
What are the 3 main parts of the cell?
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Cells are the basic and structural components of life. Every cell though is distinct, but certain components are common to all cells. Cellular elements are the complex biomolecules and structures consisting of cells, and thus living organisms.
Complete answer:
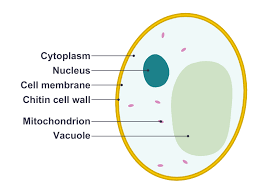
There are three major parts of a cell: a cell membrane, a nucleus, and a cytoplasm between the two. There are hundreds or even thousands of complex structures of fine fibers or minuscule but distinct structures inside the cytoplasm, called organelles.
Cell membrane: A cell or plasma membrane encloses every cell in the body. The cell membrane distinguishes substance inside the cell, intracellular outside the cell, from the substance. It maintains the integrity of a cell and controls the movement of materials within and outside the cell. For the required exchange all materials inside a cell must have access to the cell membrane (the boundary of the cell).
The plasma membrane is a double layer of molecules of phospholipids. Proteins throughout the cell membrane provide structural support, form channels for materials to pass through, act as receptor sites, function as carrier molecules, and provide identifying markers.
Nucleus and Nucleolus: The nucleus that is formed around a fluid nucleoplasm by a nuclear membrane is the cell's control center. Chromatin fibers inside the nucleus contain deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the genetic material of the cell. The nucleolus is a dense ribonucleic acid (RNA) region inside the nucleus and is the site of ribosome formation. The nucleus determines how the cell will act, as well as its basic structure.
Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm within the cell is the gel-like substance. It is the chemical reaction medium and provides a forum on which other organelles inside the cell can act. A cell's cytoplasm carries out all of the cell expansion, growth, and replication functions. Materials pass by diffusion within the cytoplasm, a physical process that can only function for short distances.
Note:Macromolecules comprising proteins and nucleic acids, biomolecular complexes like a ribosome, and structures like membranes, and organelles. They provide structure and support, promote growth through mitosis, permit passive and active transport, generate energy, generate metabolic reactions, and assist in reproduction.
Complete answer:

There are three major parts of a cell: a cell membrane, a nucleus, and a cytoplasm between the two. There are hundreds or even thousands of complex structures of fine fibers or minuscule but distinct structures inside the cytoplasm, called organelles.
Cell membrane: A cell or plasma membrane encloses every cell in the body. The cell membrane distinguishes substance inside the cell, intracellular outside the cell, from the substance. It maintains the integrity of a cell and controls the movement of materials within and outside the cell. For the required exchange all materials inside a cell must have access to the cell membrane (the boundary of the cell).
The plasma membrane is a double layer of molecules of phospholipids. Proteins throughout the cell membrane provide structural support, form channels for materials to pass through, act as receptor sites, function as carrier molecules, and provide identifying markers.
Nucleus and Nucleolus: The nucleus that is formed around a fluid nucleoplasm by a nuclear membrane is the cell's control center. Chromatin fibers inside the nucleus contain deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the genetic material of the cell. The nucleolus is a dense ribonucleic acid (RNA) region inside the nucleus and is the site of ribosome formation. The nucleus determines how the cell will act, as well as its basic structure.
Cytoplasm: The cytoplasm within the cell is the gel-like substance. It is the chemical reaction medium and provides a forum on which other organelles inside the cell can act. A cell's cytoplasm carries out all of the cell expansion, growth, and replication functions. Materials pass by diffusion within the cytoplasm, a physical process that can only function for short distances.
Note:Macromolecules comprising proteins and nucleic acids, biomolecular complexes like a ribosome, and structures like membranes, and organelles. They provide structure and support, promote growth through mitosis, permit passive and active transport, generate energy, generate metabolic reactions, and assist in reproduction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




