
What are the basic layers of the wall of the alimentary canal?
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: The alimentary canal is a long passage running from the mouth to the anus including all the organs of the digestive system in humans and other animals.
Complete answer:
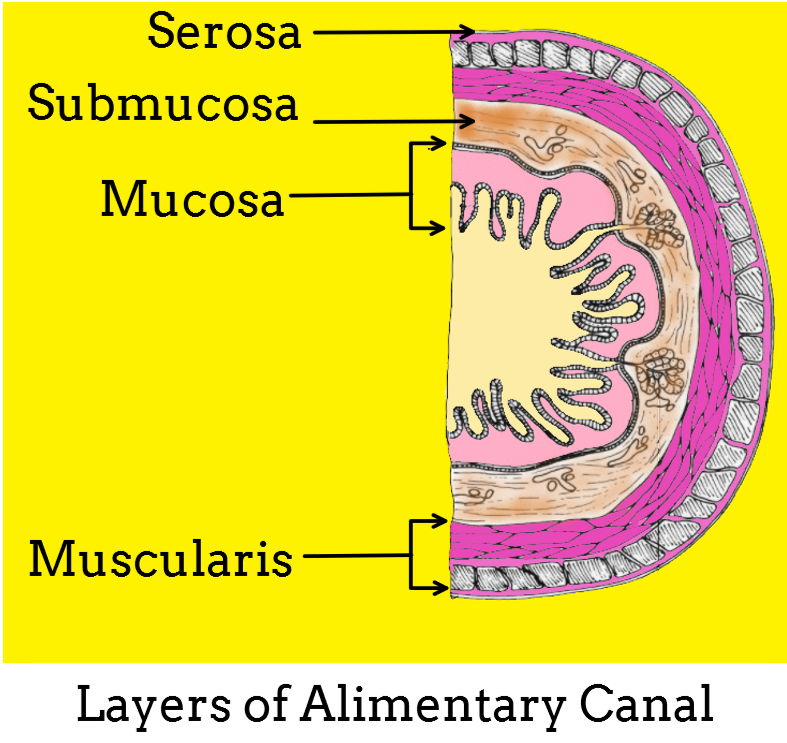
Throughout its length, the alimentary tract is composed of the same four tissue layers: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa.
-The mucosa is the innermost layer. It secretes a large amount of mucus and therefore is known as mucus membrane. The mucosal layer is lined by stratified squamous epithelium in the mouth and esophagus, and by columnar cells in the stomach and intestine. It lies in direct contact with ingested food, the lamina propria (connective tissue layer), and the muscularis mucosa, a thin smooth muscle layer.
-The submucosa lies externally to the mucosa. It is a broad layer of dense connective tissue; it connects the overlying mucosa to the underlying muscularis. It includes blood and lymphatic vessels, and a scattering of submucosal glands that release digestive secretions.
-The muscularis layer of the gastrointestinal tract is made up of smooth muscle arranged in an inner circular layer and an outer longitudinal layer. They cause strong peristaltic contraction and help in the propulsive movement of food, mixing of digestive juices, and digestion.
-The serosa is the outermost protective layer lying externally to the muscularis. It is present only in the stomach and intestinal part. The mouth, pharynx, and esophagus possess another protective dense sheath of collagen fibers. It is called the adventitia.
Note:
-The mucosal layer is rich in goblet cells which secrete mucus. In the small intestine, the mucosa is modified to form numerous small projections known as ‘Villi’. They increase the surface area of the intestine for absorption.
-The mucosa of duodenum consists of Brunner's glands that secrete bicarbonate ions and mucus.
-The Myenteric or the Auerbach's plexus located between the two layers of muscularis maintains the peristaltic movement of the intestine.
Complete answer:
Throughout its length, the alimentary tract is composed of the same four tissue layers: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa.
-The mucosa is the innermost layer. It secretes a large amount of mucus and therefore is known as mucus membrane. The mucosal layer is lined by stratified squamous epithelium in the mouth and esophagus, and by columnar cells in the stomach and intestine. It lies in direct contact with ingested food, the lamina propria (connective tissue layer), and the muscularis mucosa, a thin smooth muscle layer.
-The submucosa lies externally to the mucosa. It is a broad layer of dense connective tissue; it connects the overlying mucosa to the underlying muscularis. It includes blood and lymphatic vessels, and a scattering of submucosal glands that release digestive secretions.
-The muscularis layer of the gastrointestinal tract is made up of smooth muscle arranged in an inner circular layer and an outer longitudinal layer. They cause strong peristaltic contraction and help in the propulsive movement of food, mixing of digestive juices, and digestion.
-The serosa is the outermost protective layer lying externally to the muscularis. It is present only in the stomach and intestinal part. The mouth, pharynx, and esophagus possess another protective dense sheath of collagen fibers. It is called the adventitia.

Note:
-The mucosal layer is rich in goblet cells which secrete mucus. In the small intestine, the mucosa is modified to form numerous small projections known as ‘Villi’. They increase the surface area of the intestine for absorption.
-The mucosa of duodenum consists of Brunner's glands that secrete bicarbonate ions and mucus.
-The Myenteric or the Auerbach's plexus located between the two layers of muscularis maintains the peristaltic movement of the intestine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




