
What are the cis and trans isomers for cyclohexane?
Answer
524.4k+ views
Hint : The cis isomer is the one where both the groups face the same direction and in trans isomer, both the groups face opposite direction.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here, cis and trans isomers of cyclohexane can be of any groups, there are no restrictions on the group that is attached to cyclohexane.
Let us first define what cis and trans isomers are.
Cis isomer is a compound in which both the groups attached to the primary carbon of basic compound are in the same direction. A trans isomer is a compound in which both the groups attached to the primary carbon of the basic compound are in opposite directions.
The image shown below is of a simple cyclohexane.
Now, let us see an example of a cis and trans isomer of cyclohexane which has the same group.
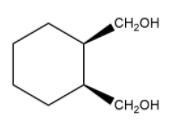
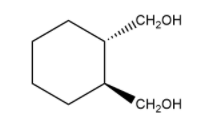
cis trans
1,2 – cyclohexanedimethanol 1,2 – cyclohexanedimethanol
Here, you can clearly see that cis isomer has both bond as solid wedge bond which represents that they both are in the same direction and in trans isomer, one bond is solid while other one is broken which shows that the direction of one of them is in different direction that the other.
Let us see another example with the same group.
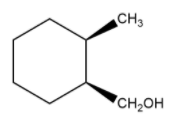
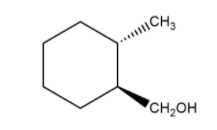
cis trans
1-methyl, 2-methanol cyclohexane 1-methyl, 2-methanol cyclohexane
Here, both the groups that are attached to the cyclohexane are different. Thus, the cis and trans isomers do not depend upon the group attached to the primary carbon, but the direction of them with respect to each other.
Note :
The cis and trans isomerism does not depend upon the nature of the group, it only depends upon the direction of the groups. Thus, any groups attached to primary carbon of cyclohexane can make cis and trans isomers.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here, cis and trans isomers of cyclohexane can be of any groups, there are no restrictions on the group that is attached to cyclohexane.
Let us first define what cis and trans isomers are.
Cis isomer is a compound in which both the groups attached to the primary carbon of basic compound are in the same direction. A trans isomer is a compound in which both the groups attached to the primary carbon of the basic compound are in opposite directions.
The image shown below is of a simple cyclohexane.

Now, let us see an example of a cis and trans isomer of cyclohexane which has the same group.


cis trans
1,2 – cyclohexanedimethanol 1,2 – cyclohexanedimethanol
Here, you can clearly see that cis isomer has both bond as solid wedge bond which represents that they both are in the same direction and in trans isomer, one bond is solid while other one is broken which shows that the direction of one of them is in different direction that the other.
Let us see another example with the same group.


cis trans
1-methyl, 2-methanol cyclohexane 1-methyl, 2-methanol cyclohexane
Here, both the groups that are attached to the cyclohexane are different. Thus, the cis and trans isomers do not depend upon the group attached to the primary carbon, but the direction of them with respect to each other.
Note :
The cis and trans isomerism does not depend upon the nature of the group, it only depends upon the direction of the groups. Thus, any groups attached to primary carbon of cyclohexane can make cis and trans isomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




