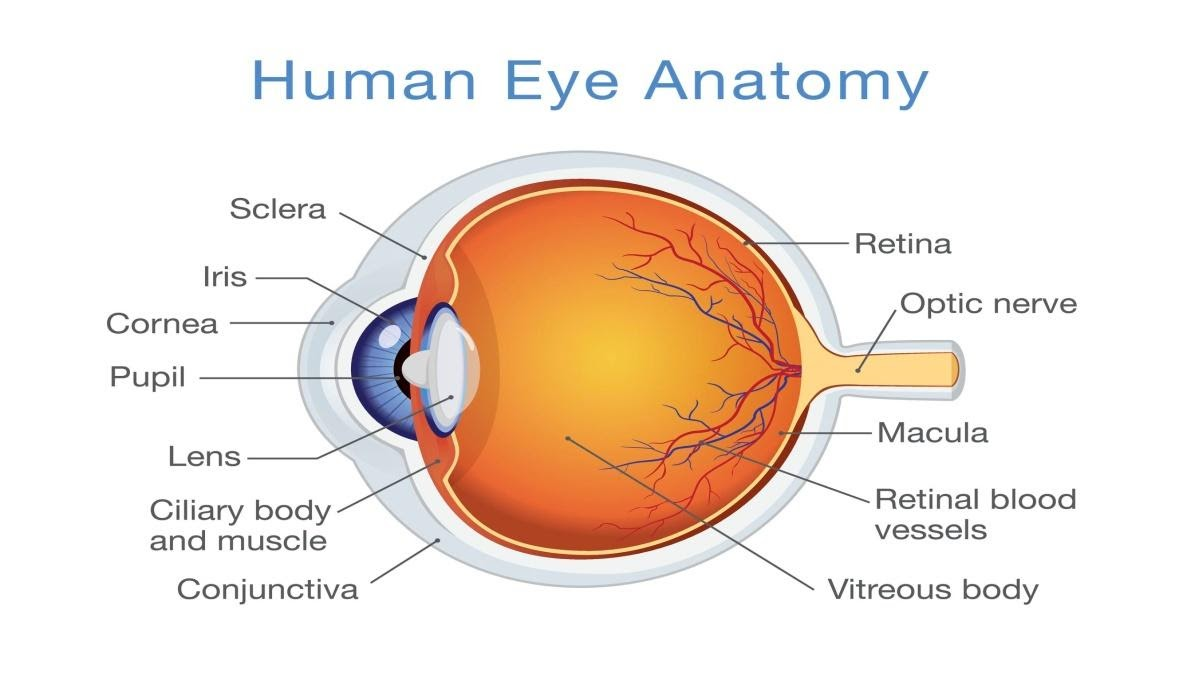
Image of an Eye Anatomy
The inside of the eyeball is further divided into three sub-divisions called the chambers, and these chambers are the anterior chamber, posterior chamber and the vitreous chamber.
Note:
Our visual organ is the eye. The cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, macula, optic nerve, choroid, and vitreous are just a few of the components that make up the eye. Cornea: the transparent front window of the eye that transmits and focuses light.
Complete answer:
A circular, bilateral organ that contains the vision-related components, an eyeball is located in the bone orbit, a bony cavity within the structure of a face skeleton. The fibrous, vascular, and interior layers of the eyeball can be classified anatomically into three divisions. Here we'll look at the anatomy of the eyeball and its clinical implications in depth.
The eyeball is made up of three layers in general, which are as follows:
1. The Outer Layer: The sclera or the outer layer is a firm, white, opaque membrane that lines the inside of the eye (the white of the eye). The cornea is a clear, thin, dome-shaped tissue that bulges slightly in the sclera at the front of the eye.
2. The Middle Layer: Also known as the choroid. The iris, the coloured component of the eye, sits in front of the choroid. The pupil is a circular hole or opening in the centre of the iris.
3. The Inner Layer: The inner layer also popularly known as the retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back two-thirds of the eyeball. The sensory retina, which contains nerve cells that process visual information and convey it to the brain, and the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), which lies between the sensory retina and the eye wall, are the two layers that make up the retina.

Image of an Eye Anatomy
The inside of the eyeball is further divided into three sub-divisions called the chambers, and these chambers are the anterior chamber, posterior chamber and the vitreous chamber.
Note:
Our visual organ is the eye. The cornea, iris, pupil, lens, retina, macula, optic nerve, choroid, and vitreous are just a few of the components that make up the eye. Cornea: the transparent front window of the eye that transmits and focuses light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE




