
What are the co-vertices in an ellipse?
Answer
528.3k+ views
Hint: From the given question we have been asked what are the co-vertices in an ellipse. For solving this question we will take a few examples of an ellipse and then we will explain the co vertices for those examples we took and then later we will generalise the concept of co vertices in r/o for any ellipse in geometry. So, we will proceed with our solution as follows.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Generally an ellipse has two axes namely major axis and minor axis.
For the geometrical figure ellipse it has parameters like two vertices and two foci etc.., which are present in the major axis of the ellipse.
Both major and minor axes pass through the centre of the ellipse which is their intersection point.
Let us assume an ellipse in its general form which is as follows.
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{1}=1\]
The graph of this ellipse in general form will be as follows.
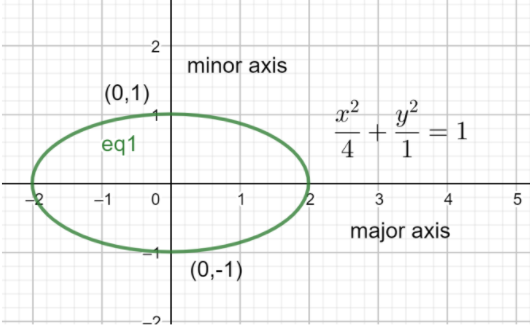
We can see that this is an ellipse with horizontal orientation and as can be seen its co vertices are \[\left( 0,1 \right),\left( 0,-1 \right)\] which are present on the minor axis of the ellipse.
Therefore, we can conclude that co-vertices are the endpoints of the minor axis of the ellipse.
Note: Students must have good knowledge in the concept of ellipse and its properties. Students must be able to differentiate in between vertices and co vertices of an ellipse. Students must not think that the co vertices is one of the points in the vertices because both the points combined are known as the vertices of the ellipse which are on the major axis of the ellipse.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Generally an ellipse has two axes namely major axis and minor axis.
For the geometrical figure ellipse it has parameters like two vertices and two foci etc.., which are present in the major axis of the ellipse.
Both major and minor axes pass through the centre of the ellipse which is their intersection point.
Let us assume an ellipse in its general form which is as follows.
\[\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{4}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{1}=1\]
The graph of this ellipse in general form will be as follows.

We can see that this is an ellipse with horizontal orientation and as can be seen its co vertices are \[\left( 0,1 \right),\left( 0,-1 \right)\] which are present on the minor axis of the ellipse.
Therefore, we can conclude that co-vertices are the endpoints of the minor axis of the ellipse.
Note: Students must have good knowledge in the concept of ellipse and its properties. Students must be able to differentiate in between vertices and co vertices of an ellipse. Students must not think that the co vertices is one of the points in the vertices because both the points combined are known as the vertices of the ellipse which are on the major axis of the ellipse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




